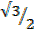Trigonometrical ratios in a unit circle
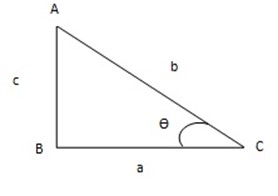
The three trigonometrical ratios of sine, cosine and tangent have been defined earlier, using the sides of a right-angled triangle as follows
If A is an angle as shown
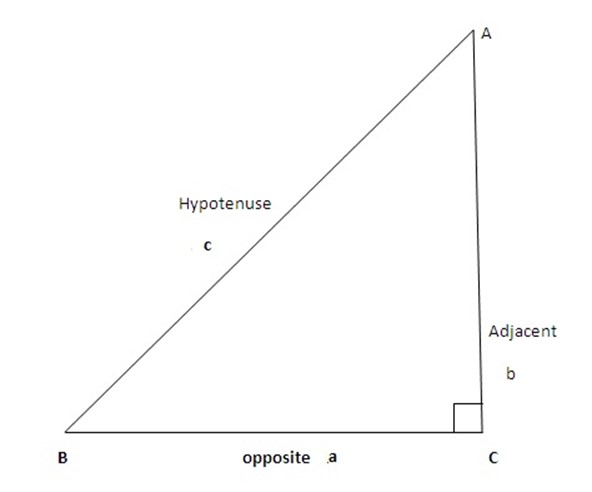
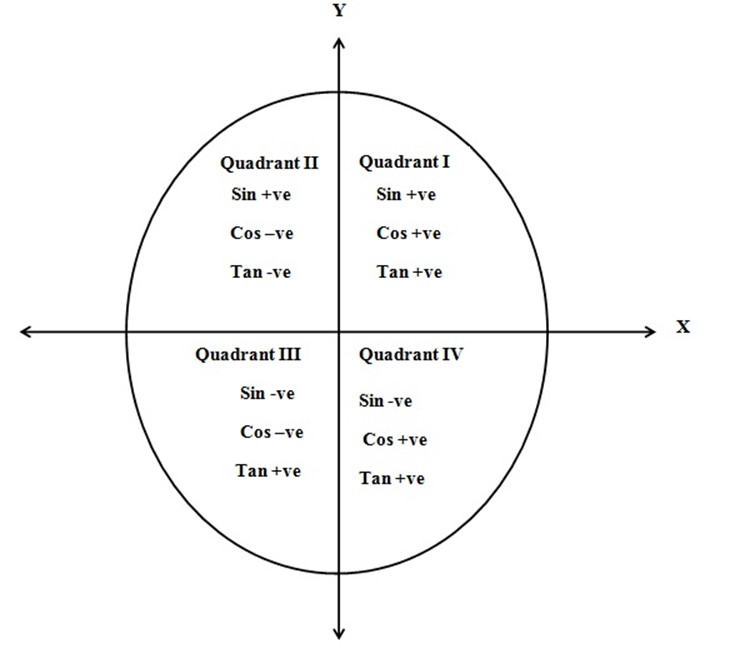
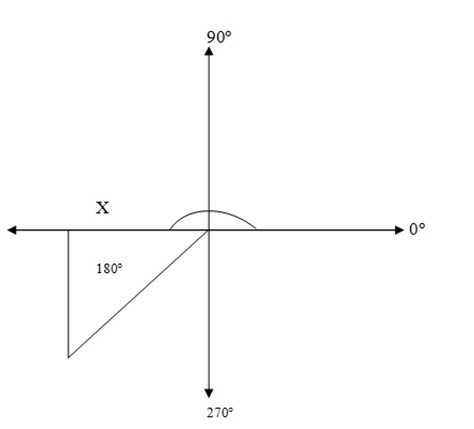
Consider a circle of units subdivided into four congruent sectors of the coordinate axes whose origin is at the center of the circle as shown below.
