THE CONCEPT OF PROFIT
Is the benefit which arises from the use of capital by someone or a firm when conducting business activities particularly in a certain period of time. Normally it is calculated by taking revenue or selling price the deduct by all expenses incurred or cost price.
OR
Profit
This refers to the surplus of selling price over cost price. It is the money made by selling something for more than its costs to buy or make it. The profit of a business is calculated in two stages.
(a)Gross profit. This is the surplus of selling price over cost price. It is calculated by subtracting the cost of sales from sales value.For example, if a business dealing in computers bought one at shs. 500,000 and sold it at shs. 1,000,000, the gross profit is shs. 500,000.(i.e 1,000,000 – 500,000 = 500,000).
(b) Net profit. This calculated by subtracting all business expenses from the gross profit.
THE CONCEPT OF MARGIN AND MARKUP.
Margin.This refers to the gross profit expressed as a percentage of selling price or turnover.
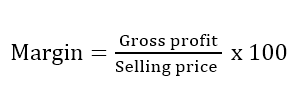
For example, suppose Alex bought goods worth shs. 1,000,000 and sold them for a total of shs. 1,300,000. His profit margin equals.
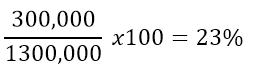
Markup.It is gross profit expressed as a percentage of cost price.
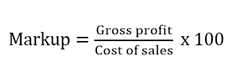
For example, if Alex bought goods worth shs. 1,000,000 and sold them at 1,300,000, his /her mark up equals
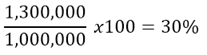
Gross loss.
This is the excess of cost of sales over net sales. It happens when the cost of sales is bigger than the value of the sales.
Net loss
This is the excess of expenses over gross profit. This is incurred by the business when the administration expenses are more than the gross profit.
Carriage inwards.
These refer to purchasing expenses e.g. the cost of transporting the purchased goods from the supplier to the business. This increases the expenses of purchases.
Carriage outwards.
This refers to a transport charge /expense incurred when transporting the sold goods to the buyer. It is a business expense.
Purchases.
Goods bought with an intention of re-selling them at a profit.
Net purchases.
In a trading period, some goods already purchased and recorded in the books of the business may returned to the suppliers for various reasons, e.g. they may be damaged or of poor quality. Goods that are retained in the business for resale are termed as net purchased.
Total purchases – Return outwards = Net purchases.
Return outwards /Purchases returns. These are purchases that are turned to the suppliers.
Return inwards/sales return. These are goods which were sold but have been returned to the business by the customer. The goods may be poor quantity or may be damaged.
CONCEPT OF STOCK TURN OVER
Is the rate which shows the number of stocks sold (turn over) during a particular period ,generally a year. It is calculated by;
Cost of sales
Average stocks
Example
ABC LTD. Produce the following information as at 31st .12.2010
Sales………………………………………..12’500/=
Gross profit ……………………………..3’000/=
Stocks(1.1.2010.)……………………..2’000/=
( 30th.June.) …………………..600/=
( 30th.December)……………800/=
Required; calculate the rate of stock turn over
Cost of sales = sales – gross profit
=12’000 – 3000
=9000
Average stocks =2000+ 600+800/3
=1133
=90000/1133 = 7.94
=8times
WAYS OF IMPROVING TURNOVER AND PROFITS.
Ways in which turnover can be increased include the following;
- Increase the use of advertising and sales promotions to increase sales as well as profits.
- Reducing prices of goods and services to increase demand for goods and services.
- Improving credit terms. This may ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage customers to buy possibly in bulk thus raising sales turnover and possibly profits.
- Reducing costs of supplies and expenses. This may raise gross profit as well as net profit because the sales prices will be maintained at their original level.
- Offering a wider range of products or services. This may attract more customers and thus increasing sales.
- Expanding business operations. Companies may choose to open additional branch or retail outlet to serve more customers or increase production of a particular product.
- Improvement in the methods of salesmanship.
edu.uptymez.com
THE CONCEPT OF COSTS
This refers to the amount of money paid by the firm in order to secure output.
TYPES OF COASTS
(a)Fixed costs.
These are costs which are incurred by the business but whose value does not change with output, they are unavoidable. They include office rent, insurance premiums, salaries of top management etc.
(b)Variable costs.
These are costs that change in relation to output e.g. raw materials, piece rate wags etc.
(c)Implicit costs.
These are costs which are not planned for.ie costs which are not be recognized when calculating profits of the business.eg family labour.
(d)Explicit costs,
These are planned for costs and are included in the budget of the business. E.g. Wages, Rent, Transport, Advertising.
(e) Average costs.
This is the cost which incurred for producing one unit of output.Sometimes is called cost per unit.
