SHARE CAPITAL OF THE COMPANY
THE CAPITAL STRUCTURE OF COMPANY
The capital structure of a Company this refers to the different categories under which the authorized capital of a company divided up. This is because the company does not normally invite subscriptions for all of its nominal or authorized capital at one time. Payments is usually by periodic amounts known as installments or calls.
The capital of the company is called share capital because it consists of and raised by selling shares. The following are types of shares capital or company capital.
- Authorized Capital/Nominal Capital Registered Capital
edu.uptymez.com
This is the maximum amount the Company expects to raise and operate with by selling shares and it is stated in the capital clause of its memorandum of Association. Assume that the Company share capital is made up of 100,000 ordinary share of shs. 10/=@
The nominal or authorized capital of the company is 100,000xshs10=sh1,000,000/= Once registrar of companies expects such a firm to operate with this amount.
- Issued and Unissued Capital
edu.uptymez.com
This is the part of the authorized capital which the company may actually has offered to the public for subscription in the form of shares. The company issues shares according to its requirements.
For example, out of the company authorized capital the directors may decide to put some of it to the public so as to start subscribing for suppose they issue only 50,000 x sh. 10 = 500,000. The remainder is 50,000 shares x sh. 10 = 5000,000. Therefore in issued
capital is sh. 500,000
- Called up share capital
edu.uptymez.com
Once the shares have been put to the public so as to start applying for , then the share hold are called upon to subscribe or to pay. They may be called upon to pay for all the shares issued or only a fraction of what was issued.
What was issued.
Assume that each shareholder is asked to pay shs 5 first for every share he taken up. Since 50,000 shares were issued the amount of called up capital is 50,000 x sh. 5 250,000. The remainder is known as uncalled up capital i.e what share holders are asked to reserve for sometime
- Paid – up share capital
edu.uptymez.com
This is the actual amount received from the subscribers by the company out of the subscribers by the company out of the called up capital. The amount unpaid is known as calls in arrears.
- Reserve capital
edu.uptymez.com
A public company may create a special category of capital known as Reserve capital in respect of called up capital of the company.
Reserve capital is the amount which is not callable by the company except in the case of the Company being wind up. Reserve capital is created by means of a special resolutions passed by the company in the general meeting.
- Loan Capital
edu.uptymez.com
This is money provided by the issue of debentures or borrowing from the bank. Such capital is a ability to the Company
- Minimum share capital
edu.uptymez.com
This is the amount stated by the promoters when making application for the registration
Company as the minimum amount required commencing business effectively.
SHARES OF A COMPANY
A share or stock is a unit in which the capital of a company is divided.
OR
A share is a unit or portion of capital to raise funds
The money raised through the sale f shares is known as hare capital” profits distributed to shareholders are known as “dividends. Holders of shares are called shareholders or members of the company
Types of shares
(i) Ordinary /Equity shares
(ii) Preference shares
(iii) Deferred shares
1.Ordinary /Equity shares
These are shares held by real owners of Company/These shares are held by persons who are full responsible for the debts of the company.
In case the company is dissolved ordinary share have the last claim on the properties of the company. These type of shares give their holders the power to formulate policies for the company.
Characteristics of ordinary shares
i. They do not carry a fixed rate of return. The amount of profit allocated to them depends upon what remains after all the creditors and shareholders with prior claim have been paid.
ii. The owner of shares receives a dividend on them only if there is sufficient profit. If profits are two low or if there is a loss the company may not pay a dividends. When profits permit, each
shareholder will receive an equal amount for each ordinary share held.
iii. When the company is bankrupt, share hold will be paid if at all in only after all other debts have been paid
iv. There is no special security for such investments other then the soundness of the company
v. In exchange for the risk, the ordinary shareholder the ultimate control of the company, in that they have one vote for each share when it comes t electing the board of directors. Who are
responsible for the general policy of the company
vi. In good years shareholders may receive higher rates of dividends than other shareholders but in bad years there may be no return ate all
vii. When the Company is winding up, the shareholders are paid money after the other shareholders and creditors.
viii. Ordinary shares are the most important and popular type of shares, It is therefore called a entire capital of the company
ix. The rate of divided on ordinary shares depends upon the profit of the Company.
x. The ordinary shareholder to not create any change on the assets of a company
xi. No burden on company resources since the dividend is t be paid out of the profit of the company, there fore they impose no burden on the resources of the company.
