Is the thin upper layer of the earth’s crust which has been weathered from the parents material and decomposed animals and plants .soil support plants growth and animal life.
FACTORS INFLUENCING SOIL FORMATION
Soil formation is sometimes called Tredogenesis.
The formation of soil is mainly initiated by weathering process. There are several factors which influence soil formation these are as follows:
a) PARENT ROCK MATERIAL
This is one of the chief factors of soil formation. It determines soil type, color, depth, rate of soil formation, structure, texture, porosity and soil fertility.
Parent rock influence soil maturity, therefore hard rocks take a long time to mature while soft rocks take a short time to mature. Shallow and poorly productive
b) CLIMATE
The most variable elements under climate are temperature, precipitation (rainfall) and wind
- Temperature affects decomposition of organic matter hence it influences the development of soil profile
- Rainfall and wind ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage the formation of soil due to their role in the erosion process
- On the other hand rainfall adds moisture which ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courages chemical and physical weathering
edu.uptymez.com
c) LIVING ORGANISM
Some plants have nodules with bacteria which add nitrogen into the soil hence improve aeration of soil. Micro organisms are active in the decomposition of the organic matter to form humus on the other hand barrowing of animals and plant roots facilitate the state of both physical and chemical weathering hence lead to the formation of soil easily.
d) RELIEF [TOPOGRAPHY]
The role of relief in soil formation is mostly in indirect way. Relief influences climate and vegetation. The most important aspect of topography in soil formation, steep slopes areas soils are shallow due to erosion while on a gentle slopes and low land areas soils are deep due to deposition of materials.
e) TIME
This involves the duration that has been taken in the process of soil formation. Time determines the maturity of soil, when soil formation has taken a long time, soil tends to be mature i.e. they are deep and well developed.
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL
Soil is virtual life support to both flora and fauna organism , because all the organisms depend on the soil as their source of food . soil is therefore important to both plants and animals life in various ways including the following:-
(i) Animal life support ;
soil acts as plant habitat in which animals uses plants as food for their survival.
(ii) Building materials
soil is used directly in making of bricks ,tiles and white wash, The materials are the used in building of houses ,bridges and other structures.
iii) Source of minerals
some soils contains minerals which can be extracted for commercial purposes . For example Titanum is obtained from soil deposit of Kwale near Mombasa in Kenya Bauxite , which is mined in Guinea in West Africa
(iv) Cultural and medicinal values
Some soils are cultural value in some communities e.g red ochre and clay are used for body decorations by Maasai communities and clay mixed with herbals and being used for medicines
(v) Farming and settlement
fertile soil influence cultivation of crops .settlement nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution also depends on arable fertile soil where as people tend to dwell in areas with food availability.
(vi) Habitat for organisms
soil functions as a habitat for organisms such as burrowing rodent, earthworms and termite. These organisms perhaps are significant in the process of soil formation
SOIL CONSTITUENTS (COMPONENTS)/COMPOSITION
Soil is made up of the following components;
1.
Organic matter
This forms 5% of the total volume of soil and is made up of plant and animal remains. This forms humus as a result of decomposition of animals and plant remains.
IMPORTANCE OF HUMUS
i) Improving the structure of the soil and its water retaining capacity limits the leaching process and improves the soil acceleration
ii) Storing and supplying nutrients to the plant like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium – high production.
iii)Humus regulates the temperature of the soil and soil pH
iv) The living micro-organisms help in decomposition.
2) 2. Inorganic matter
This forms 45% of the total volume and is made up of minerals from the parent rock. Minerals constitute several nutrients which are needed by plants.
3) 3.Soil water
Forms 25% of the total volume and it is one of the most important soil components. It is derived essentially from rainfall especially from infiltration and through flow.
IMPORTANCE OF WATER
a) It regulates temperature in the soil
b) It helps in the solution and transfer of nutrients in the soil
c) Too much water in the soil leads to the leaching of mineral nutrients in the soil
d) It controls chemical processes like weathering as well as mechanical weathering.
4) 4. Soil air
It forms 25% of the total volume. It consists of the soil atmosphere from which plants and soil organisms obtain oxygen for their metabolism and dispose of carbon dioxide and other gases.
SOIL PROPERTIES
A: PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
1. SOIL PROFILE
This is the vertical section from the surface to the parent rock characterized by distinct layers usually of different texture and colors.
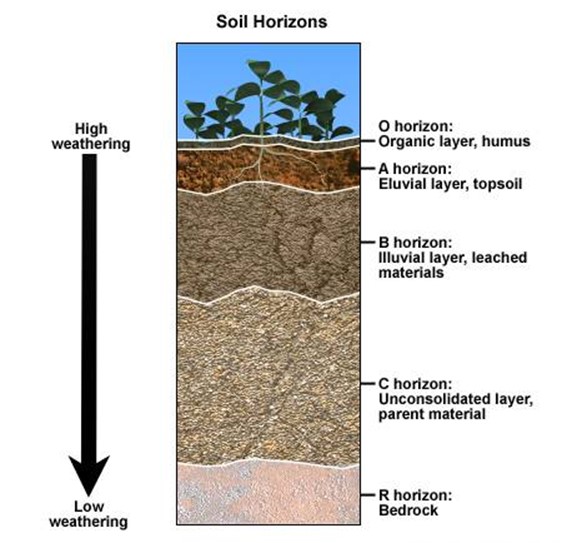
A- horizon
Is the topmost layer and can include organic matter to form humus. Horizon ‘A’ varies in color from place to place for example dark, grey etc. this zone is also called the zone of Elleviation from which materials are washed down ward. It is in this place where leaching process takes place.
