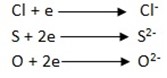
Non-metals these are elements which react with the electrons by gaining to form negatively charged ions

Where e = electron.
Example
There are only 17 non-metals (excluded H) arranged at right in the periodic table. They are electronegative elements with high electronegativity and ionization energy. They have a tendency to accept electron and form anions.
Characteristics of non-metals
- They are oxidizing agents. This is because they are electron acceptor or they gain electrons. The substance which gains electrons is said to be oxidizing agent.
- They have low melting point and boiling point.
- They have low density.
- They gain electrons during chemical reactions.
- They have low physical strength.
- Their oxides are acidic in nature.
edu.uptymez.com
Chemical Properties of non-metals
- Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides, which are acidic in nature. Hence non-metallic oxides form an acidic solution when dissolved in water and turn litmus solution red. For example, carbon is oxidized to form carbon dioxide, which is acidic in nature.
edu.uptymez.com

| Non metal | Its oxide |
| Chlorine –Cl | HCl or HOCl |
| Carbon- C | CO2, CO |
| Sulphur – S | SO2, SO3 |
| Nitrogen – N | NO2, N2O4 |
edu.uptymez.com
-
Most of non-metal oxides form gas with acidic, the neutral or basic
edu.uptymez.com
Common properties of gases
| GASES | SMELL | NATURE | SOLUBILITY | COLOUR |
| Ammonia NH3 | Urine smell | Basic or alkaline | Soluble | Colorless |
| Carbon dioxide CO2 | Odorless | Acidic | Soluble | Colorless |
| Carbon monoxide CO | Odorless | Neutral | Insoluble | Colorless |
| Sulphur dioxide SO2 | Irritating chocking smell | Acidic | Soluble | Colorless |
| Chlorine Cl2 | Irritating chocking smell | Acidic | Soluble | Greenish yellow |
| Hydrogen sulphide H2S | Rotten eggs or cabbage | Acidic | Soluble | colorless |
| Nitrogen dioxide NO2 | Irritating chocking smell | Acidic | Soluble | Reddish brown yellow |
| Nitrogen monoxide NO | Odorless | neutral | Insoluble | Colorless |
| Hydrogen chloride HCl | Irritating chocking smell | acidic | Soluble | Colorless |
edu.uptymez.com
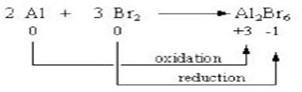
2. Non-metals are good oxidizing agents and are oxidized in almost all of their reactions. Like aluminum is oxidized with bromine to form aluminum bromide.
3. Non-metals have a tendency to oxidize metals.
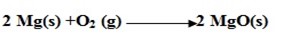
4. They can easily oxidize those compounds with which they react.

5. Less electronegative non-metals like carbon & hydrogen can act as a reducing agent for some compounds like ferric oxide and copper (II) oxide.