N.B The great risk of business falls upon the ordinary shareholders because.
They have no fixed rate of dividend.
The amount of profits allocated to them depends upon what remains after all the creditors and shareholders with a prior claim have been paid.
(ii) There is no special security for this investments other than soundness of the company
(iii) IN good years they may receive higher rates of dividends than the other shareholders but in bad years there may be no return at all.
(iv) In good years they may receive higher rates of dividends than the other shareholder but in a bad years there my a been return at all.
2. Preference shares
Preference shares, as the name suggests have certain preferential rights or privileges in respect of the payment of dividend or repayment of capital as compared to other types of shares.
Characteristics f preference shares
(i)They earn a fixed of dividend, say 5% or 10% preference shares
(ii) They have first priority in sharing dividends
(iii)In case of insolence the holder of preference shares receive their proceeds before ordinary shareholders
(iv)The dividends paid are higher than in case of ordinary shares.
(v)Those too are held by the owners of the Company and form part of the Company capital with a fixed rate of dividend.
(vi)Most preference shareholders have no say in the control of the Company, as they have a privileged position as respect to dividends.
Types of preference shares
(a) Cumulative preference shares, These are type of shares which are entitled to a fixed rate of dividend till they are paid, Holders of these are assured of their dividends every year. If a Company does not
pay dividend in one trading year, then payments are carried forward t the next year, In other words, dividends keep on accumulating till paid.
Holders of these are assured of their dividends every year. If a company does not pay dividend in one trading year, then payments are carried forward to the next year. In other words, dividends keep on
accumulating till paid. That is to say if there are no dividend paid this year, next year or the next year after that the amount has to be paid.
(b) Non cumulative preference shares, This will be entitled to a fixed rate of dividend, but only for the year for which a dividend is declared. Otherwise, it does not accumulated and arrears are not carried
forwarded.
(c) Redeemable preference shares, These are shares offered by the Company for sale to the public but they can be bought back or repossessed by the company when necessary or after a specified period
of time. The shareholders are paid a high rate of interest when such shares are taken away from them. These are issued when the company wants more money temporarily.
(d) Irredeemable preference shares
These are shares offered to the public for sale and cannot be reposed or bought back by the company under any circumstances. If a shareholder wants to leave the company and wants his money back, he can sell his shares t the public
(e) Participating preference shares
These carry a fixed rate of dividend and the holders are entitled to any extra profit which rains after all shareholders have received their dividends
(f) Guaranteed Preference shares
These shares are guaranteed for a fixed rate of dividend by a third party. If the profits of any one year are no sufficient to pay such dividend, the guarantor (s) have to pay the same off their private resources
(g) Convertible Preference shares
These are those shares which the holders can convert into equity (ordinary) share at specified period of time. The right of conversions to be authorized by the Articles of Association of the Company
3. Deferred shares
Here the business my want to convert to public limited company and with to retain powers of control and right to high profit. Thus they create a class of deferred shares giving them special voting powers and the rights to dividends
TERMS USED IN THE SHARE MARKET
- Share at par
edu.uptymez.com
This is when the money offered for purchase is equal to the face value of the value. For example if the face value nominal value of share is Tshs. 400, the amount offered for sale is Tshs 400. A share is above par, if it sells more than its nominal value and . A share is below par if it seller less than nominal value.
- Share at perineum
edu.uptymez.com
This is when the price paid for that share exceed the value of that share e.g the value of share is Tshs 500 and it is offered for Tshs. 600
Reasons why company decide to sell shares at premium
(h) Company finds it fair to sell shares to the existing share holders who may have paid more than the par value of their shares.
(i) Company might want to intercept parts of the company profits that would have gone to the speculators.
(j) The books of accounts require the premium to be shown separately in share premium account and not share capital account
(k) Premium is not trading profit therefore it may not be distributed as dividends it can be used to write off preliminary expenses, write off commission or debentures on issue of shares and raising new cash
from shareholders
FEATURES OF RIGHT ISSUE
(i) Right issue of shares is made by issuing provisional letter of allotment which shows the share, the member is entitled to take up and the price payable for the shares.
(ii) Members my take the issue wholly or may renounce the issue by selling his right to another party
(iii) It is apportioned to their present holding of shares of similar or specified shares.
(iv) An issue at less than market value of the existing share will lower the value of the existing ordinary shareholders equity.
