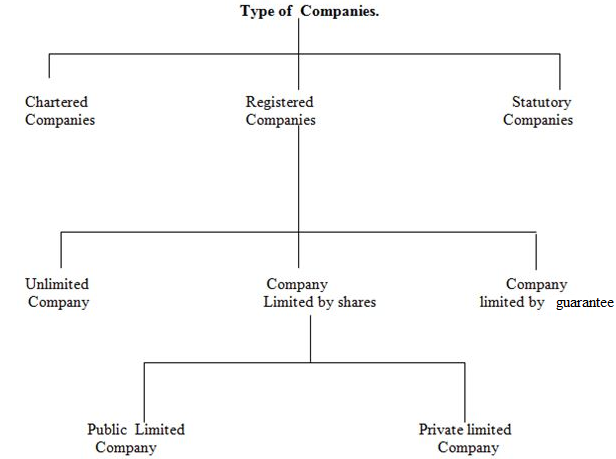
TYPES OF COMPANIES
There are two major types of companies:
1. Statutory companies
2. registered companies.
3. Chartered companies (extra)
1. Statutory companies
There are companies created by the Act of parliament, owned and controlled by the government.
2. Registered companies
These are companies that are formed and registered under the companies Act of 1962 and they are the most common type in Africa.
3. Chartered Companies
These are companies which are established under the royal charter.
TYPES OF REGISTERED COMPANIES
Registered companies may be classified basing on the following categories:
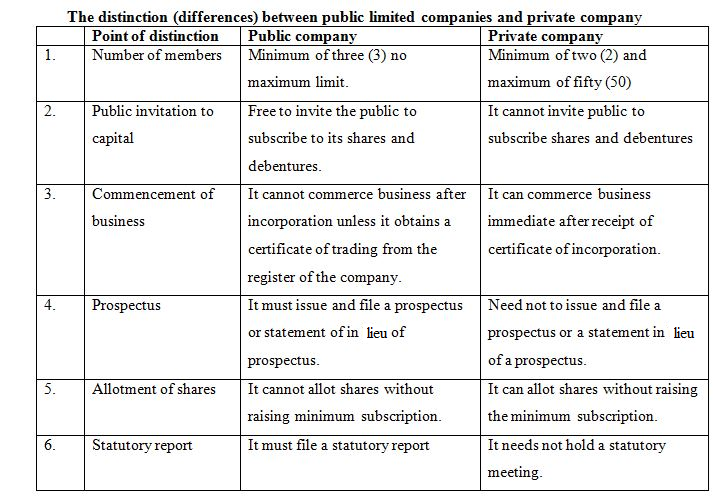
(a) According to the number of members.
(i)Private limited companies
(ii)Public limited companies
(b) According to the liability of members.
(i) Limited companies
(ii) Unlimited companies
(c) According to the number of shares.
(i) Companies limited by shares
(ii) Companies limited by guarantee.
A diagram showing different types of companies
- PRIVATE LIMITED COMPANIES
edu.uptymez.com
This is a company with membership ranging from 2 – 50 according to the Companies Act of 1890
Characteristics of private companies
(i) Membership.This ranges from 2 shareholders to 50.
(ii) Liability.Member’s liability is limited to their capital contribution.
(iii) Registration.It is registered under the companies Act with the world “Limited” at the end of its name.
(iv) Transfer of shares. Ownership of shares cannot be transferred from one person to another nor can the share be sold to the public.
(v) Management. It is controlled by a board of directors elected by shareholders.However, the ultimate control rests with the
shareholders as they have the power to replace the directors.
(vi)Taxation. It is subject to corporation tax on the profits made.
(vii)Time to begin operating. A private company can begin operating as soon as it receives a certificate of incorporation.
(viii)The business is separate legal entity.That is it owns property quite different from the shareholders.
(ix) Shares.The capital is divided into equal units called Shares
(x) The shareholders have no direct contact with the customer or employees. This is because of the large size of the company
and the number of the employees in the business.
(xi)There is assured continuity.It is not affected by the death, Bankruptcy, of one of the members.
Advantages of private limited companies
(i) A limited company has independent legal status and hence the limited liability enjoyed by its shareholders.
(ii) With limited liability the company is able to attract capital from people who would not otherwise be prepared to invest.
(iii) In private company, the founders of the business can usually keep control of it by holding majority of shares.