6. Generally, no reaction takes place between non-metals and acids. But non-metals react with base’s to form salts. For example, chlorine reacts with calcium hydroxide to form bleaching powder.
OXIDIZING PROPERTY OF NON METAL
An oxidizing agent is a substance which accepts electrons; a reducing agent is a substance which donates electrons. Oxidizing and reducing agents can be identified in redox reactions. The elements with low electronegativity (metals) tend to form ions by losing electrons (oxidation) and so can act as reducing agents; the elements with high electronegativity (non-metals) tend to form ions by gaining electrons (reduction) and so can act as oxidizing agents. The strongest reducing agents are found in Group 1 whilst the strongest oxidizing agents come from Group 7. The electrochemical series indicates the effectiveness of oxidizing and reducing agents.
One of the main properties of non metal is to gain electron. None metal have 4 to 6 electron in outer most shell.
example
- Nitrogen:2:5
- Oxygen :2:6
- Chroline:2:8:7
edu.uptymez.com
To become stable the outer most shell must be filled. Hence it is for non metal to gain an electron to become stable
example
- Nitrogen gain 3 electron = 2:8
- Oxygen gain 2 electron = 2:8
- Chlorine gain 1 electron = 2:8:8
edu.uptymez.com
Any chemical substance gain electron is oxidizing agent.Alsoall non metal is OXIDIZING AGENT
The number of electron gained per atom signifies a valency. A Cl gain 1 and oxygen gain 2 hence valency of Cl is 1 and for oxygen is 2.
- OXIDIZING POWER OF HALOGENS
edu.uptymez.com
These are elements found in the group VII of the periodic table and are salt producers.
Oxidizing power of halogens decrease as one move down the group, this is because of tendency of electronegativity decrease.
Examples of halogens are; chlorine, bromine, fluorine and Iodine
All halogens name end with suffix -ine
Properties of halogens
- Are salt producers.
- Are most electronegative elements. With fluorine being the most electronegative and Iodine the least in the group. The electronegativity decreases downwards the group.
- Some of them are gases, solids and others liquids at room temperature.
edu.uptymez.com
| Halogen | state at room temperature |
| Fluorine | Gas |
| Chlorine | Gas |
| Bromine | Liquid |
| Iodine | Solid |
edu.uptymez.com
4. They are colored.
| Halogen | Color |
| Chlorine | Greenish-yellow |
| Fluorine | Purple |
| Bromine | Brown-reddish. |
| Iodide | Brown |
edu.uptymez.com
5. They are strong oxidizing strong oxidizing agents i.e. they gain or accept electrons.
DISPLACEMENT REACTION INVOLVING HALOGENS
In displacement reaction one element take part of another in a compound. A more reactive non metal displace a less reactive non metal from a solution of one of its salt.
In group VII are more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halogen from another halide salt.
For example;Chlorine displace bromine or iodine
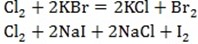
Chlorine
Chlorine is the greenish yellow gas which turns dump blue litmus red and bleaches it. Chlorine is a chemical element with symbol Cl and atomic number 17. Chlorine is in the halogen group (17) and is the second lightest halogen following fluorine. The element is a yellow-green gas under standard conditions, where it forms diatomic molecules. Chlorine has the highest electron affinity and the fourth highest electronegativity of all the reactive elements. For this reason, chlorine is a strong oxidizing agent. Free chlorine is rare on Earth, and is usually a result of direct or indirect oxidation by oxygen.
The most common compound of chlorine, sodium chloride (common salt), has been known since ancient times. Around 1630 chlorine gas was first synthesized in a chemical reaction, but not recognized as a fundamentally important substance.
Preparation of chlorine from potassium permanganate KMnO4 and hydrochloric acid
When potassium permanganate reacted with concentrated HCl, chlorine gas is formed, which is collected by the downward displacement.
Consider the diagram below.
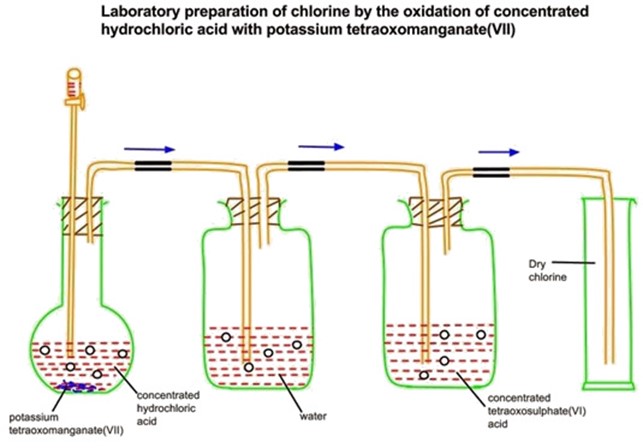
KMnO4(aq) + HCl(aq) → 2KCl + 2MnCl2(aq) + 8H2O(l) +5Cl2(g)
Preparation of the chlorine gas, hydrogen sulphide (H2S) and carbon monoxide in the fume chamber/ cupboard
Normally these gases are prepared in the fume chamber for the following reasons.
Because some of them are toxic and poisonous this can cause death to occur. So when the gases are prepared into the laboratory; windows and doors should be left open to allow good ventilation of the air in the laboratory, when the poisonous/toxic gases are produced, they can escape freely from the laboratory to the atmosphere to allow the leaked gaseous molecules to accumulate in the laboratory.
The Test for Chlorine Gas, Cl2 (g)
1.Chlorine gas is green-yellow in color.
2.Chlorine gas has a pungent choking smell.
3.Chlorine gas turns moist litmus paper from blue to red and moist universal indicator paper to red – it is acidic. After turning red both papers are then bleached white.
4.Chlorine gas will put out a lit splint.
Specific Test for Chlorine Gas
Chlorine is the only gas that has a bleaching affect
Properties of chlorine
- It is a greenish-yellow gas.
- It has an irritating shocking smell
- It is soluble in water.
- It is slight denser than air.
- It turns blue litmus red then bleach.
edu.uptymez.com
Chlorine gas is soluble in water.
When chlorine gas is dissolved in water, it dissolves to form hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hypochlorous acid (HOCl)

