CONVERSION OF A PRIVATE COMPANY
There are several restrictions on private company which may result in a limited financial resources, limited production activities, limited technical and admistrative abilities. Due to these factors business may not be expanded and private company faces high cost per unit, limited sales and low profit. These hindrances constrain to decide in conversion of private company into t public company.
In order to convert into public company, it is necessary to alter the articles of association by a special resolution. The following alterations have to be brought in the provisions of articles of Association.
(i) Shareholders may transfer their shares
(ii) They may invite the public for subscription of shares and debentures
(iii) Maximum number of shares i.e fifty will be struck off from the articles.
New Articles of Association will be submitted to registrars office within two weeks of such alteration
The following necessary documents must be filed with registrars office a long with altered articles of Association
(a) A list of persons containing their names addresses and other particulars who have agree to act as directors
(b) The written consent of the directors
(c) Declaration of the directors that they have paid the qualification shares
(d) Declaration of the directors that they have paid their qualification shares or statement of the fact that they have already taken up and paid for their qualification shares.
(e) A prospectus or statement of live of prospectus
(f) A declaration from the directors or secretary or advocate that all the provisions of the company radiance have been fulfilled.
After submission of the foregoing document to the registrars office, private company may be converted into public Company
TERMINATION OF A COMPANY
(WINDING UP OR LIQUIDATION)
This means that the end of the life of a company. In simple words it’s the closing down of the business.
A s we have discussed earlier that a company is created by law therefore it cannot die a natural death like a human being. The termination of its existence is affected law. Thus winding up of the company is a legal procedure.
When a company is a legal procedure. Its property is administered for the benefits of its creditors and members it is called winding up or liquidation.
What is liquidation?
Is the process of closing or termination a company through selling of its assets normally for cash
A LIQUIDATOR
Is a person or institution appointed by shareholders or creditors to supervise the liquidation of a potential company including the valuation of company assets and liabilities.;
– Deal the payment of company debts
– Work on any surplus or deficit after liquidation.
METHODS/WAYS/MODES OF WINDING UP OF A LIMITED COMPANY
(PRIVATE AND PUBLIC COMPANY)
- Compulsory winding up by court
- Voluntary winding up
- Winding up under supervision of court
- By having its name struck off the register by the registrar
edu.uptymez.com
- Compulsory winding up by court. The main reason for winding up by the court are as under
edu.uptymez.com
(a)Special resolution
A special resolution has been passed by the company to be wound up by the court
(b) Failure to commence business
If a public company does not commence business within one year of the date of it incorporation or suspends business for a certain period, the court may order its winding up
(c) Statutory report or Delay in meeting where default is made in not submitting the statutory meeting within prescribed time or has not held two consecutive annual general meetings.
(d)Members reduced below minimum
A public limited company may be wound up by court if its members are reduced below seven (7) and less than two (2) in case of primate limited company
(e)Inability to pay its debts
(f)Where the court is of opinion that it is jus and equitable that the company should be wound up
- Voluntary
winding up
edu.uptymez.com
Voluntary liquidation is imitated by resolution of the company itself. A company may be wound up voluntary in the following circumstances
(i) When the period (if any) fixed by the articles for the duration of the company has expired or when the event (if any has accrued upon occurrence of which the articles provide that the company has passed an ordinary resolution requiring the company to be wound up
(ii) When the company has passé a special resolution redoing the company to be wound up voluntary
(iii) When the company has passed an extra ordinary resolution to the effect that the company cannot carry on business owing to its liabilities and that it is advisable to wound up
(iv) The death of the founder and owner may result in any shareholders choosing not continue operations
(v) Liquidation is actually a means of helping the company to continue. Companies that are encountering a period of loss may choose to liquidate subsidiary companies as a means of setting outstanding debts of the parent company.
(vi) The voluntary winding up of the company is of two kinds.