(iv) Larger capital.Because of being larger in membership, companies are in a better position to raise much more money or
capital than sole traders and partnership.
(v) Assured continuity of business. Since the death, bankruptcy or withdrawal of any one member does not affect the
company, companies have assured continuity.
(vi) Limited liability. All members can enjoy limited liability unlike in partnership.
(vii) Specialization is possible. Companies are financially strong enough to employ specialist so specialization of activities
becomes possible.
(viii) More source of funds. The sale of company share on the stock exchange stimulates investment even from small servers.
(ix) Sharing of loss. Large members and the fact that the capital is divided into different classes of shares means that the risk of loss
is also shared and spread among members.
(xi) Shareholder are safeguarded . Publicity of company accounts safeguard shareholders against fraud.
Disadvantages of private limited company
(i) Any transfer of shares is restricted. It must be approved by board of directors.
(ii) A private company is not allowed to call upon the public for funds in the form of shares or debentures. So it is difficult
to raise money for expansion.
(iii) Costly and difficult to establish. They required formal procedures like registration, payment of fees an duties not often required
in small business.
(iv) Observation of state law and regulations. Companies are more subject to state laws and regulations. Eg. No company is allowed
to undertake any form of business outside that agreed upon with registrar.
(v) Delay in decision making. Decisions may be delayed since business is conducted by a few elected members. The Board of
Directors must meet before important decisions are reached.
(vi) Shareholders non – participation in management. A part from the largest shareholders who sometimes become managing
directors the management of the company is separated from its governorship. Shareholders may be mainly concerned with
dividends and overlook long term policies being handled by salaries officers.
(vii) Difficult to control the company control of the company. Is not easy as a partnership because of its large size and as a firm
increases in size management become more complex and there are a few trained managers to run such a business
successfully.
(viii)Poor workers relationship. Where there are no personnel officers to keep in touch with the employees , personal relations
between the workers may be poor.
(viii) Higher taxes companies pay a higher tax on their incomes. This affects the companies earnings.
2. PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY
This is a company with a minimum of seven members and no specific maximum membership. The maximum membership is normally determined by the number of authorized shares of the company. The public limited company may have its name ending with “PLC” i.e Public Limited Company (in Britain) or “Inc ” i.e incorporated ( in US ) . Its name must however, end with the word “Limited”.
Features / characteristics of public limited company
(i) It has a minimum membership of seven persons and no specified maximum membership.
(ii) It invites members of the public to subscribe to its shares.
(iii) It shares are easily / freely transferable from one person to another.
(iv) It must have a minimum of three directors. A director is a person who manages the affairs of the company.
(v) It must have an authorized minimum share capital figure.Authorized share capital is the total value of all the shares that has been
authorized by the government.
(vi) A person wishing to leave the company must sell off his shares to another person.
(vii) It can only start normal operations after receiving a certificate of commencement.(Certificate of trading).
(viii) The name of the company must end with the words Public Limited Company.
(ix) The liability of the company is limited.
(x) The entity is separated from the members who form it.
Advantages of Public limited Companies
(i)It has independent legal existence, limited liability for shareholders and continuity of the business.
(ii)It is allowed to appeal to the public for funds, whereas the promotes of a private company have to rely on friends and
relations for capital.
(iii)There is no restrictions on the transfer of shares.
(iv) Public companies are normally larger than most others business. As a result companies often benefit from economies of scale.
These result in the cost per unit of output falling as the level of output rises.
Disadvantages of Public limited company
(i) The formalities of farming a public limited company are quite complex.
(ii) Rising capital can be very expensive.
(iii) A public company may grow so large that it becomes difficult to manage.
(iv) Public companies are subject to so many government regulations. Regulations are imposed to protect either shareholders or the
general public.
(v) Members have little control over the activities of the company.
(vi) The accounts of the company must be published. So, there can be little secrecy or privacy about its affairs.
(vii) Risk of take – over bids by other company’s shares can easily be bought on the stock exchange.
ADVANTAGES OF JOINT STOCK COMPANIES (LIMITED COMPANIES)
(i) More capital/large capital. More capital can be raised since it has many shareholders who subscribe it and a company can also
offered better collateral as security for loans.
(ii) Limited liability. Liability of members is limited. Their personal properties can not be sold to repay company debts. Their stake
to the company is limited to their capital contribution.
