This is the process of making goods or rendering services for the satisfaction of human wants e.g. process of changing the goat skin into pairs of shoes.
Production can also defined as the creation of utility . there are several types of utility .these are :
FORM UTILITY
This is the utility which provided by the manufacturing or constructive industries which deals with changing the form of production .
TIME UTILITY
This is the utility which is provided by warehousing which deals with changing the time of consumption
PLACE UTILITY
This is the utility which provided by transport which deals with the changing of the place of consumption
POSSESSION UTILITY
This is the utility which is provided by trade which deals with changing the ownership of consumption
PURPOSE OF PRODUCTION
The main purpose of production is the satisfaction of human wants and needs through creation of utility of goods and services .
NEEDS – these include all goods and services which are necessary for human existence . needs of modern society and broadly grouped into five groups namely food ,accommodation ,clothes education and health care
WANTS – these include all goods and services that are required to supplement the needs of human being .
CHARACTERISTICS OF WANTS
1. WANTS ARE INSASTIABLE
This means wants can not be satisfied . .there are always new wants to satisfy .Man always cultivates for the new wants and he /she never satisfied at all i.e. wants plenty and infinite.
2. WANTS ARE HABITUAL.
Certain wants are created and sustained though a habit e.g. cigarettes smokes ,drinkers etc and in the many cases they depend on the financial position of a person.
3.WANTS ARE RE-CURRENT
Wants cannot be satisfied once and there fore all the keep on recurring quite often.
4.WANTS ARE COMPLEMENTARY
Satisfaction of single wants way make necessary to consumer a number of product e.g. hot drinks will require tea leaves or cocoa ,milk .sugar ,water and fuel to boil the component ink and pen electricity lamp and switches.
5.WANTS ARE COMPETITIVE
The are many product to satisfy a single want e.g. a want for the soft drink .there are cocacola ,pepsi etc hence he/she has to make selection from many goods.
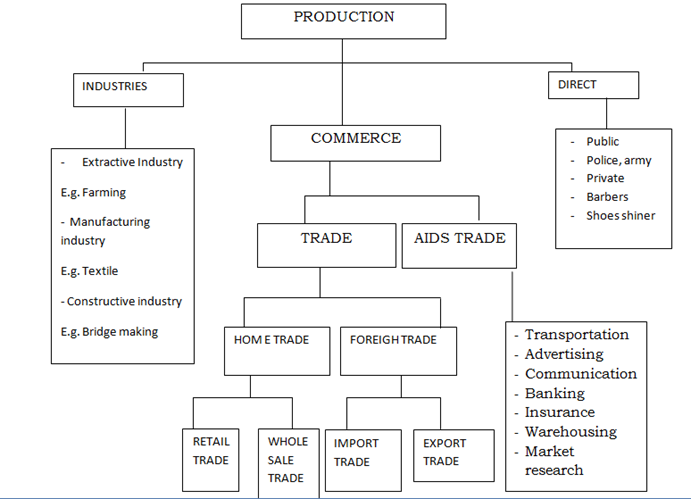
PRODUCTION FLOW CHART
PRODUCTION COSTS/COSTS OF PRODUCTION
Production costs refer to the expenses or money used in the process of production. For example amount of money used to purchase raw materials, rent, salaries e.t.c.
TYPE OF PRODUCTION COST
Production costs are mainly categorized into two groups
(i) Fixed costs
(ii) Variable costs
1. FIXED COST
These are the costs which do not change as output changes. i.e do not vary without e.g. Rent, Interest, Salaries etc.
Fixed Cost = Total costs – Variable Cost
F.C = TC – V.C
2. VARIABLE COSTS
These are costs that vary directly with the output of the goods produced e.g wages of direct labour, raw materials, water, electricity etc.
Variables costs = Total costs – Fixed assets.
V.C = TC – F.C
3. TOTAL COSTS
These are overall expenses incurred in the production process i.e It is the sum of fixed costs and variable cost.
TC = F.C + V.C
4. AVERAGE COSTS
These are costs per unit of output produced
Average Costs = Total cost
Output(Q)
AC = Total cost
Q
5. MARGINAL COSTS
These are additional costs incurred due to extra unit of output produced.
Marginal Costs = Change in total cost
Change in output
MC = DTC
Dq
Where DTC = Change in Total costs
Dq = Change in output
6.EXPLICIT COSTS
7.IMPLICIT COSTS
8.ETC
PRODUCTION STAGES / LEVELS OF PRODUCTION
There are three stages of production namely :
PRIMARY PRODUCTION
This is the first stage of production which deals with the extraction of raw materials from nature e.g. fishing ,mining agriculture etc often the output of the production is the input of secondary production .But the output of primary production can be used direct by the consumer e.g. all fruit ,vegetable etc.
