THERMOCHEMISTRY
This is also termed as Energetics.
Definition
Is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with energy changes that occurs during the chemical reaction.
The energy change during the chemical reaction is either positive or negative.
It is denoted by  H.
H.
ENTHALPY OF REACTION/HEAT OF REACTION
Definition
Enthalpy is the energy change which takes place during chemical reaction.
THE COMMON ENTHALPIES OF REACTIONS
The following are the common Enthalpies of reactions:-
1. STANDARD ENTHALPY OF COMBUSTION
This is the heat energy given out when 1mole of a certain substance is completely burnt in a given moles of oxygen at standard state.
If H for combustion reaction is negative i.e. The reaction is exothermic.
H for combustion reaction is negative i.e. The reaction is exothermic.
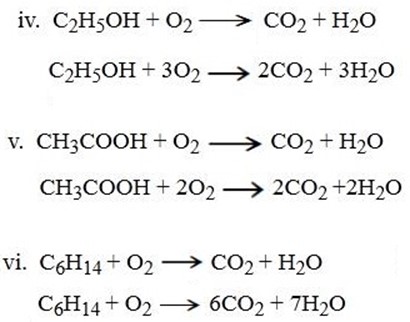
Example of combustion reaction
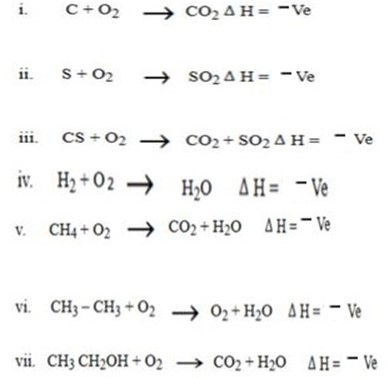
HOW TO BALANCE THE COMBUSTION REACTIONS
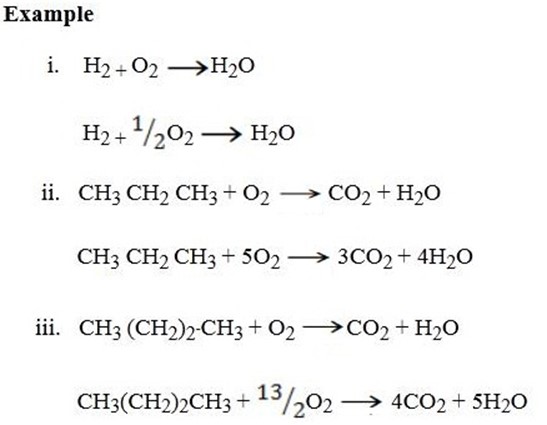
In balancing the combustion reactions we normally balance the other materials apart from hydrogen and oxygen first.
Secondly balance hydrogen then finally oxygen.
2. STANDARD ENTHALPY OF FORMATION
This deal with the formation of compounds. It is donated by ΔH°f.
Definition
Standard enthalpy of formation is the heat change which occur when 1mole of substance is formed from its element at standard state. Standard enthalpy of formation can be positive or negative.
ΔH°f may be +Ve or -Ve.
ΔH°f = +Ve Endothermic.
or
ΔH°f = -Ve Exothermic.
Example
Standard enthalpy of formation of CO2.
C+ O2 → CO2 ΔH°f.
ΔH°f of CO2 = ΔH comb of C
Example
ΔH°f of CH3COOH
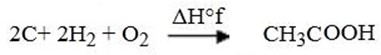
Example
ΔH°f of CH3 – O – CH3

3. STANDARD ENTHALPY OF NEUTRALIZATION (EN)
Definition
This is the heat energy given out when one mole of water is formed from the reaction between acid and base at standard state. Or
This is the Enthalpy change which take place when one mole of water is formed from reaction between acid and base at standard condition.
Example
HCl + NaOH  NaCl + H2O
NaCl + H2O  H = – Ve
H = – Ve
4. ATOMIZATION ENERGY
Definition
Atomization energy is the energy absorbed when a molecule or electron is converted to gaseous atoms. Atomization energy applied for non-compound and 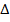 H is positive.
H is positive.
Atomization of energy is denoted by “Eat”.
Example
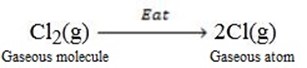
Br2
(g) 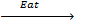 2Br(g)
2Br(g)
O2(g) 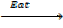 2O(g)
2O(g)
5. SUBLIMATION ENERGY (Es)
It is also known as dissociation energy.
Definition
Sublimation energy is the energy absorbed when one mole of solid atom is converted into gaseous atom.
Sublimation energy is applied for metallic atom and  H is positive.
H is positive.
Sublimation energy is denoted by ‘Es’.
Example
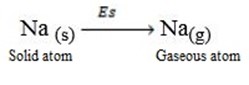
Al(s)  Al(g)
Al(g)
Mg (g)  Mg(g)
Mg(g)
Ca (s) 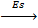 Ca(g)
Ca(g)
6. IONIZATION ENERGY (EI)
Is the energy used to remove an electron from the outer most shell of an atom, gaseous atom or ions to form an ion(s).
It is denoted by “EI “.
Ionization energy can be categorized as first 1st, 2nd and 3rd depending on the nature of stable ions that can be formed from an atom.
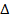 H is positive.
H is positive.
Example1

Ca +(g) 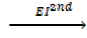 Ca2+ +
Ca2+ + 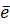
Example 2
Al (g) 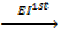 Al + +
Al + + 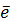
Al + 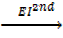 Al2+ +
Al2+ + 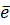
Al + 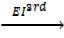 Al 3+ +
Al 3+ + 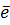
7. ELECTRON AFFINITY ( Eaff )
Definition
Is the energy required when one mole of non- metallic gaseous atom combine with one mole of electron.
It is denoted by Eaff.
Example
Cl (g) + 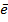
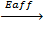 Cl–
Cl–
O (g) + 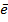
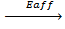 O–
O–
8. LATTICE ENERGY (EL)
Definition
Is the energy given out when one mole of ionic compound is formed from its ions.
It is denoted by EL.
Example
Na + + Cl– 1
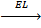 NaCl
NaCl
Al 3+ + 3Cl-1 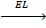 AlCl3
AlCl3
Mg 2+ + 2Br– 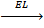 MgBr2
MgBr2
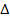 H = -ve
H = -ve
9. STANDARD ENTHALPY OF SOLUTION
Definition
Is the heat change when one mole of a compound is dissolved in a given moles of water at standard conditions.
Na Cl + Aq 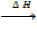 NaCl (aq)
NaCl (aq)
10. STANDARD ENTHALPY OF FORMATION
Is the heat change which occur when one mole of a substance is formed from its element at standard conditions.
eg. C+ O2→CO2(g) ΔHf = -393KJmol-1.