A laboratory is a special room designed for carrying out scientific experiment. A biology laboratory is a special building designed for carrying out biological experiments. A laboratory should have adequate space for carrying out experiment, proper lighting, good ventilation, source of water, means of heating and adequate space for storing apparatus, chemicals and specimens.
LABORATORY RULES
In biology laboratory we use hazardous chemical, fragile equipment or dangerous specimens. For this reason, it’s important to follow a certain rules and regulation for our safety and safety for others.
These rules are;
- Do not go into the laboratory in the absence of a teacher or laboratory technician.
- Do not handle or use apparatus, chemicals or specimens in the absence of a teacher.
- Do not taste/ eat substances during experiment
- Know the location of all exits
- Do not leave experiment unattended
- Turn off gas and water taps when not in use
- Do not burn substances towards other people in the laboratory
- Do not take laboratory equipments, chemicals or specimens out of the laboratory
- Do not play or run in the laboratory
- Read the labels or containers before using the contents. Do not interchange label.
- Dispose all waste materials after all experiment.
- After each experiment clean all the equipments you have used
- Avoid touching yourself while performing experiment, clean your hands with soap and water after Experiment.
- Do not touch electrical equipment with wet hands.
- If you don’t understand something ask your teacher.
- Know the location and operation procedure of all safety equipment e.g. First aid and fire extinguishers.
- Dress properly for laboratory activities, tie back long hairs. Do not wear dangling Jewelers, Sandals. Shoe must cover a leg completely.
- Report all accidents immediately to your teacher or technician
- Never use dirty, chipped or cracked equipment.
- Handle live spacemen carefully. if an animal bites or insect stings you, report the accident to your teacher
edu.uptymez.com
Distinguishing the biology laboratory from other facilities
The biology laboratory is different from other school facilities such as classroom, library or physics and chemistry laboratory.
A class room has desk and chairs, students are taught in a class room.
A library has variety of reading materials some libraries have tables and chairs where we can sit and read.
A biology laboratory has models, specimens, cage, aquaria and chart which may not be in physics or chemistry laboratory.
Some of unique things found in biological laboratory are preserved specimens of organisms such as insect, micro organism and plants.
WARNING SIGNS/ SAFETY SYMBOLS
These are warning signs that are found on apparatus and chemical containers in the laboratory. Some may be found in or on the boxes used to hold either chemicals or apparatus. These signs must be obeyed in order to ensure safety in the laboratory before one uses a chemical, one should know whether that chemical is Toxic, Corrosive, Flammable, Oxidant, Explosive, Harmful or Irritant.
TOXIC
Toxic substances are dangerous and may cause death immediately or after a few days. When handling toxic substances one should be very careful. In case a chemical gets into contact with your skin it should be washed out with a lot of water.


CORROSIVE
Corrosive substances can burn one’s skin. They can cause blindness in case they come into contact with the eyes. Example Of corrosive are sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and concentrated alkalis e.g. Sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide.

FLAMMABLE
These are substances which can catch fire easily. The substances should never be brought near open flammable

OXIDANT
These are chemical that can accelerate burning in the presence of an oxidizing agent, a small fire can be made bigger. Example in the heating of potassium permanganate mixed with saw dust

EXPLOSIVE
An explosion is a forceful rapid reaction, which involves throwing off of particles at high speed. Chemicals carrying the sign of explosive may cause explosion if not handled carefully and according to the instruction.

HARMFUL/IRRITANT
These are chemicals which can make you sick but it does not kill you, it can cause illness. This substance may not kill immediately, but may have effects after long exposure.