(a)Members voluntary winding up/shareholders voluntary winding up
A voluntary liquidation is an action that may be taken by hare holders of a company in order to honor the outstanding dots of the company in order to honor the outstanding debts of the company. With a voluntary approach to liquidation, the directors and shareholders agree to the process and initiate the procedure willingly, with no outside pressure or other entity. In this case the directors of the company are required to file a decoration of solvency.
The declaration of solvency is the document that states that states that the directors believe that the assets of the company will be sufficient to pay off its debts. The directors will then appoint a liquidator liquidators are professionals who task of identifying and selling off all the assets associated with business entity.
A liquidator may be appointed by court as part of the dissolution process of a company or be hired by the company as part of voluntary liquidation process. In this scenario, liquidations of all major assets will commence. Once al assets are placed in news papers and other media for the creditors to come forward to prove and claim heir debts, All outstanding debts are settled first, the share holders thereafter divide the remaining assets and the company will be considered closed. On the appointment of the company ease to exist. The liquidate calls the final meeting of shareholders and he submits a final account of the company affairs to the members and sends a copy to the registrar. Then after that then after that the company is dissolved and ceases its legal entity.
(b) Creditors voluntary winding up
A company may pass a resolution at general meeting that it cannot continuous its business due to heavy liabilities, Then a creditors meeting is called by sending each creditor with a written notice for this purpose. The creditors are given the full statement of the company position the full statement of the company position the list of creditors an their estimated claims. Then the creditors appoint a liquidator who exercises his powers for the winding of the company and supervises the sale of assets and payments to creditors. O completion of winding up, the liquidator have to call a final general meeting of the members and a meeting of the creditors. The notice for such meetings are usually are usually published in the news papers. In the meeting the liquidation has to give reports regarding the accounts and assets of the company. A copy of the report is also sent to the registrar. The register an receiving the accounts and other relevant documents takes the action of dissolution of the company.
A copy of the report is also sent to the registrar. The registrar on receiving the accounts and other relevant documents takes the action of dissolution of the company.
- Winding up under supervision of court
edu.uptymez.com
A court can also order the winding up of the company under the following conditions.
(i) If the court is satisfied that the company is unable to pay its creditors.
(ii) When there are frauds or irregularities in the voluntary winding up
(iii) The liquidator performs his duties in a partial manner. In that case the court can appoint an official receiver who carries on he process of winding
(iv) If the rules of the winding up are not completely followed.
(v) The liquidator is not taking a keep interest to dispose off the company assets
- Striking off the register
edu.uptymez.com
A company may strike off the register by the register by the registrar. This may take place when the registrar has reasonable ground for believing that the company is defunct. He give due notice to company at its registered office of his intention to struck it off the register.
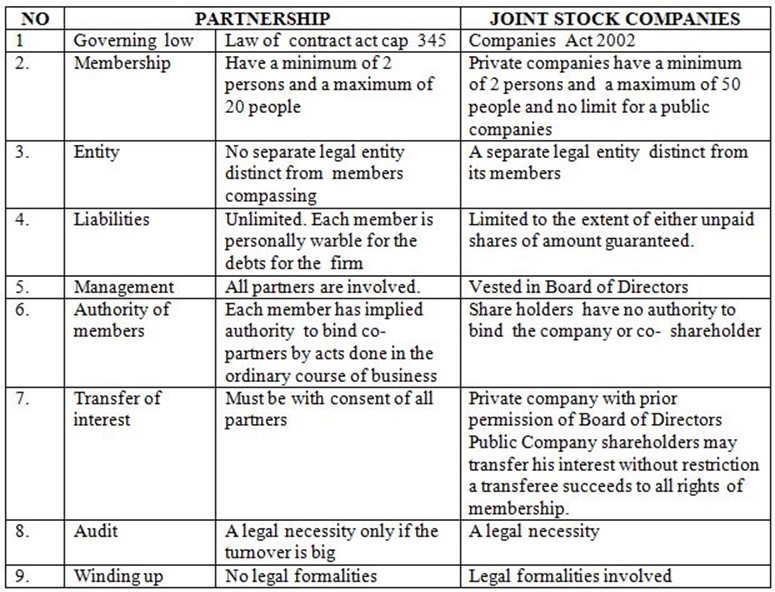
DISTINCTION / DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PARTNERSHIPS AND JOINT STOCK COMPANIES
PARASTATAL ORGANIZATIONS
Are those organization which are partly or wholly owned and managed by state (government) which engaged in either production activities or previous of services.