Let ø be any acute angle (0 < ø < 900) and let P with coordinates (x, y) be the point where OP intersect with the circle then
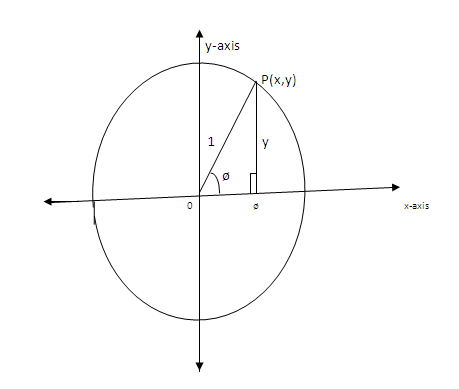
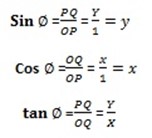
SIGNS OF THE TRIGONOMETRICAL RATIOS
The trigonometrical ratios can be positive or negative depending on the size of the angle and the quadrant in which the angle is found.
The results obtained are illustrated below. There results will be a help in determining whether sine, cosine and tangent of an angle is positive or negative.
Obtuse angle 900<θ<1800
Sin (180-θ)0 = y
Cos (180-θ)0 = – x
Tan (180-θ)0 = – 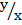
Sin θ = 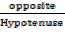 =
= 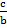
Cos θ = 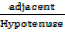 =
= 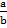
Tan θ = 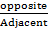 =
= 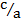
Tan θ =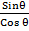
Tan θ = 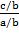
Tan θ = 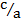
EXERCISE
1. Write the signs of each of the following
a. Cos 1600 = negative
b. Cos 3100 = positive
c. Cos 750 = positive
d. Sin 2200 = negative
e. Cos 3350 = positive
f. Tan 1900 = positive
2. Express the following in terms of sine, cosine or tangent of an acute angle
a). Cos 3080
=3600– 3080
= 520
=Cos 520
b). Sine 217 0
= ( -217 – 180)0
= -( 370)
= Sin -370
c). Tan 1750
= -(1800 – 1750)
= -50
Tan -50
d). Tan 3330
= -(360 -333)0
= -270
= sin-270
e). Cos 1030
= – (180 -103)
= -770
= cos -770
3. Express the following in terms if sine
a). Sin 130 0
= (180- 130)0
= sin 500
b). Sin 2300
= -(230 -180) 0
= -sin 500
c). Sin 310 0
= – ( 360 – 310)0
= -sin 500
Examples
1. Let θ be any angle and P with coordinates (-4, 3) be a point in the terminal point of op, see the figure below. Find
a. sinθ
b. cosθ
c. tanθ
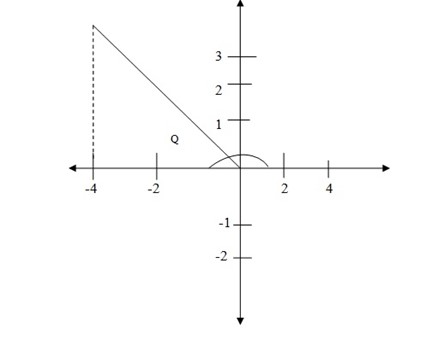
(OP)2= (-4)2+ (3)2
OP= 5
a. Sin θ = sin ( 180- θ) = 3/5
b. Cos θ = cos ( 180 – θ) = -4/5
c. Tan θ = tan (180-θ) = – ¾
EXERCISE
1. Find the cos θ and tan if θ is the angle made by the positive x- axis, from the line from the origin to each of the following points.
a. ( 2,6)
Solution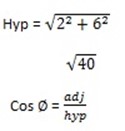
Cos θ = 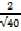
Sin θ = 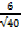
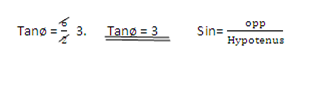
b. (-12 , 5)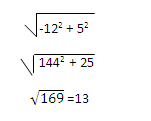
Cos θ = –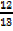
Tan θ = – 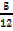
Sin θ = 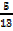
c. (-4,-3)
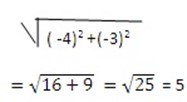
Cos θ = –
Tan θ = – 
Sin θ = –
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE ANGLES
NOTE;