SECONDARY PRODUCTION
This is the second stage of production which deals with processing raw materials extracted and collected by the primary production i.e. output of primary production e.g. manufacturing industries deals with it and constructive industries e.g. government manufacturer ,textile industries, bridge making .
TERTIARY PRODUCTION
Production process is incomplete in the second stage because do not reach to consumer .since we know the aim of production is to satisfy human wants and needs .
There are services such as transport , while selling , nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution and exchange and personal services such as medicines , security etc
METHOD OF PRODUCTION (TYPES OF PRODUCTION)
There are mainly two methods of production namely;
DIRECT PRODUCTION
This is the method of production where by goods and services are produced by an individual for his/ her own use .No surplus is obtained hence no exchange to take place .The method also known as SUBSTISTANCE PRODUCTION
INDIRECT PRODUCTION
This is a method of production where by goods and services are produced by an individual for the sake of exchange i.e.selling to other people .This method is also known as MARKET PRODUCTION.
MASS PRODUCTION AND THREE “S”
The mass production is the process of producing large amount of output by using fewer workers .
The term can be affected by the following factors
Simplification
This is the process of simplifying the manufactured products and keeps them in the functional .this means that the simplified product will be cheaper and customer will afford to buy if the previous was worn out.
Standardization
This is the process of putting the goods into the standard parts. This means the items produced can be used in the various alternative therefore this widen the markets for the product
Specialization
This is the process of concentrating the effort on a particular job . this means one will perform a work which he/she is suited to do best .therefore the productivity will tend to increase due to the fact that a person may concentrate in his/her activity
SPECIALIZATION AND DIVISION OF LABOUR
Specialization
Is the process where by a person would be required to concentrate on one activity/ job in which has the best skills or can do better.
.
Division of labour
Was defined by E.THOMAS that , it is an arrangement of labour power in such a way that maximize the amount and quantity of output.
ADVANTAGES OF SPECIALIZATION
- time and energy saving
edu.uptymez.com
Since a person concentrate on his/her field then the time which will be used for switching from one job to another will be saved as also energy will do the same.
- increase production
edu.uptymez.com
Different people with their professional are given their field , the production of output will increase because labourers have different skills and knowledge.
- degree of choice
edu.uptymez.com
People are able to choose their field because in the specialization, a person is given a work/job which he/she can do best
- development skills
edu.uptymez.com
Having to do the same work repeatedly , a person may be becomes highly skilled in his field by knowing where the mistake was and where it is ,people become qualified totally in their works.
- Inventions and innovations are ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>couraged in production process due to the use of machines hence high quality output is produced.
- Avoids boredom in the process of production since labourers concentrate only in activities where they have the best skills
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGES OF SPECIALIZATION
- Boredom – this is due to doing the same task again and again hence monotonous
- Unemployment- this is due to use of machines in production process
- High cost of buying machinery-
- Limited form of production- this due to the factor that a person concentrates on one production activity
- Loss of craftsmanship of natural resources due to the use of machines
edu.uptymez.com
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
These are resources available to produce goods and services needed and wanted by the community .There are four factors of production
1. LAND
This includes not only land itself, but all that grown on it such as natural forest and any thing obtained from lakes ,sea ,rivers, oceans and canals .Land provide a space where factories are built and it is the ultimate source of all materials .
How land aids production?/ IMPORTANCE OF LAND
- It provide space where productive activities can be located.
- It provides raw materials and other commodities which can be used in production.
- It is a form valuable natural resources.
- It contains minerals which are very useful almost to all productive forces.
- Provides agricultural commodities of all types which can be used as raw materials.
edu.uptymez.com
CHARACTERISTICS OF LAND
- Land is the gift of nature. Basically man has just found land for his/her use and has done nothing to bring it into existence.
- Land is limited in supply. Land strictly limited in supply but its supply can be conducted in absence of it i.e. industries are located on the land.
- Land is an immovable factor of production. Land can not move from one place to another .
- is subjected to the law of diminishing return. The law applied to the agricultural sector where when more factor of production (labour) are employed the output decreases.
edu.uptymez.com
PRODUCTION OF LAND
- Fertility
edu.uptymez.com
Improvement and development made on the land (agricultural techniques)
Situation is to population and market i.e. space for housing and production
Geographical situation (temperature zone , tropical or southern and northern hemisphere and desert.)