These organization mostly established by the act of the parliament e.g. TRA , DAWASCO, TANESCO, UDA etc
Types of parastatal organizations
There are two types of parastatal organizations namely as
- Authority
- Corporations
edu.uptymez.com
The following are the sources of finance to parastatal organizations
- Loans
- Share capital
- Dividends
- Grants
- Subsidies
- Other external aids
edu.uptymez.com
DIFFERENCES AND SIMILARITIES BETWEEN PARASTATAL ORGANIZATION AND PUBLIC COMPANIES
DIFFERENCES
- Appointment of directors and their removal in parastatal is done by the president while in public companies is done by shareholders
- Membership majority of shares in parastatal owned by the government while in companies majority of shares owned by the public
- Parastatal do not prepare memorandum of association and articles while in preparation of companies there must be
- Dividends, while dividends in parastatal is taken by the government while in public companies dividends will be shared by shareholders
edu.uptymez.com
Similarities
- Both aimed at providing services to the public
- Both are managed by board of directors
- They both own properties like assets, stocks, bank etc
- They both subjected to liabilities like creditors liabilities
edu.uptymez.com
ANALYZE THE PROBLEMS FACED BY PARASTATAL WHICH MAKE THEM FAIL TO EXIST
-Mismanagement and misappropriation of fund (fraudulent)
-Lack of competent and qualified personnel/staffs
-Lack of sufficient markets
-Market competition
-Bureaucratic capital
How these problems were solved
The decision taken by the government to solve problem faced by these parastatal organization was to
-Privatize
-Liberalize
WHAT IS PRIVATIZATION
Refers to the concept of changing public owned sectors like companies and parastatal organizations to be owned by private people
WHAT IS LIBERALIZATION
Refers to the concept of creating free market and trade to bring about competition in the provision of public services
What are the impacts of privatization and liberalization of trade in Tanzania
Positive impacts
- It attracts foreign strategic investors in a country
- It ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courages competition
- It reduces government burden and responsibilities
- It facilitates transfer of new technology from foreigners
- Creation of employment opportunities
- Provision of varieties of choice due to existence of many industries
- It leads to the improvement of living standards of the people
- It creates international relationship between countries
- Act as a source of government revenue/income
edu.uptymez.com
Negative impacts of privatization
- It leads to the loss of jobs to unskilled labors due to the introduction of new technology
- It leads to destruction of culture
- It leads to the cost sharing policy on social services
- It may cause economic instabilities
- It leads to emergence of classes/inequality
- Increase in the cost of living
- Decline of domestic industries due to high level of foreign competition
- It increases dependent ratio in the country
edu.uptymez.com
Positive impacts of trade liberalization
- Competition
- Employment
- Reduction of government burden
- Revenue
- Attraction to foreign investors
- Varieties of choice
- Freedom of production and consumption
edu.uptymez.com
Negative impacts of trade liberation
- Decline of domestic industries
-
Destruction of culture
Emergence of classes
- Loss of jobs
- Cost of living increased
- Economic instability
edu.uptymez.com
OPERATING A BUSINESS UNIT
All business units whether incorporated or unincorporated are operating within government bodies called BRELA and TIC
WHAT IS BRELA?
Is the term refers to business registration licensing agency which is an agency of the government given an authority and established to provide and ensure that all business are operated in accordance with the laid procedures and regulations as well as sound commercial principles.
