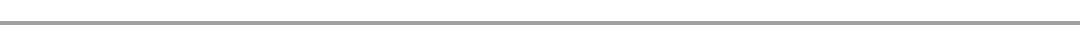Is the Compulsory Contributions from different Source of Income to the government for the purpose of finance Its activities.
WHY TAXATION OR WHY DO THE GOVERNMENT TAX/PURPOSE OF TAXATION/REASON OF TAXATION
1. To cover the cost of general administration
Government charge taxation purposely to cover such as defense and social services provided by the state i.e.
- Army
- Police
- Hospital
edu.uptymez.com
2. Control harmful goods like alcohol etc
To check the consumption of goods which can be harmful to human being.
To control the consumption of harmful goods such as spirits and tobacco by increasing its taxation.
3. To reduce income inequalities
The government adopt a system of taxation which reduce the gap between the lower income earner and higher earner through (PAYE)
‘Pay as you earn’
PAYE
Is a progressive income tax system which imposed to a person according to his or her Income.
4. for furtherance of economic activities
The revenue is needed by the government in order to establish or improve economic activities such as road constructions, industries etc.
5. To control inflation
Government charges taxes to control inflation by reducing the amount of money in circulation and hence the purchasing power of the public increase.
6. To reduce a deficit in the balance of payment
-Tariffs are imposed on imports in order to reduce deficit in the balance of payment.
7. Protect local industries
The government imposes heavy tax on imported goods, on the other hand the government reduces tax on locally produced goods to promote local
industries.
OBJECTIVES OF TAXATION
The following are the main objectives of taxation;
- Financial or revenue objectives
edu.uptymez.com
It is the main source of the funds/income
2. Economic objectives
- Control and regulate people‘s consumption.
- Ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>couragement of investments by reducing tax to the investors.
- Regulate the price level; This is done by the increase or reduction of taxes on other goods.
- Protection of inflation of local industries by discouraging the importation by increasing tax to the imported goods.
- Ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>couragement of exports; Taxation used for motivation the exportation by reducing the taxation to the business who exports goods to abroad.
- 3. Social objectives
- Impose high tax on harmful goods i.e. spirits, tobacco.
- Financing sports and games as well as entertainment e.g. music.
- Protect the country against the dumping reduce inequality.
edu.uptymez.com
CHARACTERISTICS OF TAXATION
There are three important characteristics of taxation.
- A compulsory contribution
edu.uptymez.com
It is the contribution to the state to cover its expenditure fail to pay you will be permitted.
2. Not a payment for a specified person for specific profit.
3. The benefits of taxation is for all citizens or people (not selective).
4. Ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage social solidarity and common obligation goods to protect the health for the economic progressive.
SYSTEM OF TAXATION
- PROGRESSIVE TAX
edu.uptymez.com
This is a system of taxation in which the amount of tax depends on the level of income (PAYE) i.e the amount of tax charged is proportional to the level of income. This system is very useful in reducing income inequalities among income earners.
OR
The higher the income the higher the tax and the lower the income the lower the tax will be paid.
Example.
|
INCOME |
PERCENTAGE |
TAX |
|
20,000 |
10% |
2,000 |
|
30,000 |
20% |
6,000 |
|
40,000 |
30% |
12,000 |
|
50,000 |
40% |
20,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
GRAPHICALLY
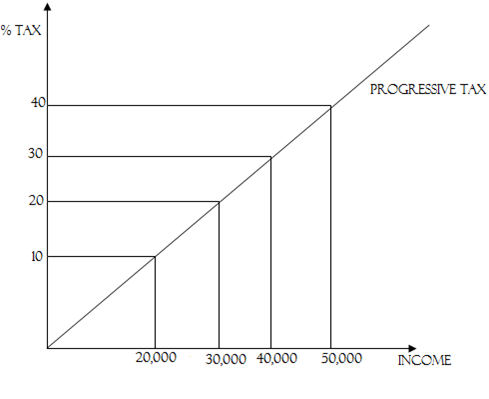
2. REGRESSIVE TAX SYSTEM
Means that the Lower the income the higher the tax and the higher
the income the lower the tax will be paid.
Example:
|
INCOME |
PERCENTAGE |
TAX |
|
20,000 |
40% |
8,000 |
|
30,000 |
30% |
9,000 |
|
40,000 |
20% |
8,000 |
|
50,000 |
10% |
5,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
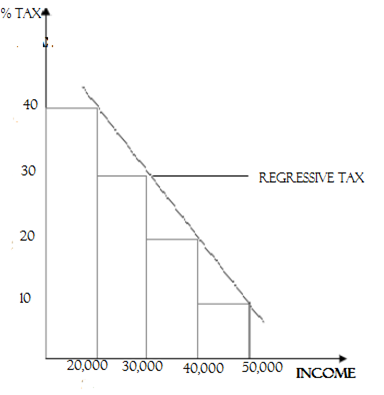
3. PROPORTIONAL TAX SYSTEM
This is the system of taxation in which the percentage of tax is the same to all level of incomes. For example :
When the person who earns T.sh. 40,000 per month pay 10% of the income as tax and a person who earns T.shs. 50,000 per month also pay 10% of the income as tax.
|
INCOME |
PERCENTAGE |
TAX |
|
20,000 |
10% |
2,000 |
|
30,000 |
10% |
3,000 |
|
40,000 |
10% |
4,000 |
|
50,000 |
10% |
5,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
Diagrammatically
CLASSIFICATION OF GROUPING TAXES
The following are the criteria used in grouping taxes;
1. According to the taxable objective
- Income tax
edu.uptymez.com
This is the tax charged to the employee (labour) salaries.