(iii) Continuity is assured. It has perpetual life or succession. The death or withdraw of a share holder cannot affect the existence
and operation of a business. This is because a company has a separated legal entity.
(iv) Expert staff. Employment of specialist staff is possible due to large capital.This means that the probability of
their succeeding is high.
(v) Shares are transferable. In case of Public companies, shares are freely transferable.A shareholder can easily convert his
shares in cash by selling them to another person.
(vi) Legal entity. It has a separated legal existence from its owners which ensures there is no conflict between the company and its
members.
(vii) Governance by legality.Share holder are safeguarded by the legal regulations underlying these companies.By law , joint
stock companies cannot start operating without required legal guidelines.
(viii) Large profits. Large profit are realized than in case of sole trade. This is because large capital is employed in the
business.
(ix) Democracy.Management is elected democratically. This is done during the annual general meeting, when all shareholders
converge to listen to the company reports.
(x) Open membership. People who have small capital which cannot enable them to set up their own business, can subscribe
capital in joint stock companies. Every person is free to become a shareholder of a public limited company by subscribing
towards its capital.
(xi) Acquiring loans.Being large, companies have enough assets which can be presented as a collateral security to the financial
institutions to get loan.
Disadvantages of joint stock companies(Limited companies)
(i) Management is difficult. Being large, management is difficult. Some joint stock companies possess many branches and
departments making supervision difficult.
(ii) Slow decision making. Decision making is normally slow, because a lot of consultations must be made and consent from
major shareholders must be received or all proposals have to be approved by the shareholders in a general meeting.
(iii) Confidentiality. It is difficult to keep the comparing financial affairs confidential because shareholders and the public have a
right to see the company’s financial information.
(iv) Formation takes long. Its formation is long and expensive procedure, requiring many legal documents. It involves
memorandum, articles of association, prospectus and many others.
(v) Double taxation. The shareholders suffer double taxation since the income of the company is taxed as well as the dividends
paid to shareholders.
(vi) Profits are shared. The sharing of profit reduces the amount of dividends received by each shareholders , unlike a sole trade,
who enjoys all the profits alone.
(vii) Initiative is limited. There is lack of personal initiation compare to sole trade. This is because the business is collectively
owned and personal interest cannot influence its operations. So an innovative.
(viii) Shareholders don’t have direct control over the business. The directors of the company are responsible for the day to
day running of the business and report to the shareholders at the annual meeting.
(ix) Conflict of interest. The directors may have their own interests which may be different from those of the shareholders, and
thus may end up conflicting with the interests of the company.
(x) Restricted operations. Its operations are restricted to the activities specified in its objects clouse in the memorandum of
association.
LIMITED LIABILITY CONCEPT
This is the fact that the liability of the company’s members is restricted to certain amounts of investment in the company plus any other amounts that may be undertaken to contribute towards the payment of company debts. The word ‘Limited’ indicates that the liability of members is restricted to these stated amount and that members cannot be made to contribute any more money or property beyond the stated amounts to settle the company’s debt.
A company may be limited by shares or by guarantee. These leads to the classification of company according to the number of shares.
(i) Company limited by shares
These is a company whose member’s liability is limited to the value of shares held by them. Thus, the liability of the members is limited to the value of share held.
(ii) Company limited by guarantee
This is a company whose members liability is limited to the amounts that the members have undertaken to contribute to the business towards the payment of its debts. These contribution may cover costs, charges, and any expenses of winding up.
OWNERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT OF COMPANY
A company is owned by the persons who have subscribed to and purchased its shares. These people are known as shareholders, and their names are entered in the company’s share register. Each shareholder has a claim on the properties of the company which is proportional to the number of shares held. The shareholders, however, have an unlimited right to transfer or sell their shares in the company Management .
Management
Management of a company is in the hands of a board of directors. The initial directors stay in office until the first Annual General Meeting (AGM) is held, at which new directors are elected by the members. The size of the board of directors is usually determined by the size of the company. A small private company could have one director, who would be the managing director of the firm. A public company must have a minimum of three directors, one of whom is the managing director. A large company, however has a team of directors who make up the board of directors. The board of directors is incharge of formulating the company’s policies and overseeing their implementation. This board is normally supported by a team of professional staff who are responsible for the day to day management of the various departments of the company. The team of the professional staff is headed by the Chief Executive officer (CEO). It is this team that is responsible for implementing the company’s policies and overseeing the day to day management of the famous departments.
