This refers to firm or organization set up to carry out some production activities such as provision of goods or services in order to achieve higher turnover,consumers satisfaction, low cost and maximize profit.
OR:
Is an institutional arrangement to conduct one or other type of business activity.
A business unit is sometimes called an enterprise, a firm or business organization. It is formed and owned by groups of people or by individuals, with the aim of making profit.
FORMS OR TYPES OF BUSINESS UNITS(UNDERTAKINGS)
There are two types of business ownership:
(i)Private owned (private sector)
(ii)Publicly owned (Public sector)
Private sector. This consists of businesses owned by private individuals, either as sole traders or as a group.
Businesses in this sector include:
- Sole trade or sole proprietorship
- Partnership
- Joint stock companies and
- Cooperatives
edu.uptymez.com
Public sector. This consists of businesses owned wholly by the government or they are semi-government.
Businesses in this sector include:-
- Parastatals
- Public corporations
- Local government authorities, e.g. city council
- Municipal council and town councils and nationalized industries.
edu.uptymez.com
Various forms of business organization may be classified as under.
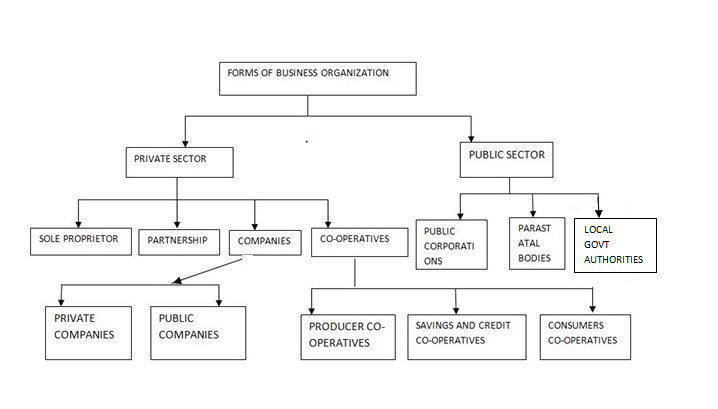
Factors influencing the size of business units
The size of business units can be large, medium and small business units.
Factors:
- Nature of industry. Businesses which require heavy capital in terms of machines and other technical equipments are termed large scale businesses.
- Nature of demand. If the nature of demand is steady and the product is more or less standardized the business undertaking is likely to be large.
- The size of capital. If the capital invested is heavy the business unit is likely to be big rather than if the capital is small or little amount.
edu.uptymez.com
Factors influencing the form of business ownership.
- Ease of formation
- Amount of capital required and the method of raising capital to be adopted
- Managerial ability of the owner
- Rights of the members to manage the day to day business
- The extent of risk involved in running business
- Continuity of the organization (prospects)
- Maintenance of business secrets
- The extent of government control.
edu.uptymez.com
- SOLE TRADE/ SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP
edu.uptymez.com
This is a business organization owned and operated by one person who raises capital either from his own resources or who may borrow from friends or banks, but cannot appeal to the public to subscribe. The owner is responsible for the success or failure of the business
OR
Sole proprietorship can be defined as a type of business organization in which one person owns, controls and control and operates a business to earn profit.
Distinguished features/characteristics of a sole trade/sole proprietorship.
The main characteristics of sole proprietorship are as under.
- Ownership. The ownership of the business unit is by one person
- Management. In sole tradership, the owner is the active manager of the business unit. If the business is large, he may deligate some of the powers to his trusted employees. However, the final authority and overall control of policy is retained with the proprietor.
- Finance. The capital necessary for operating the business is normally provided by the owner himself. However if additional funds are required, the capital can be increased by borrowing.
- Size of the business unit. The size of business unit is usually small.
- Risk. The sole proprietor operates the business for his own personal interest. Therefore, he is responsible for all risks of business.
- Unlimited liability. The liability of the sole proprietor is unlimited. In the event of insolvency of the business, he will be responsible for making good the deficiency from his personal wealth even to the extent of selling his personal assets.
- Entity. The business is not a separate legal entity from the sole trader. It means that by law the business and its owner is treated as one.
- Freedom of action. Sole trade can take prompt and immediate action within a legal frame work.
- Continuity. The continuity of the firm is based on the health of the owner.
- No legal formalities. There are no legal formalities to set up the business. However, there may be legal restriction on the setting up of a particular type of business.
- Profit. As the owner bears full risk of the business, he therefore, retains all profit with him.Formation of a sole proprietorship business.
edu.uptymez.com
When an individual plans to start a business, his/her main objective is to earn profit. But there are number of factors to be taken into consideration. For example, for any business to be successful.
Planning and research. Proper planning and research is very essential before the business is formed.