1. If θ is positive, the negative angle corresponding to θ is (-3600 +θ)
2. If θ is negative, the positive angle corresponding to θ is (3600 +θ)
Example
1. Find the positive or negative angles corresponding to each of the following angles.
a. 3040= ( -3600 + θ) = (- 3600 + 304 ) = -56 0
b. -115 0 = ( 360 0+ θ) = 3600 + -1150 = 2450
2. Find the sine, cosine and tangent of each of the following angles.
a. 1440
Solution
1440 = 1800 – 1440 = 36 0
= sin 360 = 0.5878
= cosine 360 = -0.8090
= tan 360 = -0. 7265
b). -2310
= 3600 + θ = 3600 + -231
= 1290
=1800– 1290
= 510
Sin 510= 0.7771
Cosine 510= 0.6293
Tan 510= -1.2349
c). 310 0
= 360 0 –3100 = 500
Sin3100= sin500 = 0.7660
Cosine 310 0 = cosine 500= 0.6428
Tan 310 0 = tan500 = 1.1918
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS
Consider a triangle A, B, C in which angles A and C are complimentary angles. ie A+C = 900
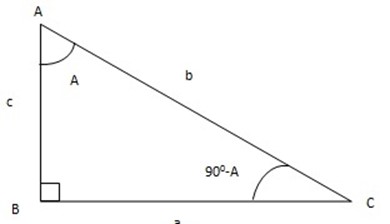
Sin A = a/b
Cos C = a/b
Sin A = Cos C = a/b
C = 90-A
Sin A = Cos (90-A)0 = Cos C = a/b
Cos A = c/b
(Sin A)2 = sin2 A
Sin 2 A + Cos 2 A = 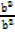 = 1
= 1
Exercise
1. Given that Sin θ = 4/9 . find Cos θ
Solution
Sin2θ + cos2 θ = 1
(4/9 )2 + cos2θ = 1
Cos 2 θ = 1- 16/81
Cos θ = 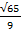
2. If Sin θ = 0.9397 and Cos θ = 0.3420. Find without using tables tan θ.
Solution
Tan θ = 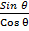 =
= 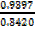 = 2.748
= 2.748
3. If Sin α = 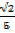 find sin(90-α)
find sin(90-α)
Solution
α + β = 900
β = 900 – α
Sin α = Cos (900– α) = Cos β = 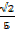
Sin2β + Cos 2β =1
Sin2β + 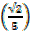 2
2
Sin2β= 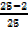
Sin2β= 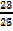
Sin β = Sin (90-α) = 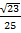
4. If Sin A = 0.9744 and Cos A = 0.225
Find without using tables Tan A?
Solution
Tan A = 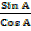
=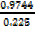
Tan A = 4.3307
5. Find without using tables sin α if cos α = 0.9272 and tan α=0.404
Solution
Tan α = 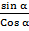
0.404 = 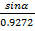
Sin α = 0.3746
APPLICATIONS OF TRIGONOMETRICAL RATIOS
Angles of depression and elevation
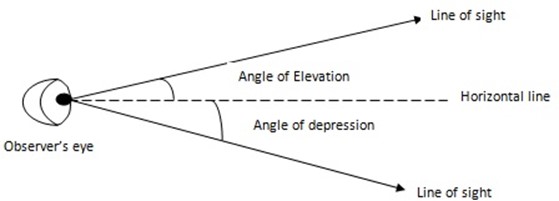
Example and exercise
1. From the top of a tower , the angle of depression of a point on the ground 1M away from the base of the tower is 600. How high is the tower?
Solution
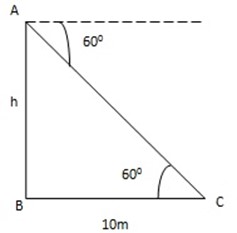
Tan600= 
Tan600= 
BA = tan 600 x 10 m
BA = 17.321m = height of a tower
2. P and O are two pegs on level ground and both lie due west of a flag staff. The angle of elevation of the top of the flagstaff from P is 450 and from Q is 600. Find distance PQ.