In the case of public limited companies, the directors are required by law to present a copy of the audited financial statement at the AGM, which is then filed with the Registrar of companies. However , private companies are not obliged to do so.
So, there are two power bases in a company which is responsible for management of the company i.e The members (shareholders) general meeting and The board of Directors (BOD).
The management of the company follows the company structure depicted below:
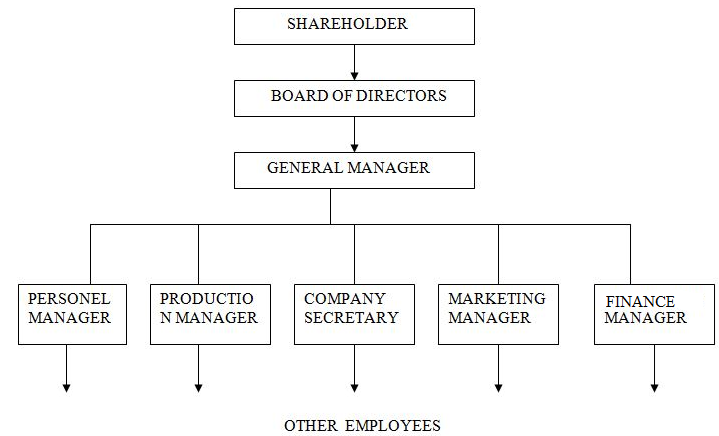
- SHAREHOLDERS
edu.uptymez.com
Shareholders are the owners of the company, they buy ordinary shares and given share certificates which proves their ownership in the company. They do not own assets of the company because, the assets of the company are legally owned by the company however they have direct rights on the assets only when the company is liquidated after paying creditors, debenture holders and preference shareholders.
The power and voting rights of the shareholders are exercised at the annual general meeting. The voting right are determined by the number of shares each one holds on the basis of one – share – one – vote.
At the annual general meeting they elect members of board of directors, and voting for changes in the Memorandum and articles of association thus effecting the structural changes in the company.
The general meeting is the highest power base in the company in which all the members or shareholders are entitled to attend.
Shareholders and their rights
(i)Proprietary(ii)Managerial(iii) Statutory(iv)Documentary and(v)Remedial.
(i) Proprietary rights
- The right to dividend on their shares at the rate desire at their general annual meeting.
- The right to transfer their shares as per article of association.
- Other rights to receive bonus shares, participation in surplus assets income on liquidation of the company, getting share certificates, etc.
edu.uptymez.com
(ii) Managerial rights
- Voting rights on all matters planed before the general meeting. A right to role on the principle of one vote one share.
- Approval of alteration in memorandum of association and Articles of association and other changes in the company set up.
- Election of directors, appointment of Auditors, appointment of managing director and other personnel.
- Approval of accounts and declaration dividends.
edu.uptymez.com
(iii) Statutory rights
- To receive share certificates.
- To receive notice, agenda, circular reports, accounts and audit reports, etc
- To transfer shares
- To impact statutory banks of the company.
- To demand post on any resolution part at the writing.
- To requisition extra – ordinary general meetings for dissolve urgent matters.
edu.uptymez.com
(iv)Documentary rights
All right granted to them by company’s Memorandum and Articles with regards to voting, election of directors, accounts, etc.
(v)Remedial
Shareholders have the right to get the affairs of the company investigated in case of frauds, dereliction of duties e.t.c so as to prevent oppressive management.
- BOARD OF DIRECTORS
edu.uptymez.com
Board of directors is the main governing body of a company. It consists of directors who are also referred to as TRUSTEES, they have to look after the company’s property and use the same to promote the interest of the company.
Why company directors
A company is a separate legal entity from its members as a separate legal entity a company cannot manage itself it needs people to manage it, that are directors.
The term director is applied to anyone instructed with management of a company who attends board meetings and takes part in their decision – making activities.
(a) Appointment
The first directors of a company are appointed by the promoters and may also be named in the Article of association.Subsequent directors are elected by the shareholders at annual general meetings of the company.
(b) Qualifications
- Only person holding the qualification shares can be elected as director.
- Number of value of shares are specified in the Articles of Association.
- A person of bank cannot be appointed as a director.
- A person who is adjudged insolvent is not qualified to be a director.
- A person who is convicted of offence and sentenced to imprisonment for more than six months cannot be elected a director.