(v) Company obtain a profit (premium) on the shares sold out to another party.
(vi) It is issued so as to raise additional capital offered first to existing holder then the public if existing holders do not take up
5. Underwriting of shares.
A public company is required to sell a minimum number of shares (called minimum subscription)
To secure the minimum subscription during the prescribed period the company may enter into contract (agreement) with an established source like banking institutions, Insurance firms or shares brokers to underwrite the issue. If the Company is not able to sell all the shares within the specified period them the contracting party ensures the sales of share is known as underwriting. That means that the underwriter undertakes to take the whole or portion of such of the offered shares which may not be subscribed for by the public. The underwriter make the payment of subscribed shares in fully to the company public. The underwrite is paid a commission as agreed between the parties and also authorized by the Articles. This is because the risk of the shares is transferred to the underwriters,
Advantages of underwriting
(i) They take up shares that are not taken up by the public
(ii) They help company in fulfilling statutory regulations and minimum subscription.
(iii)They assure quick sale of securities in the market.
(iv)Stimulates industrial development and creates more employment opportunities in the country
(v) They stand guarantee and help the promoters in undertaking the risk of starting or enlarging a project.
(vi)They provide information in regard to capital market condition, general responses of investors to issuing company.
(vii) When the issue is underwritten, the company is assured of the required capital
(viii) If the underwriters have good reputation in the market, it raises the status of the company
(ix)The company can get the benefit of specialized knowledge of the underwriters in the marketing of stock n and shares and this can help the company in future ventures.
(x) If the public subscribes to the share then the underwriting contract can also be dissolved
Share warrant
Is a bearer document of title to share and can be issued only by public limited Company and that to against full paid u shares. Only it cant be issued by private limited company because the share warrant states that the bearer is entitle to a number of hares mentioned in. It is a negotiable instrument and is easily transferable by mere delivery to another person. The holder of share warrant is entitled to receive dividend as decided by company
7.Stock
Is a type of security that shown ownership in a corporation (w) and represents a claim on part of the corporations assets and earnings. Ownership in company is demined by number of shares a person owned divide by total number of shares outstanding. Also called equity.
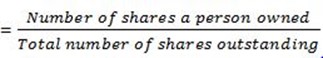
OR
Stock is the name given to a block of shares. Shares may be converted into stock if there is a provision in the Articles of Association. Shares can be converted into stock only if they are fully paid up. That is how the word joint stock company was introduced to describe limited company
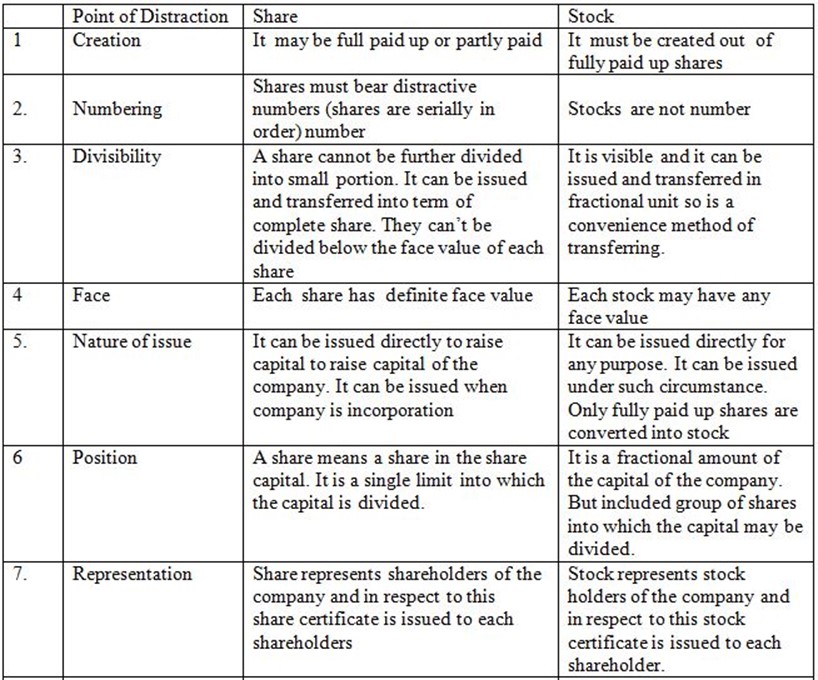
DISTINCTION (DIFFERENES BETWEEN SHARES AND STOCK

Difference between Transfer and Transmission of shares
- Transfer of share means transferring the shares on the name of same other person on a voluntary basis while transmission of shares means passing the property/title in shars by operation of law from member to his legal representative on either death, insolvency or lunacy of shareholder.
