What is ecology?
Ecology is a scientific study of relationship of organism with their natural surroundings
OR
- Ecology Is the study of relationships of living organisms to each other and their surrounding (physical surrounding)
edu.uptymez.com
Importance of studying Ecology
- It gives us scientific foundation of understanding some fields of studies such as agriculture which concern with crop cultivation and animal husbandry, forestry, fishery and so on
- The study of ecology gives us the basis for predicting and remedying environmental degradation (how to conserve environment)
- Help us to understand the likely consequences of massive interventions in the environment e.g. construction of huge dams, deforestation to open space for plantation, agriculture etc.
- Ecology is an important interdisciplinary science linking physical, biological and social science.
-
Ecology has given rise to a growing public awareness on environmental issues. This has given rise to development of laws on environment protection, formation of new political perspective e.g. environmentalism in Europe, emergence of environmental consultancies, development of environmental data services / base, etc.
Definition of terms
edu.uptymez.com
- Environment Refers to the surrounding of organisms. OR
edu.uptymez.com
- Everything that surround an organism and influence it.
edu.uptymez.com
- Population is a group of organisms of one species occupying a defined area or habitat at the same time.Community – Any group of organisms belonging to a number of different species that co-exist in the habitat or area and interact through trophic and spatial relationship.
- Ecosystem – A community of organisms and their physical environment interacting as an ecological unit.
- Habitat is a typical environment of a particular organism or population or community.
edu.uptymez.com
OR
An area occupied by a particular organism or population or community.
- Biosphere – Is the total volume of the earth in which life permanently exists.
edu.uptymez.com
Approaches to Ecology
A proper understanding of ecology requires simultaneously consideration of all factors interacting in a particular place.
Ecologists adopt one of the several main approaches when undertaking a new investigation.
Five approaches can be identified.
- Ecosystem Approach
edu.uptymez.com
This approach focuses on the flow of energy and cycling of matter in the ecosystem i.e. between the living and non-living component of the ecosystem. In this approach an ecologist relationship (such as feeding) between organisms and environment rather than description of the species.
- Community Approach.
edu.uptymez.com
This focuses in particular on the biotic component of the ecosystem. In this approach e.g. one examines the plants, animals and microbiology of recognizable biotic unit such as wood land, grass land and heat land. The functional aspects of physical environment is not studied in detail, it emphasis on identification and description of species present and factor that control their presence. Community approach is synonymous to synecological approach.
- Population Approach (Ant ecological approach)
edu.uptymez.com
This approach focuses on identification and description of individual species in relation to its environment.
- Habitat Approach
edu.uptymez.com
This focus on description of typical environment of a particular organism, population, community or ecosystem.
- Evolutionary and historical approach
-
This focuses on the changes that have occurred in the organisms over time and the development of technology and culture of the human species.
THE ECOSYSTEM
- The ecosystem refers to a community of organisms and their physical environment interacting as an ecological unit.
- The term describe the whole complex of organisms living together as a sociological unit and its habitat.
edu.uptymez.com
Component of the Ecosystem
- The ecosystem is made up of living and Non- living components
- The living component of the ecosystem is known as biotic component, these include plants, animals, microorganisms e.t.c
- The Non- living component is known as Abiotic component. The Non- living component of an ecosystem is divided into:-
- Soil
- Water
- Climate
edu.uptymez.com
Soil and water contain a mixture of inorganic and organic nutrients.
Climate includes environmental variables such as light, air, water, temperature.
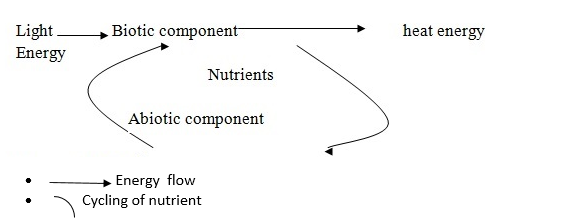
ENERGY FLOW AND NUTRIENT CYCLING
The essence of ecological studies lies in understanding how connections between the different organisms and their Abiotic environment work.
Energy flow and biochemical cycling are important functional links between the different ecosystems.
The two factors maintain the stability of the ecosystem. Stability of ecosystem means that the ecosystem can adjust to changes within itself.
The ecosystem is also sustainable i.e. it continues on its own without the necessity for human intervention.
Energy is defined as the capacity to do work.
Living organisms are likened to machines in that they require energy to keep them working i.e. to stay alive.
The Ecosystem like machines is kept working by an input of energy and nutrients. The ultimate source of energy in the ecosystem is the sun.
The sun is a star which releases vast amount of solar energy in space. The solar energy is captured by autotrophs in photosynthesis converting it into chemical energy (in form of food sources)
In the Biotic component photosynthetic organism utilize the sun’s energy directly and pass it to the other components of the ecosystem.
The energy is passed from the photosynthetic organism to the other through feeding relationship. The passage of energy through various component of the ecosystem is known as Energy flow. It is referred to as energy flow rather than energy circulation because (the energy released from the sun after passing through the component of ecosystem does not go back to the sun it is dissipated in the atmosphere as heat remain locked in some component of the ecosystem) it is changed into forms which cannot be used again by the system mainly heat energy.
BIOCHEMICAL CYCLING (Cycling of Matter)
The chemicals found in living organisms are derived originally from the abiotic components of the ecosystem such as soil, water, air to which eventually return by the way of decomposition dead organic matter.
Bacteria and fungi bring about decomposition obtaining the energy from the dead organism in the process.
Biochemical cycling is the constant cycling of chemical matters needed by living organisms within the ecosystem, the process is called biochemical cycle since both living and non- living part of the ecosystem is involved.
Light Biotic component heat energy
Nutrients
Abiotic component
- Energy flow
- Cycling of nutrient
edu.uptymez.com