BIOLOGY APPARATUS
Biology apparatus are the tools and equipments needed in order to study Biological experiments effectively.
|
APPARATUS |
USES |
|
edu.uptymez.com |
Hand lens |
Used to magnify specimen/object. |
edu.uptymez.com |
Sweep nets |
Used to catch small flying organisms. E.g. Butter flies, housefly |
edu.uptymez.com |
Fishing nets |
For catching fish and aquatic animals |
edu.uptymez.com |
Petri-dish |
Is a shallow glass where specimen are put for close observation |
edu.uptymez.com |
Mortar and pestle |
Is small hard bowl used for crashing or grinding substances |
edu.uptymez.com |
Crucible |
Is a container in which substances are heated to very high temperature |
edu.uptymez.com |
Thermometer |
Used to measure temperature |
edu.uptymez.com |
Dissecting Kit |
Is a kit that contain all tools for making dissection of specimen |
edu.uptymez.com |
Spirit – burner Bunsen – burner |
Used as a source of heat |
|
10. |
Dropper |
Used to add liquid during experiment |
|
11. |
Spatula |
Used for taking some substance from the container |
|
12. |
Test tube holder |
Used to hold test tube |
|
13. |
Test tube |
Used to hold and heat chemicals |
|
14. |
Test tube rack |
Storing test tube |
|
15. |
White tiles |
Used to put specimen during experiment that involve colour changes |
|
16. |
Watch glass |
Is a shallow dish that used as evaporating surface or cover for beaker |
edu.uptymez.com
THE MICROSCOPE
The microscope is an instrument used to magnify very small specimen so that can be seen clearly.
THERE ARE TWO TYPES OF MICROSCOPE
1) Light microscope
2) Electron microscope
Light microscope can magnify object up to 2000 times. This is the type of microscope that is commonly used in school laboratory.
Electron microscope can magnify a specimen up to 50000 times.
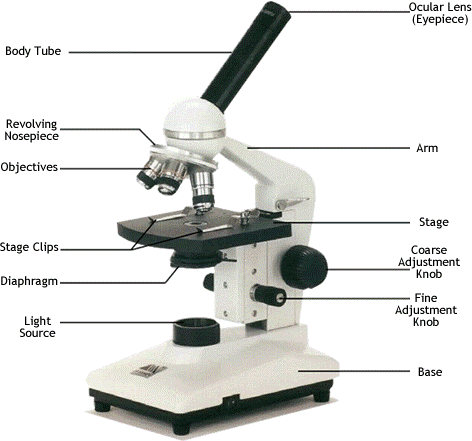
PARTS OF A LIGHT MICROSCOPE AND THEIR FUNCTION
|
1) |
Eye piece |
Has a lens which magnify specimen |
|
2) |
Body tube |
Support the objective revolving nose piece |
|
3) |
Rotating nose piece |
Support the objective lens |
|
4) |
Objective lens |
Magnify the specimen under observation.It has three lenses, lower power, medium power and high power |
|
5) |
Course adjustment knob |
Raises or lowers the body tube in order to bring the image into focus |
|
6) |
Arm |
Support the body tube, knobs, stage diaphragm and mirror. It’s one of the part which is held when moving the microscope |
|
7) |
Fine adjustment |
Raises or lowers the body tube in order to bring the image into sharp focus |
|
8) |
Ocular tube |
The tube allow light to pass straight from the objective lens to the eye piece lens |
edu.uptymez.com
THE STRUCTURE OF THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
How to use light Microscope
- Place the microscopes on the laboratory bench or table make sure it’s not near the edge.
- Mount the specimen on a microscope slide, cover it with the cover slip.
- Make sure that the low power objective lens is on line with the eyepiece lens.
- Place the slide with the specimen on the stage.
- While looking through the eyepiece, use your hand to adjust the stage so the light is directed at the specimen on the stage.
- Adjust the course adjustment knob to bring the specimen focus.
- Adjust the fine adjustment knob to bring the specimen into sharp focus.
- Rotate the nose piece to a lighter power objective lens if you want to observe more details on the specimen.
edu.uptymez.com
How to care for light Microscope
- Turn the adjustment knobs slowly, always start with course adjustment knob.
- Always lift microscope using both hands, one hand holding the arm and other holding the base.
- When not in use cover the microscope with clean cloth and store it in a dry, dust free space
- Clean dirty lenses using lens tissue or soft cloth.
- Don’t place the microscope at the edge of the table or bench as it could be knocked over.
- When not in use for a long time remove the lenses and put them in desiccators.
- Don’t touch the microscope with wet hands
- Don’t touch the surface of the mirror of the lens with your fingers.
- Lubricate moving parts regularly.
- Always use a cover slip in order to protect the lens of the microscope from the substances in the specimen.
- Remove the slides from the stage immediately after use.
edu.uptymez.com