- Transferor or transferee takes initiative of transferring shares while the legal heir of the deceased shareholder takes initiative of transmission of shares.
- The transmission is not a deliberate action but result of operation of law after he dies, becomes bankrupt or insane while in transfer it is a deliberate action by shareholder
- In transfer stamp duty is payable on market value of shares white in transmission duty is payable
- Transmission cant be refused as it is under operation of law while in transfer the directors can refuse on certain ground. In transmission certain document like court order of insolvency, death certificate are required while in transfer an instrument of transfer has to be duly excited by transferor or transferee.
edu.uptymez.com
METHODS OF SHARE ISSUE
- Offer by prospectus
edu.uptymez.com
Direct approach to the public share and sold and a fixed offered price.
- Officer for sale
edu.uptymez.com
A company will sell its entire issue to an issuing house which then sells them to the public at or slightly higher price to cover fees and expenses
- Offer by tender
edu.uptymez.com
Rather than fixing the price in advance, company sometimes issued shares to the public by inviting them to state a price at which they are prepared to buy. His issue price then fixed according to
demand and anyone offering less this receives no share. (each person states minimum price and company gives to person whose set maximum price.
- Placing
edu.uptymez.com
A large number of share issue are placed by the issuing house with a selected group of its clients, usually large financial institutions rather than the general public.
- Rights issue
edu.uptymez.com
Existing shareholders are offered the right to buy additional shares in the company at price lower than market price.
- Bonus issue
edu.uptymez.com
Share issued free to existing holders in proportion to their holdings eg bonus issue for every 10 share held. This makes shares more marketable by reducing their market price.
- Scrip issue
edu.uptymez.com
Sometimes instead of paying a cash dividend, a company offers shareholder a choice of receiving inform of extra shares
WHY DO SHARE PRICES FLUCTUATE
- It changes according to the market’s activity. The buyer and sellers cause prices to change and therefore share prices change as consequence of demand and supply, Its this dance between buyers and sellers, demand and supply that decides how valuable each share is
- If more people want to buy share than sell it the prices goes up conversely, if more people want to sell share then buy it, there is more supply than demand, the prices goes down.
- Shares represent ownership in a company. So even if you own just one single share of a company, you own a part of it no matter how minute. Therefore the price of share indicates what investors feel the company is with.
- If a company earning(profits) are good and its prices jump up. But if the company makes no money, then the price of share will fall
- Investors decision are influenced by their out look and opinions. When the outlook is positive investors are eager to buy so prices rise but when its is negative they are eager to sell so price.
- Technical factors. Stock pries move in trends. Investors are attracted by rising prices and spooked by falling prices. Specialists make sure that prices contently change in order to draw in buyers and sellers.
- Changes in government policy such as restrictions an consumers spending will probably cause a fall in the share price of company. Restrictions of spending cause a low money simply hence prices of shares automatically decreases.
- When the market conditions of a country is bad i.e there is recession then price of all commodities will which means even price of shares will be low.
- Changes n the rate of interest of the government securities will sometimes affect share hence the price of shares decreases.
- World political and economic events will have an effect on share of company especially those which have large export trade. This is because those companies get affected with all the issues going are in other areas where their goods are being exported to.
edu.uptymez.com
MINIMUM SUBSCRIPTION
A company can not allot shares unless the amount mentioned as minimum subscription I received within 120 days of the date of the issue of prospectus. Minimum subscription is that part of the issued capital which should be received within 120 das. It is the minimum amount which in the opinion of the directory is necessary to provide for the following.
(i) Purchase price for any property
(ii) Underwriting commission if payable
(iii) Preliminary expenses
(iv) Repayment of money is borrowed for an of the above purposes
(v) Working capital or any other expenses
(vi) Restriction of minimum subscription is meant to prevent the formation of companies with in adequate capital so that only companies which can raise enough capital and meet the minimum requirement are allowed to start their business
NOTE
When a company is unable to raise required capital through selling shares, it may resort to the following;
– Through bank loans an overdraft
– Borrowing from friends
– Asking promoters to contribute more money
– By issuing debentures
DEBENTURE
The terms “debentures” is derived from the Latin word ” debere” means to own a debt. Therefore a debenture is a long term finance raised by a company through public borrowing. If a company finds its authorized share capital in adequate it can raise money by selling debentures for its long term financial needs.
