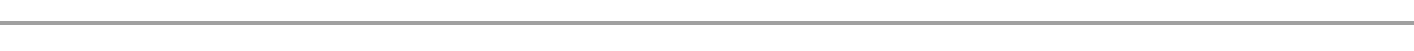Stock administration – is the management of stock in the business to ensure that there is sufficient quantity of goods without holding more or less stock than is required.
FUNCTIONS OF STOCK ADMINISTRATION
Stock administration involve the following functions
1.Receiving of goods – receiving of goods includes the following activities
- Accepting deliveries from transporters or carriers
- Inspecting or checking the condition of goods against quantity, quality and types of goods
- Unloading of goods
- Comparing goods received with order documents
- Notifying the purchasing department about the receipts and general condition of the good
- Keeping records of stock/ goods received
edu.uptymez.com
2.Placing items – this involved with allocating or placing the goods in an appropriate places. Stocks must be arranged in a goods order in such manner that it will reveal the old goods from new ones
3.Care of stock – goods received must be kept in a good condition by cleaning them, dusting and sorting out spoils goods
4.Issuing of stock – this means going out or delivering out goods against vouchers to ensure proper records of stock movement
5.Stock control – this is checking and keeping records of the quantity and value of articles or goods in stock for a particular of time
WHY STOCK CONTROL IS NECESSARY / IMPORTANCE OF STOCK CONTROL
Stock control is necessary because
- It helps to know whether sufficient stocks are available to carry out normal order
- It helps the management to obtain new supplies before problem stock runs out
- It helps the management to know about stock turn over so as to distinguish between slow and fast moving items
-
Stock control is necessary for insurance purpose
STOCK TAKING
Stock taking – this is the process of finding the quantity and value of stock held. It is a physical counting and making list of all stock held which is normally conducted at the end of each final year.
PURPOSE OF STOCK TAKING
- To know stock pilferage
- To check accuracy of records
- To check weakness in the system of stock control
-
To support the value of closing stock which will be used in final accounts
STOCK LEVELS
Stock levels: are volumes or points of stock reached at different time stock levels includes the following
-
Minimum stock level
(Receive stock or buffer stock)
This is the lowest quantity of stock which should be kept to safeguard (protect) sales against unforeseen delays in delivery or production
-
Maximum stock level
This is the highest level of stock reached immediately after receipts of a new delivery. Stock should not be allowed to exceed.
DETERMINATION OF MAXIMUM STOCK LEVEL
The stock level can be determined by
- Financial capability of the business
- Storage capacity (space available)
- Cost of storage
- Seasonal factors ( especial agriculture products )
- Stability of prices
-
Average stock level
This is the average number of stock levels within a certain period of time (usually a year)
CALCULATION OF AVERAGE STOCK
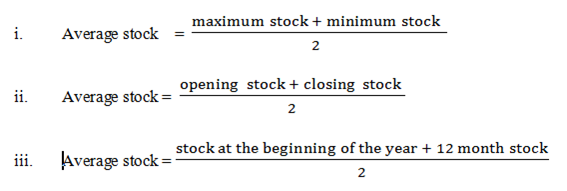
Example
If a firm has opening stock valued at Tshs 2500/= and closing stock valued at 1500/= Tshs calculate average stock
-
Stock order point or Re- order level
Is the level expressed in unit of issue at which another order is to be pressed before stock fall below the minimum level.
OR
Is the level at which ordering or placing of new items must be done.
DETERMINATION OF ORDER POINT
Order point is determine according to;
- Volume of lastly sales or consumption
