Is a branch of science which deals with the study of chemical/physical processes in which electricity is either produced or consumed.
REDUCTION-OXIDATION (REDOX) REACTIONS
Reduction is the addition of electrons to an atom or ion.
E.g. (i) 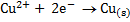
( ii) 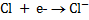
There is an overall decrease in oxidation state.
Oxidation is the reaction in which electrons are being lost therefore removal of electrons from the atom or ion.
E.g. 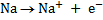
Redox reaction is the reaction in which both oxidation and reduction processes takes place at the same time. In a redox reaction, electrons are transferred between ions or atoms thus electrons are lost and gained in the same reaction.
NOTE: – In a balanced redox reaction, the number of electrons lost should be equal to the number of electrons gained.
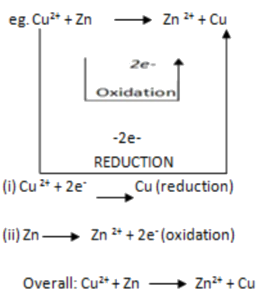
From the above reaction (overall reaction)
The substance in a redox reaction which loose electrons is called reducing agent or reductant i.e. Zn the substance in a redox reaction which gains electrons is called oxidizing agent (oxidant) i.e. 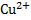
NOTE: An oxidizing agent which cause other species to undergo oxidation but itself being reduced.
Not all reactions are redox reaction :-
(i) 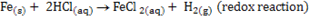
(ii)
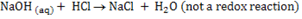
Reason
To identify a redox reaction one should look for the change in oxidation number of an element in the course of the reaction. If there is increase in oxidation number, oxidation has taken place and if there is a decrease in oxidation state, reduction has taken place.
Guidelines or rules for determination of oxidation number of an element in a compound.
1. In a free element, each atom has an oxidation number of zero.
2. For ions consisting of single atom, the oxidation number is equal to the charge of that ion.
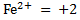
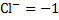
3. The oxidation of hydrogen is 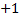 except in ionic hydrides where the oxidation is
except in ionic hydrides where the oxidation is 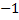 . E.g. NaH, KH.
. E.g. NaH, KH.
The oxidation state of oxygen is -2 in most compounds except in peroxide where the oxidation state becomes -1 and +2 in oxygen fluoride 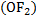 due to electronegativity of fluorine.
due to electronegativity of fluorine.
4. The algebraic sum of oxidation number in a neutral compound must be zero and a polyatomic atom must be equal to the ion charge.
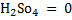
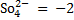
E.g.: calculate the oxidation number of the underlined elements in the following.
(i) 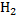 S
S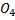
(2×1)+ S + (-2×4) = 0
2 + S – 8 = 0
S = +6
(ii) Cr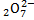
2 Cr + (-2 x7) = -2
2 Cr = 12
Cr = +6
(iii) N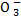
N + (-2 x 3) = -1
N – 6 = -1
N = +5
(iv) KMn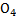
1 + Mn + (-2 x4) = 0
1 + Mn – 8 = 0
Mn – 7 = 0
Mn = +7
(v) P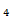
4P= 0
P=0
(vi) N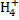
N+ (1x 4) = 0
N = -4
(vii) S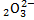
2S + (-2×3) = -2
2S – 6 = -2
2S = 4
S = +2
Disproportion reaction
Is the reaction in which an atom undergoes both oxidation and reduction reaction simultaneously in the same reaction.
OXIDATION – REDUCTION PROCESS
(i)
(ii) 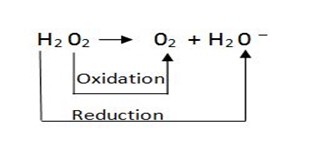
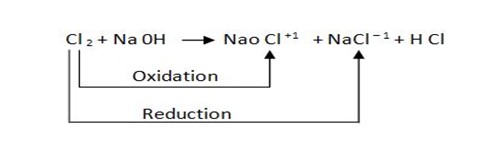
Rules for balancing redox reaction
eg.
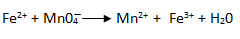
1. By using oxidation number identify which element is oxidized or reduced.
eg.
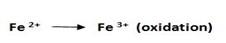
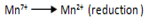
2. Write the half reaction for each process.
eg.
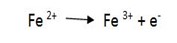
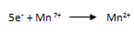
3. Balance the atoms that are reduced or oxidized.
4. Balancing number of oxygen atoms
a) In acidic solution
i. Add water molecules to the side that is deficient of oxygen atoms.
ii. Add appropriate number of hydrogen ions to the other side to complete oxygen balance.
eg:-
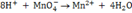
b)In basic solution.
i. For every oxygen atom required add OH– to the side deficient of oxygen atoms.
ii. Add water molecule to the other side to complete the oxygen balance
eg:- 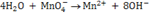
5. Balancing the number of hydrogen atom
(a) In acidic solution.