LEACHING
Is the washing down of nutrients in solution from the topmost layer to another layer
B- horizon
This zone is also known as the zone of accumulation. In this layer the materials washed from ‘A’ horizon are deposited or accumulated.
C- horizon
Is the partially weathered parent rock from which the soil develops, it is underlined the D horizon which is the fresh [unweathered] parent rock.
D-horizon(Bedrock)
It is the unweathered parent rock. it is the parent in sense that it is the source of the in organic content of the soil
2. SOIL DEPTH
Soil depth varies from place to place depending on maturity. Maturity is influenced by the nature of the rock as well as duration of the soil forming processes which have been operating.
Soil depth is important for agricultural activities. Thus deep soil is important for agricultural activities while shallow soil is not good for cultivation.
3. SOIL COLOUR
Soil color is determined by the materials and the mineralogical composition from which the soil is derived and organic matter content. It varies from one place to another. Soil color can be classified and described in terms of ;
a) Dark [ black, grey, dark brown etc ] and cinnamon
b) Bright [ yellow, orange, red, reddish brown and yellow brown ]
c) Light [ white, whitish grey]
4. SOIL TEXTURE
This refers to the degree of coarseness of soil (especially soil mineral particles). It can also be referred to as variations in the particle size, caliber or mechanical composition
According to the soil texture, soil can be classified as;
a) Coarse sand (2 to 0.2mm)
b) Fine sand
c) Silt (0.02mm)
d) Clay (less than 0.002mm)
e) Loan soil is a mixture of sand, clay and silt.
NB; measuring of soil texture can be done through the use of finger testing
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL TEXTURE
1) It influences soil porosity, permeability, structure and retention capacity
2) It influences plant growth and root penetration
3) It influences the cultivation during agricultural activities
4) It influences soil resistance against erosion
5) It influences soil fertility
5. SOIL POROSITY
These are the total volume of the pores or empty spaces between particles of the soil materials especially in the soil. Soil porosity is mainly influenced by soil texture, organic matter, soil structure, individual undisturbed soil aggregate compounds referred to as peds.
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL STRUCTURE
i) It determines water retention capacity and aeration
ii) It is an indicator of soil fertility or suitability for agricultural activities, settlement locations and construction
iii) Good structure facilitates the activities of the micro organism
iv) It influences the cultivation process
v) It influences the plant growth by influencing the root penetration and water retention
-Therefore it is quite fundamental to note that the best soil is that which influences the water holding and aeration capacities of the soil.
6. SOIL STRUCTURE
This is the arrangement of soil particles into aggregate compounds particles. Individual undistributed soil aggregate referred to as peds.
7. SOIL TEMPERATURE
Soil has a certain degree of temperature and this tends to vary from one place to another due to the variation in the climatic condition.
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL TEMPERATURE
1) It controls biochemical and chemical processes especially the decomposition of organic matter and plant growth. Thus plant growth and decomposition tend to be fast in warm areas and slow in cold areas, this is due to the fact that growth cells and micro organisms tend to be very active in the warm areas unlike in the cold areas where they tend to be inactive or less active.
2) It also determines the existence of micro organisms in certain areas. In extremely hot areas and cold areas may not support the survival of animals and other micro organisms
3) It controls the amount of moisture in the soil where there is high evaporation soil moisture is less or the soils are dry
B : CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
These include soil properties like soil reaction (PH), reaction exchange and leaching.
1) Soil reaction ( soil PH)
This is the term used to describe the degree of acidity and alkalinity in the soil and it is related mainly to climate. This degree of acidity and alkalinity is expressed in the PH value which is the measure in terms of hydrogen ions concentration held by the soil colloid. Soil PH scale range from 1 to 14 where ph 7 is neutral, the condition below 7 is acidic while the condition above 7 is alkalinity which means it has more alkalis.
IMPORTANCE OF SOIL PH
- It helps in determining the selection of crops and agricultural nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution
- It affects plant growth such that where there is too much acidity there will be poor plant growth. This is because the increase of acidity leads to the increase in leaching with affects soil structure
edu.uptymez.com
LEACHING
This is another chemical property of soil referring to the process in which nutrients are washed down in solution from the top – soil laver. During leaching process the base are washed down leading to concentration of hydrogen ions which in turn cause the increased acidity in the top soil.
Leaching is very effective in wet conditions
SIMPLE HYPOTHETICAL PROFILE FOR MATURE SOIL
The soil profile varies from one place to another depending on the variation in environment conditions.
For example under deciduous forest, soil with little organic matter can be produced (brown either or brown forest soil) while in mid latitude grasslands deep black earth soil (chernozem) is formed.
Chernozem has a lot of organic matter. In the desert area the soil profile usually lack the Ao horizon due to scarcity or absence of vegetation.