FUNCTIONS OF BRELA
- To ensure that business comply with the laid down regulations to the satisfaction of government and business community
- To ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage and facilitate local and foreign business environment
- To administer company and names laws
- To administer intellectual property laws
- To improve service delivery by the adaptation of modern business practice
- To protect development of creativity in artist, literally works with the right of owners
edu.uptymez.com
CO-OPERATIVES
Introduction
The word “Co-operative” is formed from two words “Co” meaning together and “operate” meaning work.
Hence a Co-operative society is a group of people who have agreed to carry out activities to attain a common objective.
Definition:-
Co-operative is a voluntary association of individuals who make efforts to achieve interest of its members.
OR
It is the type of ownership whereby people with common interest join together to achieve certain economic and social objectives.
Co-operative societies differ from other major forms of business organization because they are not set up to make profit, but to help the members.
A Co-operative society is formed by at least 10 people (members) who wish to help themselves. Members of the society draft rules and regulations for the purpose of governing their society.
In Tanzania Co-operative societies started during colonial period with the prime objectives of assisting farmers, in production and marketing crops.
Co-operative societies continued existing even after independence until 1976 when they were abolished after failing to meet their primary objectives.
FORMATION OF A CO- OPERATIVE SOCIETY
In East Africa, a minimum of 10 people agaged 18 years and above may come together and form a co-operative society. No member is allowed to subscribe more than 20 percent of the society’s share capital.
The steps involved in the formation of a co-operative society are as follows:
- Ten (10) or more people come together.
- They draft the by-laws for the society.
- The by-laws are submitted to the commissioner for co-operatives for approval and registration of the society.
- A certificate or registration is issued to the new society by the commissioner for Co-operatives. Once this certificate has been obtained, the society can start operating.
edu.uptymez.com
FACTORS NECESSARY FOR THE SUCCESS OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETY.
- Adequate financing/sound economic base.A co-operative society needs money for erecting office and storage buildings, setting up processing plants, purchasing transport vehicles and farm inputs, and for paying farmers promptly on delivery of produce.
- Adequate volume of business.The volume of business should be large enough to enable a society to benefit from economies of large–scale operation.
- Goals and objectives:-The goals and objectives of a co-operative must be clearly defined and known by every member.
- High level of managerial ability and honest.Weak management led to the collapse of many co-operatives societies. Leaders must be honest. Managers and their staff should be trained on how to run a business, including book-keeping.
- Interference.There should be no or little interference in the day to day activities of the management staff by committee members.
- Loyalty.All members should be loyal to the co-operatives so that they can fully support the societies activities.
edu.uptymez.com
PRINCIPLES AND CHARACTERISTICS OF CO-OPERATIVE SOCIETIES
These are the rules and regulations set to govern co-operative societies.
For an organization to be called a co-operative society, it must adhere to the following principles:-
- Open and voluntary membership.It is a voluntary association of people and membership is open to all those who can fulfil the requirements of co-operatives. The minimum number required is 10. Those wishing to join a co-operative must be adult (18 years of age and above). Also member are free to leave and are not limited by social, political, tribal, racial or religious differences.
- Democratic administration.The affairs of the co-operative is and must be administered/managed in a “democratic manner” Each member must have only “one vote” even if the holds a great number of shares he sells or buys from the society in a large quantity. The principal states “one man one vote”.
- Equality.All members in a co-operative society are equal regardless of their religion, race, political status, tribe, height, sex, age, financial status, e.t.c.
- Dividends or repayments.Profits made by the co-operative society are distributed amongst members in a form of dividends or repayments, at the end of the trading period according to one’s contributions towards the co-operative. However, this is not based on capital contributions, but according to how much a member has sold to co-operatives. (incase of producers) or has purchased from the society. (incase of consumers).
- Limited interest on share capital ideally, co-operative societies do not pay interest on share capital. But if members provided for it in their constitutions, the interest given should be fixed, and should be known by all members.