Add hydrogen ions to the side in deficient of hydrogen atoms.
(b) In basic solution.
(i) To every hydrogen atom required add water molecule to the side deficient of hydrogen atom.
(ii) To the other side add hydroxyl ion to complete hydrogen balance.
6. Balance the charge by adding number of electrons to the side which is more positive.
7. Multiply oxidation/reduction by the smallest number to ensure that the numbers of electrons cost/gained are equal.
8. Add the two balanced half reactions by omitting species which appear on both side to obtain the final equation.
9. Check the final result to ensure that species and charge are balanced.
eg. Overall reaction
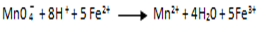
Example 2
(a) Balance the following redox reaction equation under acidic medium.
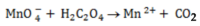
SOLUTION
1. Half reaction equation
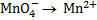
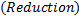
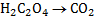
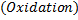
2. Balance under acidic medium
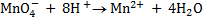
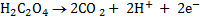
3. Balanced charged.
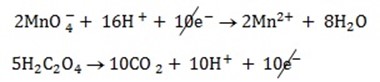
4. Overall reaction equation
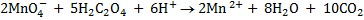
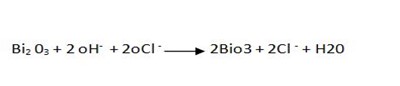
(b) Balance the following redox reaction equation under basic medium
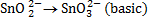
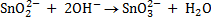
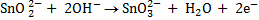
Therefore overall reaction :-
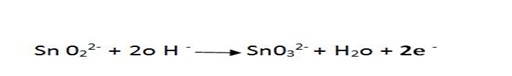
eg 2. 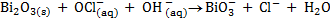
1.Half reaction
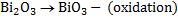
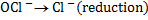
2.Half reaction under basic medium
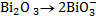
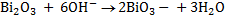
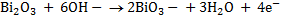
3.Half reaction under basic medium
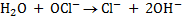
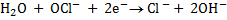
4. Balanced of charged
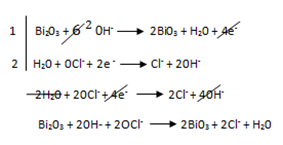
Overall reaction equation
Example 3
Balance the following redox reactions according to the media given.
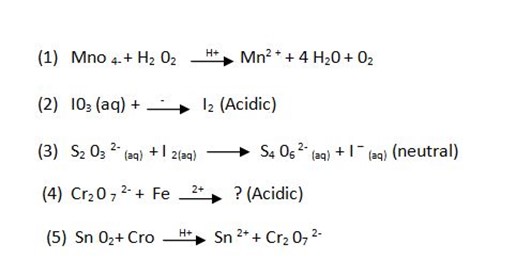
ANSWERS
Solution

Solution
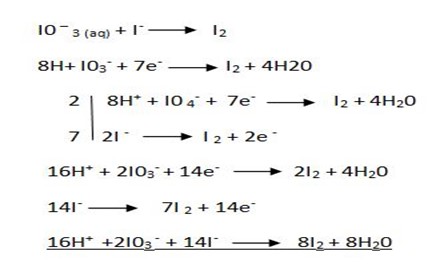
3. Solution
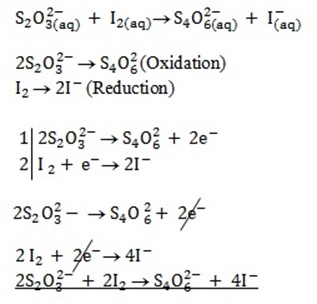
Solution

Solution
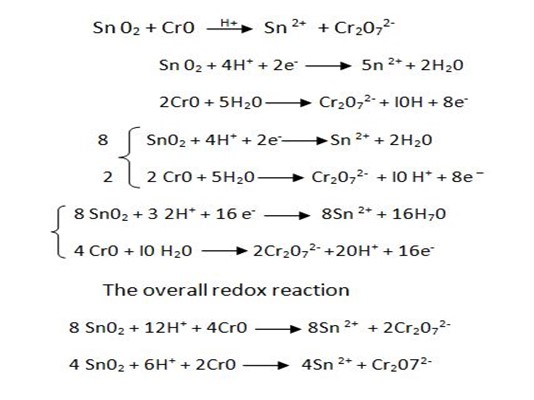
∴
SnO2 is an oxidant
CrO is an reductant