- The period between placing or ordering and receiving deliveries
-
Minimum stock level
CALCULATION OF ORDER POINT
Formula
Order point: = (Daily sales x Delivery time) + minimum stock
edu.uptymez.com
Example 1
If a form is having a daily sale of 10 units and minimum stock of 100 units.That has between placing and receiving the order is 20 days, you are required to find the order point
Solution
Order point = Daily sales x Delivery time + minimum stock
Data given
Daily sales = 10 units
Delivery time = 20 days
Minimum stock = 100 units
Order point = (10 x 20) + 100
= 200 + 100
300 units
Example 2
Calculate the order point from the following information
- Daily sales 20 cartons of soaps (each carton contains 10 bars of soaps )
- Delivery time = 2 weeks
- Minimum stock = 500 bars of soap
edu.uptymez.com
Solution
Data given
1 carton = 10 bars
20 carton = 200 bars
1 week = 7 days
2 weeks = 14 days
There order point = (Daily sale x Delivery time) + minimum stock
(200 bars x 14 days)+ 500 bars
= 2800 + 500
Order point = 3300 bars of soap
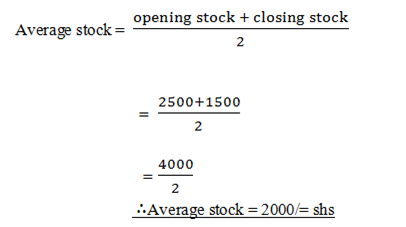
TURN OVER/SALES
Turnover is the net sales during the trading period it is calculate as follows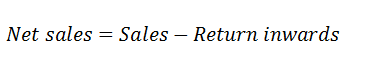

Rate of stock turn over
This is the number of times the average volume of stock held have been sold during any given period. It is given a s follows
Rate of stock turn over:
Example:
Given
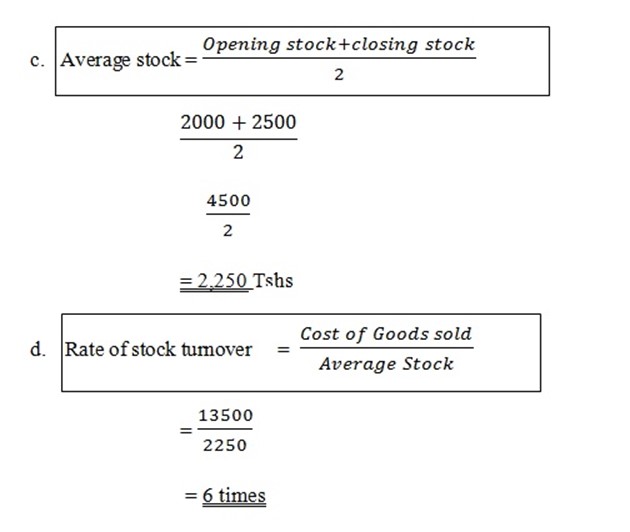
Opening stock = 2,000/=
Closing stock = 2,500/=
Purchases = 14,000/=
Sales = 25,000/=
Expenses = 4000/=
Calculate
- Cost of goods sold
- Average stock
- Gross profits
- Net profit
-
Rate of stock turn over
Solution

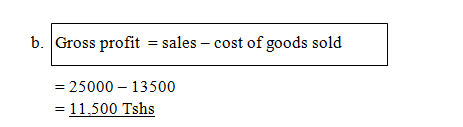
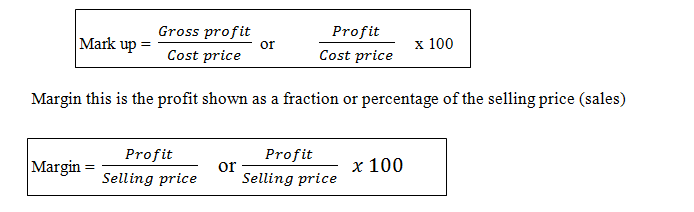
MARK – UP AND MARGIN
Mark –up: This is a profit shown as a fraction or percentage of the cost price ( cost of goods sold )
edu.uptymez.com
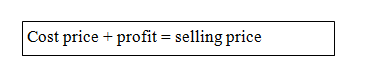
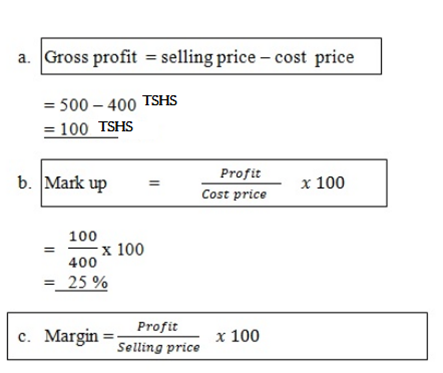
Example:
Given
Cost price 400
Selling price 500
Calculate
- Gross profit
- Mark up as a percentage
-
Margin
edu.uptymez.com
= 100/500 x 100
Margin=20%
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MARK UP AND MARGIN
Both margin and mark up figures refers to the same profit but expressed as a fraction or percentage of different figure there is bound to be a relationship it one is known as a fraction the other can be found.
If the mark up is known to find the margin take the same numerator to numerator of the margin then for the denominator for the margin take to the total of the mark up denominator plus denominator plus the numerator
Example 1
Margin =→less Mark up
1/n =1/n-1 x100
Margin =→Add Mark up
1/n =1/n+1 x100
- Mark up margin
- ¼
- 2/11 2/11 + 2 = 2/13
- Margin mark up
- 1/6 1/6 – 1 = 1/5
-
3/13 3/13 – 3 3/10
Example
The following figures are for 2005
Stock at 01. 01 . 2005 400
Stock at 31. 12 . 2005 600
Purchases 5200
A uniform rate of mark up of 20% is applied find out
- Cost of goods sold
- Gross profit
-
Sales figure
Solution
-
Cost of goods sold = opening stock + purchases – closing stock
= 400 + 5200 – 600
= 5600 – 600
= 5,000 Tshs
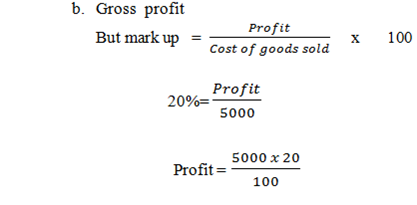
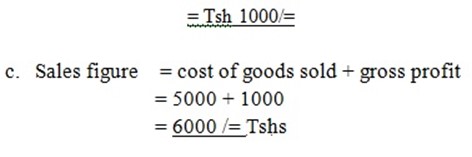
-
Sales figure = cost of goods sold + gross profit
= 5000 + 1000
= 6000 /= Tshs
EXERCISE
Given the following figure for 2006
Stock at 01. 01. 2006 500
Stock at 31. 01. 2006 800
Sales 4000
A uniform rate of margin of 25% is in use calculate
- Gross profit
- Purchases figure
-
Cost of goods solid
edu.uptymez.com