- Sales tax
edu.uptymez.com
Is the tax imposed to the business men or women during the sales processing ”VAT”.
- VAT
edu.uptymez.com
Value added tax is the tax imposed for every stage of production and nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of goods and services.
- Capital gain tax ( industrial)
edu.uptymez.com
Is the tax imposed on the gain made by seller of a capital asset during the disposal (sale).
- Property tax
edu.uptymez.com
Is a tax imposed on the property such as building (house).
2. According to the visibility
- Open tax (direct tax)
edu.uptymez.com
Is the tax charged direct from the main source of income i.e. company.
- Hidden taxes ( indirect tax)
edu.uptymez.com
Is the tax charged during purchase of goods and services.
3. According to their effect on the tax buyer
- Progressive tax
- Regressive tax
- Proportional tax
edu.uptymez.com
4. According to the way it is collected
- Assessed taxes (custom tax)
edu.uptymez.com
Imposed when the person imported goods from outside the country. Specific add value according to the quantities.
- Deductive taxes
edu.uptymez.com
Is imposed on the income of the employer salaries.
- Excise tax [ inside]
edu.uptymez.com
Tax for the goods produced within the country.
5. According to the tax payer
- Sole proprietorships /sole traders
edu.uptymez.com
Is a person who owns business singly privately.
- Corporate taxes
edu.uptymez.com
Is the tax for the company operations.
6. According to the recipient
- Govern taxes
edu.uptymez.com
Taxes imposed by Tanzania revenue authority (TRA)as a whole.
- Municipal tax
- Village taxes
edu.uptymez.com
PRINCIPLES OF TAXATION (CANNONS OF TAXATION)
A good tax system should be based on the following basic principles;
-
Equity
The burden should be equal according to the income i.e Pay as you earn (PAYE).
-
Certainty
The tax payer should know how much he/she pays to the state.
-
Convenience
The time and manners of collect tax should be known to the tax payer and tax collectors i.e. labours during the harvest.
-
Productivity
The tax should be used in economic development i.e. construction of roads and industries.
-
Economy
The amount collected should be higher than cost of collection.
-
Elasticity
The tax should be charged according to the economic changes example inflation.
edu.uptymez.com
TYPES OF TAXATION
- Direct taxes
- Indirect taxes
edu.uptymez.com
DIRECT TAXES
Is the tax levy directly from the main source of income.
- Income tax
- Corporate tax
edu.uptymez.com
Or
Is a type of tax where the impact fall to one person.
ADVANTAGES OF DIRECT TAXATION
- Low cost of collection
edu.uptymez.com
Low cost because the collectors know the source of income where to collect.
- Tax payer know how much to pay [certainty]
edu.uptymez.com
If you know how much to pay you can arrange your budget.
- It stimulates the tax payer
edu.uptymez.com
It ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courages the tax payer because they know how much he/she contributes to the state.
- It is progressive in nature
edu.uptymez.com
It brings equality because high incomes pay high tax while low income pays low taxes.
INDIRECT TAXES
This is the tax levy on price of commodities and services.
ADVANTAGES OF INDIRECT TAXATION
- The tax payer does not feel the burden direct.
- The tax payer does not feel pain because the tax charged during the purchases of goods and services.
-
Easy method of collection.
Collection is simple because the tax is imposed during purchasing.
-
Difficult of evasion /evading.
Escaping is difficult this is due to the fact that the tax is levied during purchasing.
-
It is convenient in nature.
Small amount is paid at the time of purchasing.
- Cost of collection is low.
-
Reached to even those with small income
The tax is charged to every person hence large income is control the use of harmful foods by increase in its price.
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGES OF INDIRECT TAXATION
- It increases the price of goods and service.
- It can cause inflation.
- It is uncertain in nature.
- It is unequitable.
- It is not possible to determine its full effects.
edu.uptymez.com
Effects of the taxation
On the tax payer
- It increase the price of goods.
- Affects the investors.
- It affects the employee ( labour).
- Effects on saving is decreased.
- No money for precaution and health.
- It affects the entrepreneur.
edu.uptymez.com
IMPACT AND INCIDENCE OF TAXATION
-Incidence is the burden of paying tax.
-Impact effects based by the 2rd person who pays tax.