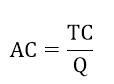
Where, AC = Average cost
TC = Total cost.
Q = Quantity/Output.
(f) Marginal cost.
This is the additional in total cost incurred for producing extra unit of output.
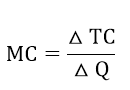
Where, MC = Marginal cost
= Change in total cost
= Change in Quantity/ output.
(g) Total cost.
This is the total amount of money used in production process. The total cost comprise fixed costs and variable costs.
(h) Cost of sales/Cost of goods sold.This refers to the purchase price of the goods that have already been sold. It represents the cost of items disposed of or sold. It help in the calculation of the gross
profit.
Turnover
This refers to net sales of the business in a given trading period.
BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS
Break even analysis is a point or situation where a firm generates neither profit nor loss.
In such case a firm is only capable to cover fixed and variable cost. Break even analysis based on the fact that
Selling price = variable cost + fixed cost
TERMS USED IN DETERMINING BREAK EVEN;
- Contribution margin
edu.uptymez.com
Is the difference between selling price and variable cost.
CM = S.P – V.C
2. Break even point ( unit) BEP (BEP(U))
It is expressed as total fixed cost divide by contribution margin
BEP(u) = TFC/CM
iii.B.E.P(V) = TFC/C.M X S.P(U)
3. Profit volume ratio(PVR); this is the ratio measures in how much sales the firm incur profit
PVR = ∆Profit/∆sales
Or
PVR = FC + Profit/Sales x 100
Or
PVR = CM(V)/Sales(u ) X 100
BREAK EVEN CHART
This is the diagram which shows sales revenue plotted against total cost. This is occurs where plotted against total cost. This occurs where the sales line intersect the total costline.
Margin of safety
This is the distance between break even point and the expected level of activity. It depicts amount by which actual activity can fall short of expected activity before a loss is incurred.
Or
Is a measure of risk to the left of break even point from the profit zone
Example;
A certain organization provides to you a certain information concerning to production of toys;
Fixed cost……………………………………………….10’000/=
Variable cost………………………………………………….4/=per toy
Selling price……………………………………………….6.50/= per toy
Production batches were 1000 toys to 9000 toys.
Required ;(a)calculate BEP in terms of number of toys and sales volume
(b)Draw break even chart
Solution;
( a) B.E.P in terms of number of toys = Total Fixed cost/C contribution margin
Whereby; contribution margin = selling price – variable cost
= 6.50 – 4
=2.8
B.E.P = 10’000/2.50 = 4000
B.E.P in terms of number of toys = 4000 toys
OTHER TERMS AND FORMULA USED IN BUSINESS CALCULATIONS
-
Solvency;
Is a situation that happens when business has more assets than liabilities, which is a capable to meet its debts from all sources.
-
Insolvency;
Is a situation that happens when a business has more liabilities than assets, which is not capable to meet its debts from all source
-
Bankrupt;
This happen when a business cease (stop) to function , sell its assets and distribute the proceeds among creditors in the ratio of their debts
-
Over-trading;
It happens when the business has no working capital.
Assets, these are items of value that belong to the business at a given period of time. There are two forms of assets; fixed assets and Current assets.
Fixed assets; are items of valuable that are acquired for the use in business. E.g. land, buildings, furniture and motor vehicles, machinery and equipment of all types such as tools, computers and photocopiers. They are durable in nature.
Current assets; are items of value in the business that can be turned into cash within a short period of time; they don’t last long in the business. They are also referred to as liquid assets. They include stock of goods, debtors, and cash in hand and pre paid expenses such as rent, water and electricity.
-Liabilities
Liabilities refer to anything a trader or business owes to someone. Liabilities are business obligations that have to be settled. The person/party whom a debt is owed is called a creditor. For example when a person purchased goods from XYZ coy ltd on credit, the XYZ coy ltd is a creditor and that person who bought the vehicle is a debtor to XYZ coy ltd.
There are two types of liabilities; Long-term liabilities and current or short-term liabilities.
-Long term liabilities; Are business debts which are payable within a period long than one year.
-Current or short-term liabilities; Are debts which are payable within a period of one year.
–Sales. The total value of goods sold during the trading period. This may also be known as Revenue.
-Stock. These are the unsold items in the business at a particular time. Stock comprises two categories opening stock and closed stock.
Opening stock. Is the unsold goods in business at the beginning of a new trading period.
Closing stock. Refers to unsold goods that remain at the end of the trading period.
edu.uptymez.com
-Expenses/ Costs. These are costs incurred in the process of running the business. These costs make the business to run efficiently and be successful. Costs include salaries and wages, postage and telephone, transport, taxes, advertising, rent, repairs depreciation and others.