Solution
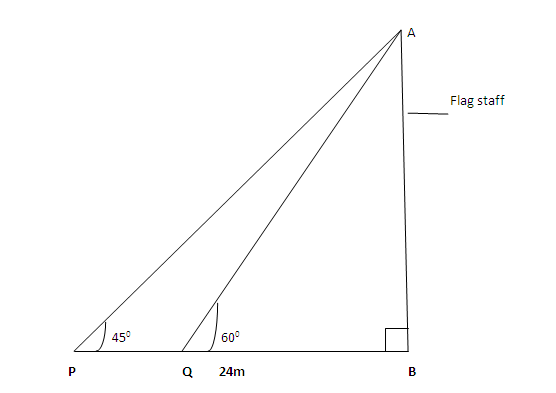
Tan450= AB
24m
AB = 24m x tan450
AB = 24m
Tan 600 = 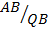
QB = 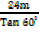
QB = 13.85m
PQ = 24m – 13.85m
PQ = 10.15m
3. At a point 182 m from the foot of a tower on a level road, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 360441. Find the height of the tower.
Solution
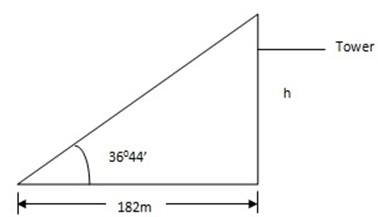
Tan 36044′ = 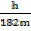
h = 0.7463 x 182 m
h = 135.8266m
4. x and y are two points on opposite banks of a river( figure below) . If PY measures 90m and XPY = 590. Find the width of the river.
Solution
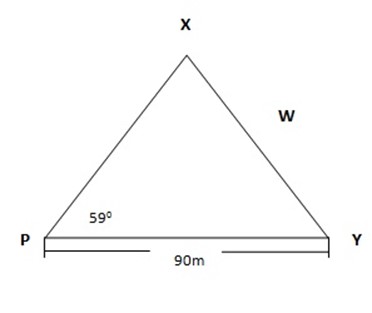
Tan590 = w
90m
W = tan590 x 90m
= 1.6643 x 90m
= 149.787m
TRIGONOMETRIC SPECIAL ANGLES
|
angle |
00 |
900 |
1800 |
2700 |
3600 |
|
Sine |
0 |
1 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
|
Cosine |
1 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
1 |
|
Tangent |
0 |
∞ |
0 |
∞ |
0 |
edu.uptymez.com

Cos θ= 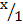
Cos θ = x
Sin θ = 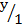
Sin θ = y
OTHER SPECIAL ANGLES:
Consider an equilateral triangle ABC
Let each side to have two (2) units
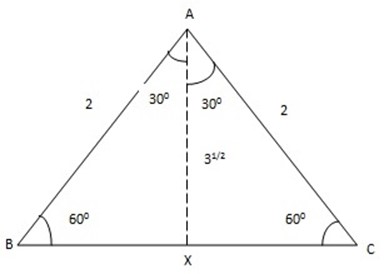
Using Pythagoras theorem
(AB)2 = (BX)2 + (AX)2
22 = 12 + (AX)2
AX = √3
Sin 600 = 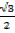
Cos 600 = 
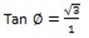
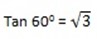
Tan 600 = 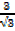
Sin 300 = 
Cos 300 = √3
2
Tan 30 0= 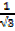
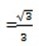
For 450
Consider an isosceles triangle ABC
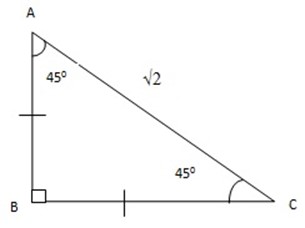
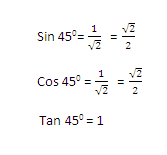
EXAMPLES
1. Find the sine, cosine and tangent of each of the following angles.
(a) -1350
= 3600 + -1350
= 3600– 1350
= 2250
=2250 – 1800
Sin 450 = 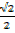
Cos 45 0 = 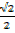
Tan (– 1350) = tan 450= 1
b. 3300
= 3600 – 3300
= 300
= sin 330 0 = – sin 300 = – 
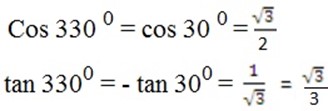
2. Find the values of the following without using tables.
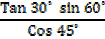
= 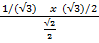
= 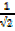 x
x 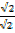
= 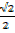
3. 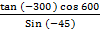
= 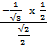
= 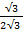 x
x 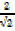
= 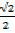
SINE RULE
Let us consider a triangle ABC, with its including angle C
Let us find the area of the triangle using its including angle and two sides.
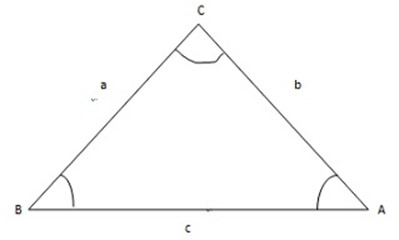
Area of triangle ABC = 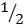 x a x b x sin C
x a x b x sin C
Area of triangle ABC = 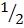 x a x c x sin B
x a x c x sin B
Area of triangle ABC = 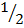 x b x c x sin A
x b x c x sin A 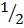 x a x b x sin c =
x a x b x sin c = 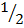 x a x c x sin B =
x a x c x sin B = 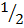 x b x c x sin A
x b x c x sin A
Dive each by 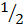 x a x c
x a x c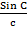 =
= 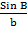 =
= 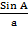
Examples
1. Find the unknown sides and angle sin each of the following triangles.
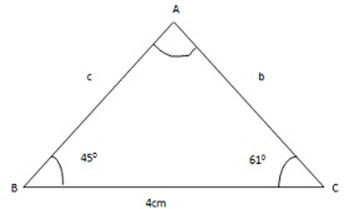
Solution
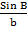 =
= 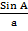
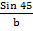 =
= 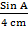
but A = 1800  ( 61+43)0
( 61+43)0
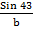 =
= 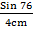
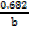 =
= 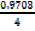
b = 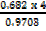
|
No. |
Logarithm |
|
6.820 x 10-1 4x 100 9.703 x 10-10 2.812 x 100 = 2.81cm |
1.8338 + 0.6021 0.4359 1.9869 0.4490
|
edu.uptymez.com
2. Juma notices that the angle of elevation of a coconut tree is 320. Walking 11 m in the direction towards the tree he notices the angle of elevation to be 450. Find the height of the tree.
Solution
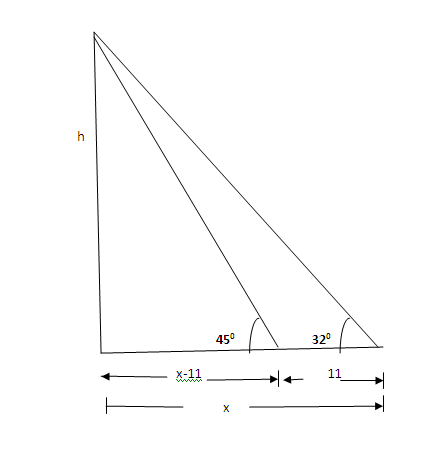
Tan45 0 = 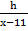