A debenture is a document (Loan certificate) that works as a poof evidence that a company has borrowed a spiced sum of money advanced or lent to the company. Debentures are of fixed amount say shs 1000 and bear a fixed rate of interest. The interest on debentures is an expense to the company which must be paid where the company is running at a profit or not. Debenture are loan or borrowed capital of the company.
Debentures are of fixed amount say shs 100 and bear a fixed rate of interest. The interest on debentures is an expense to the company which must be paid where the company I stunning at a profit or not. Debenture ar Lean or borrowed capital of the company. Debenture holders have no control over the day to day running of the company, however in the event of company failure, they have claim on the assets of the company after trading creditors but before preference shareholders and ordinary shareholders
Main features of Debentures
(i) It is instrument indicating the indebtedness of the company
(ii) It has a nominal value like share
(iii) It is a document issued under the seal of the company
(iv) The terms of issue, the repayment of the principal are specified
(v) A fixed rate of interest is paid on debentures’ This interest is a charge on the profit an loss account of the company
(vi) Generally the debentures are covered company
(vii) In case of winding up debentures holders are paid their money before the shareholders
(viii) The rights and power of debenture holders are mentioned in the certificate issued at the time of accepting loans.
TYPES OF DEBENTURES
Debentures may be classified into two ways (According the security pledged against them
- Necked/ordinary/Simple/unsecured debenture
edu.uptymez.com
These are types of debentures which are not secured. No property is pledged against them. If the company goes bankrupt or liquidated the holder of necked debentures are ranked amount ordinary creditors of the company
2.Mortgage/secured debenture
These are debentures which are secured. Some properties of the company are pledged against them. If the company are pledged against them. If the company goes bankrupt such properties can be sold to pay off the holders of mortgaged debenture.
b) According t redemption
1. Redeemable debentures
These are debentures which are bought or repayable back by the company such that the amount borrowed again them is refunded by the company after a specified minimum period and before a specified maximum period eg 2,3,4,5 or 20 years. The interest is paid periodically but he principal amount is returned after a fixed period.
Irredeemable debenture
These are debentures which are never refunded or not repayable by the company refunded or not repayable by the company, the money borrowed against them remains outstanding until the Company is liquidated/winds up
c) According to registration
1. Registered debentures
These are debentures which are issued in the name of the owners of the debenture, in that the name of the owner appears on the face of debenture as well as in the books of the Company
- Bearer debentures
edu.uptymez.com
This are debentures which do not show the name of the owners on the face of the debenture. Is entitled to receive interest payment on the due dates
(d)According to convertibility
This are debentures which do not show the name of the owners on the face of the debenture. The holders of bearer debenture is entitled to receive interest payment on the due dates
(2) In convertible debentures
These are debenture which can not be converted into shares of the company
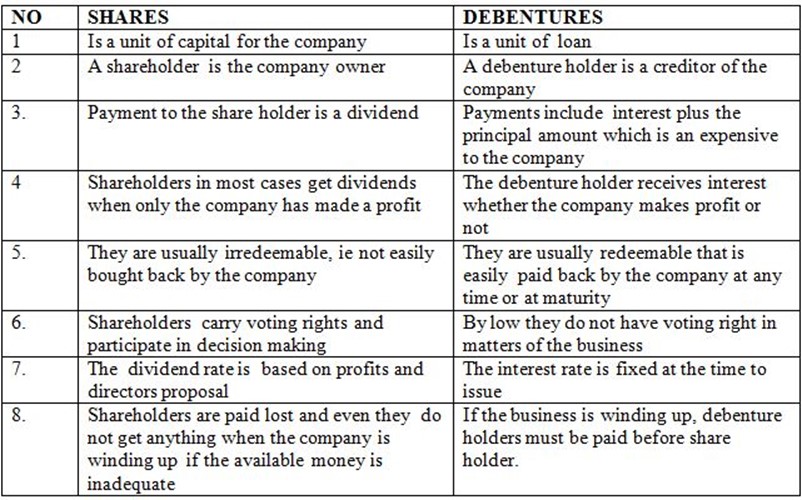
DIFFERENCES /DISTINCTION BETWEEN A SHARES AND DEBENTURE