Kind of goods or services to be traded. A sole proprietors should be clear about the kind of goods or services he/she wants to deal in.
Capital or investment. The kind of capital or investment available to start the business must be taken into consideration.
Size and nature of the business. The sole proprietor should know the size and nature of the business so that the required amount of capital can be raised.
Location of business. Many business have failed or succeed depending on the location. This again depends on the nature of the business.
Legal formalities. These include registration of the name of business, licenses and some other requirements depending on the kind of business.
Risk. Also the sole proprietor should know the risks involved in the particular type of business.
Kind of customers. The sole proprietor has to know the kind of customers the business is targeting, for example it is the students, low income earners of high income groups.
Time factor. This is also important because every business has a low or high season. For example a shop dealing in school books or uniforms will do good business during the back to school season. Those dealing in clothes and shoes will do good business around festive seasons like Christmas.
Competition. During festive seasons like Christmas almost every business has competition from other people dealing in the some kind of goods or services. Therefore before starting a business it is very important to know the competition and how it will affect the business.
Management of sole proprietorship
In sole proprietorship the owner is usually in charge of day to day running of the business. If the business is large he may give some duties to his trusted employees or family members but the overall control and decision making powers rests with the owner. The sole proprietor decides on how to manage the business in the most effective way. If his decisions are good the business will prosper and if they are bad then it will adversely affect the business.
Some of the policies which are decided by the proprietor
(i) The time of operating the business
(ii)Promoting through advertising or special offers
(iii)Dealing with suppliers and customers
(iv)Bank transactions
(v)Whether to open other branches or remain in one premise.
(vi)Future planning
Sources of finance for the sole proprietor
For any business to start, availability of capital is the most important factor without capital it can be very difficult for a new business.
Some of the sources of capital for a sole proprietorship business are:-
(i)Savings. Some people plan in advance to start a business and for that they start saving in order to accumulate the required amount.
(ii)Assistance from friends and relatives. Some people ask their near and dear ones for some assistance in the form of money to start a business. They either agree to return the money and sometimes they are given as a donation.
(iii)Proceeds from a sale of asset(s). This is a common way of raising capital to start a business. For example, if a person is intending to start a business has a house or a car then he or she can sell that asset and use the money to start a business or expand the already existing business.
(iv)Bank loan. A sole proprietor may apply financial institutions. But this can be difficult at time because a bank requires security against the loan and some time an individual who plans to start a new business may not be able to fulfill the requirement. A security can be inform of property or shares.
(v)Credit. Some people know big companies dealing in certain kinds of products and they can approach them to give them goods on credit. This normally happens person to person. For example, an individual has some friends or relatives who are either working in or owning on manufacturing or a wholesale business. Such people can help the trader to get goods on credit but this is usually based on trust. It is very important for the sole trader to have strict control and discipline so that he can sell and pay back for those goods at an agreed time. In this way his credit ratings will improve and he can expand business.
(vi)By ploughing back the profits. The business itself by ploughing back the profit.
(vii)Finding by NGO’s.There some Non-Government organizations which helps some people to start a business by providing capital assistance.
Closure/dissolution of sole trade business
This is the termination of the legal life of the business or end of the business
A sole trade may come to an end due to the following reasons:-
(i)By voluntary decision to do so
(ii)Death of the sole proprietor will cause an end to the business
(iii)Bankrupt. When a sole trader becomes bankrupt may cause an end to the business
(iv)Involving in illegal business. If the sole proprietorship is caught dealing with illegal business e.g illegal drug, pedding or when the sole trade becomes unlawful due to changes in the law.
(v)Transfer of the business by the owner to another party.
(vi)Persistent losses incurred by the business.
(vii)Government policy that venders the activities of business illegal.
Merits/advantages of soletrade.
(i)Simplicity of formation.A person can undertake any lawful business activity for profit motive. The person has to develop an idea set the goals and then develop it into a profitable operation.
(ii)Personal incentive. A sole proprietor takes personal interest for the success of a business. In this way, he can maximize his profits.
(iii)Close supervision. A sole proprietor can supervise his business closely and he has direct contact with employees.
(iv)Need for small capital.It is easier to set up since it does not require a lot of capital.
(v)Business secrets can be preserved. Unique clues of business developed by his fact, foresight can be preserved and these secrets may remain unknown to competition and others.
(vi)Quick decision and prompt action. The sole proprietorship need not consult others or seek their approval. Quick decisions and prompt actions help to improve efficiency of business operation.
(vii)Flexible. A sole trade can make a major policy decisions change the nature of the business or its premises easily.
(viii)Economy in size and operation management of sole proprietorship is not expensive. The proprietor controls all the activities with much each and may sometimes operate without the need of assistants or if any are few numbers.