h = tan450 ( x – 11)
h = x – 11…..(i)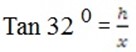
h = tan 320 X x
h = 0.6249x………….ii)
compare i) and ii) eqns
x-11=0.6249x
x-0.6249x=11
0.3751x= 11
x=0.0341m
COSINE RULE
Consider a triangle ABC whose coordinates are A ( 0,0) , B ( c, 0) and C (b cos A , b sin A)
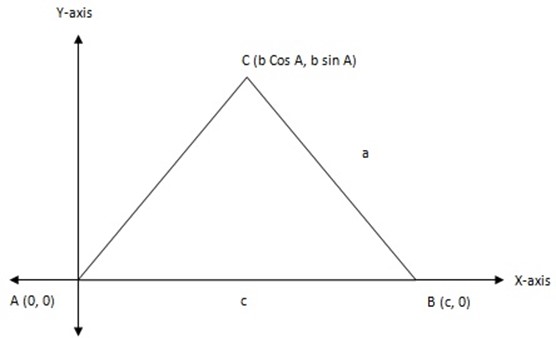
Cos A = 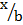
Sin A = 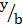
X = b cos A
Y = b sin A
a2= (b cos A – c)2 + ( b sin A – 0)2
a2= b2 cos 2A – 2bccos A + c2 + b2 sin2 A
a2= b2 sin 2A + b2cos 2 A – 2bccosA+ c2
a2 =(sin2 A+ cos2A)b2 + c2-2bccosA
a2= b2+ c2 – 2bc cos A
b2= a2+ c2 – 2ac cos B cosine rule
c2= b2+ a2 – 2 a b cos c
Example
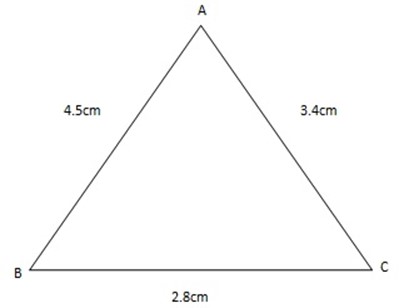
Find the value of angle A.
a2= b2+ c 2 – 2bcCos A
(2.8)2= (3.4) 2 + (4.5) 2 – 2 x 3.4 x 4.5 x cos A
32= 32 + 52– 2 x 3 x 5 x cos A
Cos A = 5/6 =0.8333
A = cos-1 0.8333
|
No. |
logarithm |
|
0.5 x 10 1 0.6 x 101 8.33 x 10-1 = 83.33 30034′ |
1.6990 – 1.7782 -1.9208
|
edu.uptymez.com
A = 33030′
COSINE OF THE SUM AND DIFFERENCE OF TWO ANGLES (A and B)
Cosine ( A + B ) = cos A cos B – sin A sin B
Cosine (A-B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
Verify that
Cos ( 90 – 60) = cos 90 cos 60 + sin 90 sin 60
Cos 30= cos 900 cos 600 + sin 900 sin 600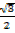 = 0 x
= 0 x 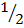 +
+ 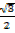
= 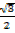
Questions
1. find the cosine of 750 without using mathematical tables.
solution
Cos 750 = cosine (30 + 45)
= cosine 45 cosine 30 – sin450 sin 300
= 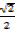 x
x 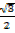 –
– 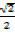 x
x 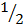
= 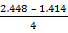
= 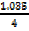
= 0.2588
We use the knowledge of coordinate geometry to find the distance and cosine rule.
Consider a unit circle of radius 1 with points P and Q and angles A and B shown in the figure.
Let the distance from P to Q be d.
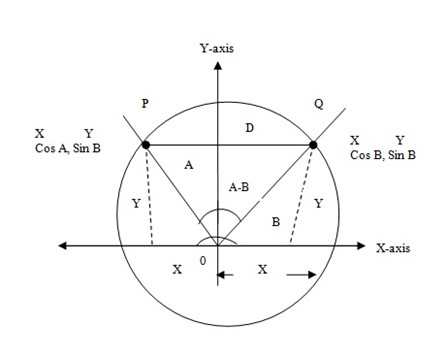
By distance formula
d2= ( cos A – cos B )2 + ( sin A – Sin B) 2
d2 = cos 2A  2 cos A cos B + cos 2 B + sin 2 A – 2 sin A sin B + sin2B
2 cos A cos B + cos 2 B + sin 2 A – 2 sin A sin B + sin2B
d2= cos 2A + sin 2 A + cos 2B + sin 2 B – 2 sin A sin B + sin 2 B
d2 = 1+1 – 2 (cos A cos B + sin A sin B)
d2 = 2 2(sin A sin B + cos A cos B) ……. (i)
2(sin A sin B + cos A cos B) ……. (i)
by the cosine rule
d2 = 12 + 12 – 1 cos (A-B)
d2 = 2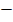 2 cos ( A-B) ……(ii)
2 cos ( A-B) ……(ii)
equate equation (i) and (ii)
2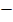 2 cos (A-B) = 2-2 ( cos A cos B + sin A sin B)
2 cos (A-B) = 2-2 ( cos A cos B + sin A sin B)
-2 cos (A-B) = -2 ( cos A cos B + sin A sin B)
Cos ( A 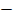 B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B …. (iii)
B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B …. (iii)
also
Cos (A+B) = cos ( A 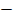 -B ) = cos A cos–B + sin A sin –B
-B ) = cos A cos–B + sin A sin –B
= cos A cos B – sin A sin B ……( iv)
THE SINE OF THE SUM AND DIFFERENCE OF ANY TWO ANGLES
Consider a triangle ABC and c as a acute angle.