- A person who does not paid the calls on his shares due six months or more cannot be elected a director.
- A person guilty of offence in promotion and Management of the company cannot be a director.
edu.uptymez.com
(c) Remuneration
Remuneration payable is determined either by the Articles in by resolution passed at the general meeting of the company. A director may be paid specified amount of fees for attending the meetings of the Board of Directors or of any committees of the Board.
(d) Powers, duties and liabilities of directors
- They are charged with the responsibility of recruiting the general managers of the company.
- The board of directors is also responsible for declaring dividends and determining what part of the profits will be retained in the business for expansion .
- They do also take major decisions affecting the day to day operations of the company and expansion of business.
- The Board of directors is liable for their actions and fully accountable to the shareholders in the general meetings.
edu.uptymez.com
- MANAGING DIRECTOR
edu.uptymez.com
The management of the company is composed also the general manager (GM) or the Executive Officer (CEO) or managing director (MD). The managing director is the director who has been entrusted with “substantial powers” of management or by a resolution passed by the company at its general meeting or by the Board of Directors.He is the top executive functioning in a two fold capacity as an elected director and also as a manager who is vested with additional powers in respect to important matters of the management of the company.The board may pick one among them to become the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) in this case is called a Managing Director (MD). He is given remuneration as a whole time director.
Departmental Managers
The general manager may be assisted by Deputy General Manager who in turn is assisted by personnel manager, production manager, finance manager, marketing manager and the company secretary.
4.Other employees
Under the departmental managers there may be middle management cadres as well as clerks and other workers in their efforts to achieve the objectives of the company.
Company meetings
A meeting is defined as the assembly of two or more persons for exchange of their views and suggestions on matters of business significance to the company. It is a corporate gathering of members or owners of the company or Board to discuss and decide the specific issues.
Essentials of valid meeting
The condition essential for a regular and legally to able meeting are as follows;-
- Notice.Members would be given proper notice of meeting.
- Agenda.Item to be considered must be listed and available to members.
- Quorum.Minimum number of members to constitute a meeting should attend.
- Chairman.A chairman to preside the meeting must be present.
- Motions.Proposal placed for preview of the meeting.
- Resolution.Motions passed at the meeting with requisite of the majority.
- Method of voting.Should be prescribed to assistance the service of the meeting.
- Minutes.Recording of the meeting should be adequate.
edu.uptymez.com
The general Meetings
The general meeting is the highest power base in the company in which all the members or shareholders are entitled to attend. The most important decisions are made in the General Meeting. Under the companies Act, there are three types of General meetings namely: The Annual General Meeting (AGM),the Extra – ordinary Meeting (EGM) and Statutory meeting.
- Annual general Meeting.It is a shareholders meeting held every year to review the progress and prospects of the company. It enables the directors to place before the members an amount of their activities and achievements for the year and seek their approval for their plans and programmes for the coming year.
- Extra – ordinary Meeting (EGM). This is the meeting other than annual general meetings which can be called by the directors or by requisition of members or by the registrar of the companies.The purpose of such meetings is to permit the discussion and transactions of business which cannot properly be postponed until the next general annual meeting.All business transacted at an Extra – ordinary meeting are treated as special business and must be specified in the notice when calling the meeting.
edu.uptymez.com
3. Statutory meeting. This is the first meeting of shareholders at which they are given details of various regulations and rules.
Resolutions of the general meeting
Decisions in general meetings are made by voting and such decisions are called resolutions. The resolutions are the decisions taken on the proposals placed at the meeting:
There are two types of resolution grouped in the basis of the extent of majority which they have been passed at the general meeting.
- Ordinary resolution
edu.uptymez.com
It is a resolution that has been passed by members entitled to do so by voting in person or by proxy. A proxy is a person representing a shareholder after obtaining the letter from the lawyer permitting him or her to attend the meeting, when the shareholder is unable to attend the general meeting. These resolutions require 51% and above votes of the member present. Matters which can be decided or voted upon ordinary resolutions include: election of directors, appointment of Auditor, declaration of dividend, adoption of accounts and directors report, and increase in the authorized capital.
- Special resolution
edu.uptymez.com
Special resolution is one which is passed with at least ¾ th (75%) majority. Items requiring special resolution under the company law include; Alteration of name clause, alteration of objectives, alteration reduction of capital, commencement of new business, appointment of share selling agents and voluntary winding up of a company.