(ix)Close contact with customers and employees. A sole proprietorship due to its size is in a position to maintain close contacts with his customers and employees.
(x)Economic and social utility. It provides opportunity for gainful employment to person with limited capital. Also it enables individuals to earn a living independently using his still and professional drive.
(xi)Sole authority. The proprietor being the sole authority, takes decisions of planning, organizing, staffing, coordinating, controlling and directing of business unit.
(xii)A sole trader takes all the profits and bears all the losses. This provides to a sole trader the high degree of incentive. Hard working can benefit a sole trader and mistakes can ruin him/her.
(xiii)Easy of dissolution. A sole proprietorship can easily be dissolved as no legal procedures are involved in it. Satisfaction of the creditors is the only claim in winding up the business.
(xiv)Location. This type of business is not limited to urban centers. It can be set up even in remote area where a large business would not be quite as profitable or easy to establish.
(xv)Minimum legal restrictions. An individual enterprise is easy to form and simple to run as minimum legal restriction are imposed on it.
Demerits/Disadvantages or limitations of sole proprietorship.
There are certain serious disadvantages which a sole trader has to face in operating the business. These limitations are as follows:-
(i)Unlimited liability. The proprietor is personally liable for all the debts of the firm. Fear of loss of personal property due to failure of business makes the proprietor very caution and conservation. As a result a business may fail to grow and keep pace with new development in its particular field.
(ii)Limited capital. Financial resources of a sole proprietorship/sole proprietor are limited to what one person has. Funds of an individual person are basically not enough to operate large scale business
(iii)Limited managerial ability. A sole trade relies upon his or her own skills and judgment for operating the business. Most of the proprietors do not possess all the management skills required for financing, marketing, purchasing, producing and supervising the business.
(iv)Doubtful continuity. Business may come to an end or a stand still due to illness, insolvency and death of proprietor. His successor may not be capable of enough to carry the business successfully.
(v)Limited scope of expansion. Due to limitation of capital and management sole proprietorship business cannot grow and expand to a large size. Its goodwill and bargaining position are also weak.
(vi)Over worked. The proprietor is overburdened with so many task i.e financing, maging advertising, and correspondence, account, records, e.t.c.
(vii)Unable to carry out research. The smallest of the capital and the fear of risks of loss may stop the owner from carrying out the market rearch which would prove more paying.
(viii)Poor decisions may be made. One person is responsible for making decisions and may not have anyone to consult.
(ix)Dependency. The life of the business depends on the ability and life of the owners i.e his/her death brings about the end of the business
(x)Lack of collateral security. A sole trader cannot easily acquire loans from the bank and other financial institutions because he/she has no collateral security e.g land title. Therefore, he/she always operates on a small scale thus does not enjoy the benefits of large – scale operations.
(xi)Losses falling on owner alone. A sole trader bears all the risks and suffers all losses of business alone because he/she has no partner to share the business burden with.
(xii)Inefficiency. The sole trader may sometimes be inefficient as he/she may not be always available for his customers.
(xiii)Low discount given to sole trader. Small sole traders will not receive useful discounts when purchasing materials or goods for resale, because unlike large organizations, they cannot by in large quantities.
Conclusion. By examining the merits and demerits of sole proprietorship, one can easily conclude that this form of business organization is most suitable in the cases:-
- Where the business is carried out on small scale, and the capital to operate is small
- Where there is ease of organization, and the owner can make independent decisions
- Where the customers have individual tastes and require personal attention.
edu.uptymez.com
- PARTNERSHIP
edu.uptymez.com
Partnership is a relationship between two or more persons carrying on a business in common and sharing the profit or loss in agreed proportion. The liability of partner is unlimited unless the partnership agreement provides for any limitations.
Features or characteristics of partnership
- Agreement. There must be an agreement which form a basis of the partnership business. The agreement may be express or implied.
- Lawful business. The agreement must be to do business with a view to get profit and such a business must be within the limits of law.
- Sharing profit. Profit should be shared equally or according to agreement. In case of loss partners have to share it too.
- More than one person. There must be at least two persons to form a partnership and should not exceed ten (10) in case of banking business, there is no maximum limit for professional partnership like lawyers, e.t.c.
- Mutual agency. Every partner is an implied agency of the other partners and of firm, i.e each partner is bound by the acts performed by other partners on behalf of the business.
- Restriction on transfer of capital. No partner can transfer his partnership rights to another person without the consent of all other partners.
- Unlimited liability. Each partner has an unlimited liability to the extent of the firms debts, i.e. if the assets of the firm are inadequate to meet its debts in full even personal assets of partners can be used to satisfy claim.