HOCl – hypochlorous acid
HCl – hydrochloric acid
- Where HCl can kill bacteria and HOCl can bleach or decolorize.
edu.uptymez.com
The acid decomposes to form oxygen and hydrochloric acid.

Chlorine gas is the bleaching agent.
Bleaching agent- is the substance which can decolorize or bleach or remove the original color of another substance, E.g.
- Blue into colorless
- Red into colorless
- Yellow to colorless
edu.uptymez.com
How chlorine bleaches colored matter such as water, clothes, litmus.
E.g. when the chlorine gas is dissolved in water it forms two acids Hypochlorous acid and hydrochloric acid. hypochlorous acid is unstable so it decompose slowly to form hydrochloric acid and oxygen , the formed oxygen combines with the colored matter to such that they undergo oxidation then bleaching occur such that the substance becomes colorless.
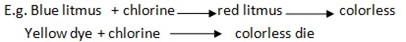
Chlorine gas or compounds added to the swimming pool and drinking water.
This is because chlorine gas dissolves in the swimming pool or drinking water to form HCl which kills bacteria and pathogens and at the same time decolorizes water thus makes water to become safe for using for human beings.
The addition of chlorine in water is called chlorination of water. The aim is to kill bacteria and decolorize water.
Water can be clean but not safe for drinking.
Because it may contain bacteria and microorganisms which cause diseases and can’t be seen by our naked eyes and so water should be boiled or chlorinated.
Chemical properties of chlorine gas
Chlorine shows the following chemical properties.
-
Reaction with metal.
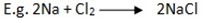
-
Reaction with water.

-
Reaction with alkali
E.g. NaOH, KOH etc
(a) Reaction with cold dilute alkali

KOCl is sodium hypochlorous.
(b)Reaction with hot concentrated alkali.

NaClO3 is sodium chlorate.
-
Reaction with ammonia gas

DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS OF CHLORINE
edu.uptymez.com
Chlorine gas can show the displacement reaction such that those elements below, it would displace.
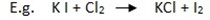
The potassium iodide solution turns to brown due to the formation of iodine gas.
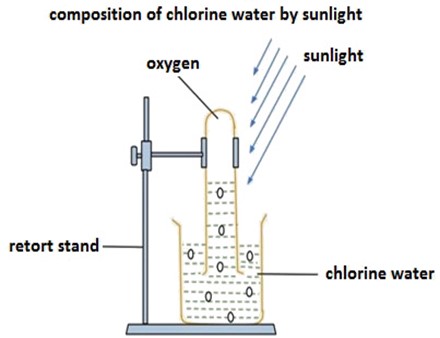
Effects of sunlight into chlorine water
Chlorine water is the unstable compound, when the heat or sunlight become into contact with chlorine water (HOCl), the chlorine water decomposes then produces oxygen and hydrochloric acid. Oxygen gas produced escape to atmosphere.

Consider the diagram below,
Commercial uses of chlorine gas
- It is used in the production of common salt, e.g. NaCl.
- Used in the chlorination of water, this is the addition of chlorine in water so as to kill the micro-organisms in water.
- Used in the bleaching action. E.g. Bleaching of water, some of the clothes can be bleached using chemical compounds made up of chlorine. Such as water guard.
- Used to make compounds used in the preparation of oxygen gas. E.g. potassium chlorate KCLO3 can be prepared from chlorine gas
-
(PVC)… materials used to make water pipes and plastics.
(PVC – polyvinyl chloride)
- Used in disinfecting.
- Used to bleach wood pulp in paper making.
- Used to make chemical such as carbon tetrachloride used in dry cleaning.