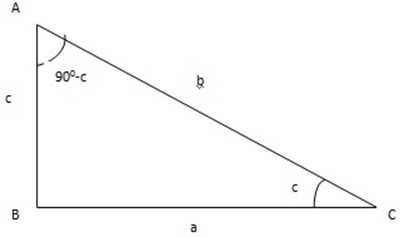
Sin C = Cos (90 – C) = 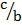 …….. (i)
…….. (i)
Now let C = 90 – A
Sin (90 – A) = Cos A = c/b …..(ii)
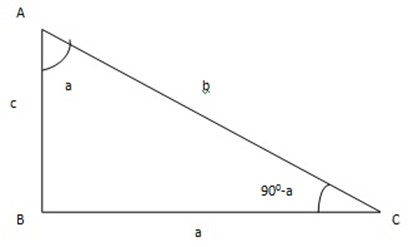
Also let c be A + B
Sin (A+ B) = cos (90 – (A+B))
Sin ( A+ B) = cos((90 – A) –B)
Sin (A+B) = cos (90- A ) cos B + sin (90- A) Sin B
Sin (A+B) = sin A cos B + sin B ( cos A)
Sine of the difference of any two angles A and B
Refer to the above expression
Sin (A-B) = sin (A + – B) = sin A cos –B + sin –B cos A
Sin A cos B – sin B cos A __ Difference of any two angles.
Exercise
1. (a) Find the truth set of
Sin θ = – 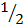 in the domain 0≤ θ≤3600
in the domain 0≤ θ≤3600
(b) verify that for any small angle A0
cos (90-A ) = sin A
Solution
a. sin θ = – 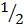
sin negative is in the 3rd and 4th quadrant
3rd
Θ-1800 = 300
Θ = 180 + 30 0
Θ = 210 0
4th
360 – θ =300
– θ = 300– 3600
– θ =- 330 0
θ = 330 0
The truth set of sin θ = 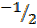 = 00 ≤ θ≤3600
= 00 ≤ θ≤3600
b. cos (90-A) = sin A
cos 90 cos A + sin 90 sin A =sin A
0 x cos A + 1 x sin A = sin A
Sin A = sin A
2. Use sin( S + -t ) to help find a formula for sin (s 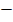 t)
t)
Solution
S 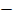 t = s + ( -t)
t = s + ( -t)
= sin S cos –t + sin (-t) cos S
= sin S cos t – sin t cos S
3 . Verify that sin (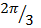 +
+ 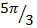 ) = sin
) = sin 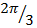 cos
cos 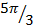 + sin
+ sin 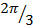 sin
sin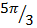
θ = 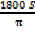
= 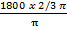
= 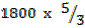
= 600 x 5
= 300 0
= 3600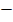 3000
3000
Sin ( 120 + 300) = 120 cos 300 + cos 120 sin 300
Sin 4200= sin 60 cos 60 + -cos 60 –sin 60
Sin 60 = 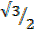 x
x 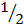 + –
+ – 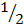 x
x 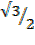
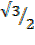 =
= 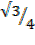 +
+ 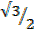
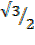 =
=