Generally, the subject matter tells us about what we study in Economics. However for the sake of conveniences, economics is concerned with the following:
1. It is concerned with how human being earns their living through exchange i.e. it is concerned with how man employs scarce resources to satisfy material wants.
2. It deals with production, nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution, exchange and consumption of goods and services.
3. It also deals with human activities which involve selling and buying. It doesn’t deal with goods and services that man produces for the sake of self-satisfaction.
These goods and services must have exchange value a part from satisfying human wants.
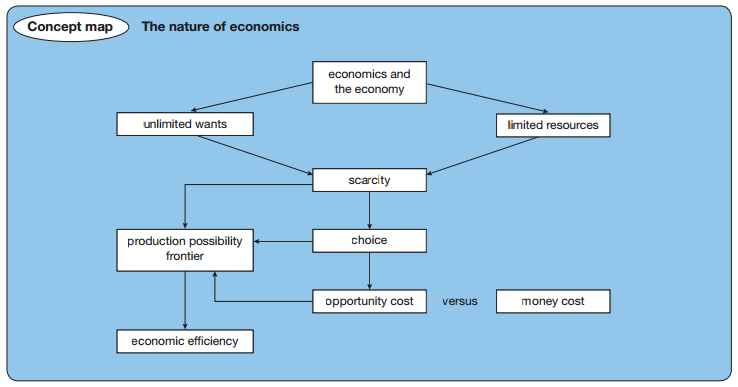
1.1 ECONOMICS TERMINOLOGIES:-
Distribution: is a process of rewarding or making payment to the factors of production such as Land -Rent, Labour- Wages, capital-Interest and Entrepreneur-Profits.
Wants: this refers to human desires.
Features of Humans wants:
-
-Human wants are unlimited,
-The resources used to satisfy the wants are (limited in number) scarce.
-Human wants can be satisfied by alternative means, E.g. Thirsty can be quenched by drinking water or soft drinks.
-Human wants are felt frequently such as food, water
-Human wants are complementary.eg; Driving is satisfied by car and fuel.
edu.uptymez.com
Needs:Are those necessary things when you loose it can cause death(Basics needs such as food,shelter and clothes).
Economics Resources:
Refers to the inputs which are needed to produce goods and services. They are also known as the factors of production or means of production. The factors of production are things which are necessary for production. The factors of production may include;
- Natural resources such as land and man-made resources such as capital.
- Human resources are such as labor and entrepreneurship.
edu.uptymez.com
Refers to the total expenditure by households or final users on goods and services which yield utility in the current period OR
Is the process of using goods and services to satisfy wants.
Are things that are produced by the factors of production like land, labor, capital e.t.c. and are consumed by man to satisfy his wants. It involves goods and services.
Production:Is a creation of goods and services for personal consumption or use.
OR
Is a process of making goods and provision of services to satisfy people‘s needs or wants e.g. Giving crops for food, building houses.
Wealth
Refers to the country’s stock of resources and goods that can be used to satisfy wants.
A country’s wealth consists of stock of resources and goods that can be used to satisfy wants. It includes; machines, buildings, and human skills.
In economics, wealth refers to all goods which possess the following qualities;
- They must have satisfaction (utility).
- They must be scarce.
- They must have value.
- They are capable of being transferred or exchanged.
edu.uptymez.com
Refers to the tangible things which satisfy human wants. Goods are categorized in the following ways;
- Free goods and Economic goods. Those free goods are provided free by the nature Eg Air, rain, ocean water.
- Private goods and public goods.
- Intermediate goods and final goods.
edu.uptymez.com
Welfare
Refers to the level of satisfaction that a person or group of people derives from the consumption of goods and services.
WELFARE ECONOMICS:The study of the impact of the pattern of resources allocation on society’s well being(or welfare)
Economist are able to judge whether the existing arrangement about
(a)the methods of production
(b)the type and quantity of goods and services produced and consumed
(c)the relative share of goods and service going to each household,are satisfactory.
EFFICIENCY: Pareto efficiency–a situation in which it is not possible to make someone better off without making someone else worse off.
EQUITY:Equity is concerned with the treatment of different individuals or groups in society.
MARKET EQUILIBRIUM:Exist when the price and quantity of a commodity match both consumers and producers.
In this case the quantity demanded and supplied are equal and the market clear.
MARKET DISEQUILIBRIUM:Exist when the price and quantity of commodity fail to match consumers and producers expectation.
Goods: – These are things which can satisfy human wants like clothes, cars, houses etc.
Goods are classified as follows;
Free goods:
These are goods which are provided freely by nature. E.g. Air, sunshine, rainfall, ocean water and forest.
Features of free goods
- They are not scarce i.e. they are abundant.
- They are not produced by human effort, hence are provided freely by nature.
- They are not transferable in terms of its ownership.
- They lack exchange value.
- They possess utility
edu.uptymez.com
ECONOMIC GOODS
These are the goods produced by human efforts and posses the following qualities;
Quality of Economic Goods
- They have utility, i.e. ability to satisfy wants/needs.
-
They have exchange value, i.e. they can be bought or sold.
(iii)They are transferable in terms of ownership from one person to another person.
edu.uptymez.com
Thus Economics is concerned with economic goods and not free goods because production in Economics is for exchange for which the economic goods possess value.
- Consumer Goods– These are goods produced for final consumption or use such as food, radio, clothes, furniture etc.
-
Producer Goods-These are goods which are produced to assist in the production of other goods. They are also known as capital goods. Producer goods include; machinery, raw material, workshop, building etc.
Perishable Goods : These are goods which can easily be destroyed or spoil like food stuffs e.g., milk, meal, fruits, vegetable etc.
Durable Goods: These are goods which can last or stay for a long period of time without being destroyed or damaged such as buildings, machines, furniture etc.
Private goods: Are goods owned by individuals for example private car, clothes, houses etc.
Public goods: Are goods owned and enjoyed by all individuals in the country. For example; roads, defense etc.
Feature of Public Goods:-Non divisibility i.e., provided in totality to the public.
Non rivalry i.e., there is no competition of consumption. One person can consume extra units without reducing consumption of others.
Intermediate goods:– Are goods in progress e.g. raw material.
Final goods:- Are goods ready for consumption.
Normal Goods:- Are the goods for which their demand increases when the real income of the consumers increases while their demand decreases when income of consumers decreases.
Inferior Goods:- Are goods which the demand of the goods by the consumers decreases when real income increases.