- Utmost good faith. Partners are required to act in utmost good faith in business and render true accounts to the firm.
- Capital contribution.The capital is contributed by partners.
- Partnership has a limited life i.e. it may be ended any time by the death, withdrawal, bankruptcy or incapacity of any partner.
edu.uptymez.com
Types of partnership
There are four types of partnership.
- Temporary partnership. This is a partnership formed for either a specific period or a specific purpose. Purpose and at the end of agreed period the temporary partnership is dissolved or after accomplishment of stated purpose. Example. A partnership formed for five years or for construction of a certain road. A temporary partnership is also called a joint venture or particular partnership. Partners of a temporary partnership have unlimited liability.
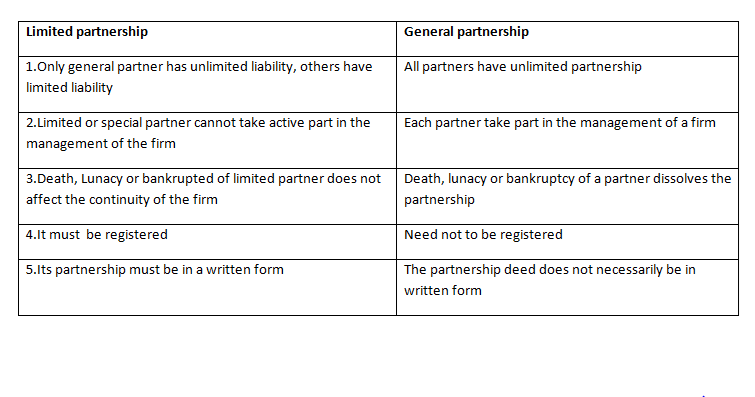
- Limited partnership. This is a type of partnership formed when partners have limited liability. All contribute capital during the formation but one partner actively manages the business and has unlimited liability and he is given greater powers and responsibilities in the business.
- Ordinary/general/unlimited partnership. This is a partnership where partners contribute capital and they all have unlimited liability i.e. if business funds cannot meet the debts the personal property of the partners is sold off to settle the debt.
- Permanent partnership. This is the type of partnership formed to last forever. If a partner dies a new partnership deed is drafted and the business continues. Permanent partnership is also called partnership at will
edu.uptymez.com
Distinction between Limited partnership and General partnership
Sources of capital
The major sources of capital for a partnership is the partners contribution. Other sources are
(i)Commercial banks and other financial institutions
(ii)Trade credit from suppliers
(iii)Re-investing profits obtained from the business
(iv)Hire purchase
(v)Leasing the business properties
(vi)Loan from non-governmental organizations (NGOS)
Formation of Partnership:
A partnership is usually set up using a Partnership deed/Agreement.
A Partnership deed or Agreement is a written agreement prepared by members who wish to start a partnership business. It contains terms and conditions made between partners to govern both the partners and the firm. It is an important tool in handling disputes, misunderstanding and disagreements in the course of running the business. It must be signed and made available to all partners and Notary public. The terms and condition in such agreement is called “Articles of partnership deed“.
Contents of partnership deed
- Name, address and occupation of each partner.
- Name, address of the business and its location.
- Rights and duties of each partner.
- Salaries to be paid to partners if any.
- The rate of interest to be paid on capital, drawings and loans allowed to the member.
- It states the procedures when a partner decides to retire.
- It states when and how books of accounts are to be kept.
- It states the procedure of electing the management committee e.g. through voting.
- States the procedures to be followed when solving disputes or misunderstanding among partners.
- States the procedure for admission of a new partner.
- States the status of each partner in the firm eg. Dormant, minor or quasi partner.
- States the duration of partnership. If it is temporary partnership.
- It shows capital to be contributed by each partner.
- States the procedures to be followed when dissolving the partnership.
- States the purpose for which the partnership business was established.
- States the ratio in which profits and losses would be shared by the partners.
edu.uptymez.com
Note:
If a partnership deed does not exist the provisions of the Partnership act of 1890 are applied.
Contents or clauses of the partnership act of 1890
- States that no salary is paid to any partner.
- Profits and losses are shared equally.
- No interest is allowed on capital contributed by partners and on drawings.
- Partners have equal participation in matters of the business eg Decision making.
- Decisions to be made are based on majority vote.
- The native of the business should no be changed without the consent of partners and the registrar of business.
- Books of accounts should be kept at the main office and every partner has the right to inspect them.
- No partner should carry out any comparing business with the partnership
- Every partner has the right to conduct business on behalf of the firm
- In case of disagreement decisions may be taken by majority of the partners.
- Interest of 5% is to be paid on any loan advanced by a partner to the business.