- Share capital.A person is considered a member after contributing to the required capital by buying the minimum number of shares. However, a member may hold several shares up to a specified limit.
- Promotion of education.It is one of the duties of co-operative society to teach its members the principles and techniques of co-operatives including how to produce economically, how to make use of new technologies, etc.
- Neutrality.This principle states that co-operatives should not take sides in any political social or economic affairs. A co-operative is expected to be free from the influence of politics, tribal affiliation, religion and other bias that can affect its performance.
- Cash payment.Basically all sales to the society and purchases from the society are made based on current market prices and for cash only.
- Honest.Its members must not be dishonest and selfish. All the activities must be carried on honestly and fairly.Even the elected executive members of the society who manage the affairs of the society should be men of character and integrity.
- Co-operative with other societies.There should be co-operation among societies, not competition. They have a lot in common and can learn from each other. Or Co-operative society should co-operate with each other locally, nationally and internationally if they are to function efficiently and serve their members better for instance, one society could help another to transport its goods to the markets and another can assist it with the means of transport.
edu.uptymez.com
12.Solidarity.There must be trust and confidence among members for the successful operator of the society. The members must be united while taking any decision regarding certain matters.
13.Mutual confidence.The co-operative members should have mutual confidence and trust in each other they should work like a team in achieving the objectives of the society. There must be spirit of “self-help” amongst the members.
14.Liability of the members of the society may be limited or unlimited. The members can decide about their liability at the time of registration.In case of limited liability society, the liability of members is limited to the amount payable on share held by them.But in case of society with unlimited liability the members are, on liquidation, jointly and severally liable for all the obligations of the society.
15.Economy.
All the activities of the company must be carried on economically and members should try to avoid unnecessary expenditure and wastage of the resources. The money should be spent wisely and in the best interest of the society.
A cooperative is another form of business units under private sector. It involves an association of individuals or firms whose purpose is to perform some business function for its members.
A cooperative society differs from other major forms of organization as it is set up not for earning profit as its main motive but with the basic object of organizing to render services to its members. The main rule of co-operative society is EACH FOL ALL and ALL FOR EACH.
MOTIVES FOR ESTABLISHMENT OF COOPERATIVES
Economic factors.Desire to improve man’s economic position through improved income and better services.
Social factors.Desire to attain social recognition and protection.
Political factors.As the country ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage co-operative the cooperative members should abide country’s rules and regulations and give moral and material support to ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courage cooperative organizations.
FEATURES OF COOPERATIVE SOCIETIES.
(i)Registration. A co-operative society is registered under the co-operative society Act of a country. Being a co-operative body, it enjoys certain privileges which are subject to control and supervision of the state.A co-operative society enjoys perpetual succession and has its own common seal. It can enter into contact with other persons. It can file and defend suit’s, and also open bank accounts in its name.
(ii)Values. co-operative are based on the values of self-help, self responsibility, welfare, democratic, equity and solidarity. Members come together voluntarily for their mutual benefit in the spirit of openness, social responsibility and caring for other.
(iii)One man – one vote.In co-operative society, member has only one vote irrespective of shares held by him. The principles of one man vote makes the society truly democratic. All the members are treated as equal control does not rest with few individuals as in other firms or organization.
(iv)Service motive. A co-operative society is primary set up for rendering services to its members in a particular field. A society however, is not prevented to earn profit on the services provided to non-members.
(v)Religious, Tribal and Political Neutrality.A co-operative society, without considering religious faith, ethnic and political affiliations works for the social and economic betterment of its members. It enjoys autonomy and independence.
(vi)Economic prosperity for the weak. A co-operative society aims to empower economically weak people by looking after. Their own affairs in co-operative with another. In a country like ours, wealth is in few hands. It has split up the society into two groups. i.e rich and poor. A co-operative society can help the common man to get together with others like himself to safe guard their common interest. There is economic participation of all the members which helps them improve their standard of living.