- Nature of surface of land . This means whether mountaineers or low and high land.
edu.uptymez.com
2. LABOUR
These are all human efforts mentally and physically which engaged in production ;
but not that labour is human effort ,but all human effort is not labour because labour must be aimed at production and paid for . thus if person plays football for his own pleasure his effort would not be called labour but if he in he works in the factory or otherwise contributing effort to any meaning of labour activities of person engaged in the giving direct services also termed as labour .
CHARACTERISTICS OF LABOUR
1.High mobility.Labourers are easily shift from one industries to another or from one geographical location to another as well as from one occupation to another.
2. its availability depend on the size and structure of the population.
3. it requires close supervision and human relation to increase its efficiency.
4. Labour differs on the level of ability and efficient.
5. Labour sells his services and not himself.
6. has feelings and emotion and likings
Labour is any human effort both physical and mental at production of goods and services. Labour is mainly classified into three categories as follows;
- Skilled labour
- Semi skilled labour
- Un-skilled labour
edu.uptymez.com
What are the importance of labour in production?
- Simplify production activities
- Facilitate other factors of production
- Reduce costs
edu.uptymez.com
PRODUCTIVITY OF LABOUR
Sometimes known as efficiency of labour which means the quantity and quality produced by the labour .if a labour produces the products of superior quality in large quantity at a specific time , labour is said to be efficient.
FACTORS AFFECTING LABOUR EFFICIENCY AND PRODUCTIVITY
- Working condition
- Means of production.ie labour intensive or capital intensive technique
- Peace of mind.
- Incentives.
- Altitudes of the workers torwards work.
- Degree of specialization and division of labor
- Efficiency of other factors of production ( especially entrepreneur)
- Education and training
edu.uptymez.com
MOBILITY OF LABOUR
This is the movement of labor from one place to another or from one occupation to another .
The mobility of labour has the following types.
- Geographical mobility
edu.uptymez.com
This is the movement of labor from one place to another the development of transport and communication services expiation of education and employment opportunities in the some areas have called the movement of labor from one area to another .
- Occupational mobility
edu.uptymez.com
This is the movement of labor from one occupation to another e .g. movement from agricultural sector to industrial sector the occupational mobility is due to the expansion of education which cause people shift from agricultural sector to industrial sector
Occupational mobility is further divided into two forms of labour mobility.
- Horizontal mobility
edu.uptymez.com
This is the movement of labor from one firm to another at the same level e.g. moving from firm A to firm B where you will remain at the same level as account.
- Vertical mobility
edu.uptymez.com
This is the movement of labor from low grade to the higher grade . the movement from accountant to the senior accountant is the vertical mobility of labor
BARRIERS TO THE MOBILITY LABOUR
a) GEOGRAPHICAL MOBILITY
- Monetary cost. moving a family with its possession can be expensive operation.
- Housing shortage.this is the common feature especially in the large town and cities . It is particularly a difficult problem in the cases of the rented accommodation.
- Social ties. many people do not need to live beyond their friend and relative and face the prospective of establishing social relationship in the strange town.
- Education.many families tend to be immobile a certain state of their children education.
- National and international immigration laws often acts as a constant.
edu.uptymez.com
OCCUPATIONAL MOBILITY
- Natural mobility. people differ in natural mobility and some occupation requires a high level of intelligence of a particular natural aptitude which is only possessed by a certain proportional of the population which could be a small proportional such as surgeons , physicians , mathematician designers etc
- Trainers.professions which demand a very long time of education and training e.g. doctor leads into groups of these profession being very small and you can not shift very easily from either job into those jobs which requires training.
- Ignorance of employment opportunities in different areas.
- limited skills of individuals hence failing to acquire jobs.
- changes in science and technology e.g. use of machines in production process.
edu.uptymez.com
POLICIES TO ASSIST MOBILITY OF LABOUR
Government should provide financial assistance in form of transport allowances and accommodation to enable people search jobs in distant areas.
Due to ignorance about the presence employment opportunities, then jobs should be advertised through different advertising media
.
ADVANTAGES OF MOBILITY OF LABOUR
- Higher employment level. Labor mobility helps to reduce un-employment because workers can move to various with place with employment opportunities.
- Higher wages. A worker move from one job to another for the sake of earning higher wages I.e. in the vertical mobility.
- Greater productivity and efficiency. This is when labour moves from low or pour working conditions places
- Job satisfaction. Labor mobility allows workers to choose jobs are interested and satisfied with. This may bring a peace of mind.
- International understanding. Geographical mobility of labour creates and strengthen ones conditional of international community understanding between different countries of the world .people of the different races , from various countries working together can become broad minded to the extent of forgetting their racial ,tribes ,religious differences.