MARKETING BOARDS
These are trading organizations set up by government or the private sector to purchase agricultural products from farmers and sell them to their consumers with an intention of promoting agriculture within the state.
Marketing boards are classified according to the type of goods they handle and areas served.
- Commodity Marketing Boards
edu.uptymez.com
This is a type of marketing board which specializes in specific agricultural products. It is responsible for buying and selling that particular product and takes its name from the product handed e.g Coffee
Marketing Board.
- Export marketing Boards
edu.uptymez.com
Such marketing boards concentrate on the marketing of various agricultural products to foreign markets.
- Advisory Marketing Board
edu.uptymez.com
Such marketing Boards concentrates on carrying out research and providing advisory services to growers of various crops. They research on modern methods of farming and new crop varieties and then
advise farmers accordingly.
- Produce Marketing Boards
edu.uptymez.com
This is a type of marketing board which handles and sells a variety of agricultural products.
- Statutory marketing Boards
edu.uptymez.com
This is formed by government under an Act of parliament (stature) They are managed by a chairman appointed by the government.
FUNCTIONS OF MARKETING BOARDS
1. Buying and selling produce
They buy agricultural products from farmers in various parts of the country at reasonable prices and sell them to consumers both locally and internationally at favourable prices.
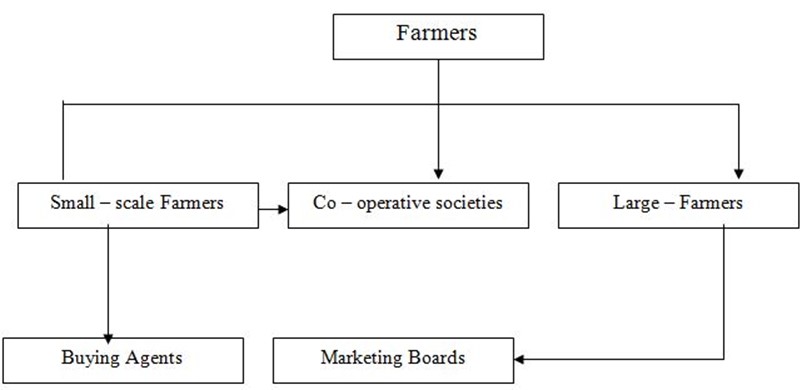
Marketing boards buy produce from farmers through the following channels:-
(a) Co – operative societies
(b) Direct sales
(c) Through agents appointed by the boards .
A figure below show channels through which farmers sell their produce to the marketing boards.
- Storage of produce.
edu.uptymez.com
They store agricultural products so as to protect them from damage by weather and to maintain constant supply.
- Provision of credit facilities / assistance.
edu.uptymez.com
They provide credit facilities to farmers associations by giving loans at low interest rate. And also assist farmers by buying fertilizers,, pesticides, farm tools, from the board at reduced price, the board
proved packaging materials to farmers like sacks, paper bags and polythene materials depending on a particularly type of produce, They protect farmers produce against diseases and pests by regular
supply.
- Carrying out research.
edu.uptymez.com
Marketing boards use some of their capital to carry out marketing and agricultural research. They send out officials to the fields to offer advisory services to farmers based on the results obtained from
the research.
- Control of production.
edu.uptymez.com
They take suitable steps to control over – production of certain crops. They impose quotas on various producers or co – operative societies, and any crop produced in excess of the quota is rejected.
- Stabilize prices.
edu.uptymez.com
Marketing boards stabilize prices thus encouraging produces to produce more. This is done by using the process of buffer stock. They buy and stock products during period of excess supply , and them
release them on the market during period of scarcity.
- Transporting products to the markets.
edu.uptymez.com
Marketing boards collect and transport products from rural areas to urban areas for sale.
- Provide statistical data to government.
edu.uptymez.com
They provide statically data such as the price of goods,, quality and quantity of goods on the markets, etc,.
PROBLEMS OF MARKETING BOARDS
- Political instability
edu.uptymez.com
This affects performance of marketing boards and farmers in any country due to reduced funding from the government.
- Over production
edu.uptymez.com
Some commodities are produced in large quantities than required in the market and as a result prices of commodities go down (fluctuation of prices)
However the boards try to solve this problem by:-
(a) Searching for new markets.
(b) Donating the surplus to the need in the form of aid.
(c) Exporting the surplus to other countries at lower prices.
(d) Storing those products that are not perishable for future use when demand is high.
(e) Destroying the surplus. Some countries burn the excess products.
- Lack of sufficient capital
edu.uptymez.com
Marketing boards lack enough funds to be able to extend their services to farmers.
- Poor transport
edu.uptymez.com
Most of the roads in East African countries where marketing boards operate are of murram and in poor state. They are impassable during the rainy periods.
- Poor quantity produce
edu.uptymez.com
Farmers produce mainly poor quality goods which cannot fetch high prices on the world market. Some farmers mix poor quality products with good ones and this lowers the general demand for such
products.
- Lack of storage facilities
edu.uptymez.com
There are few warehouses for storing excess products until they are required.
There are not enough cold stores for perishable goods. As a result, most products end up getting spoilt.
- Illiteracy of farmers
edu.uptymez.com
Some of the farmers do not know how to read and write. Thus it is difficult to educate and advise them on better production techniques to use.
- Poor management of funds and lack of skills.
edu.uptymez.com
Managers of marketing boards are often political appointments. They may lack the necessary management and financial skills to administer the funds set a side by the government to boost agriculture.
- Competition from business persons
edu.uptymez.com
Some business people have ready cash to pay for the produce. This ennglish-swahili/courage” target=”_blank”>courages farmers to sell to business people instead of the board which takes longer to pay.
Because of this, boards find themselves with insufficient quantities of produce to handle.
WHY GOVERNMENT PARTICIPATES IN THE OWNERSHIP OF BUSINESS ENTERPRISES.
(causes /Reasons of Public undertaking)
- High initial cost.
edu.uptymez.com
Construction of roads, railways, schools and hospitals to improve the countries infrastructure requires vast capital expenditure and therefore the government has to invest.
- Provision of essential commodities and services. Water and sewerage corporation and waster collection plants need heavy investment and are less attractive investments for private sector, yet essential.
- Prevention of monopolies.
edu.uptymez.com
Governments participate in commerce to deter the emergency of monopolies who exploit the government.
- Regional balancing.
edu.uptymez.com
The government invests in infrastructural facilities with the aim of attaining fair nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of development projects throughout the country.
- Ensuring national security.
edu.uptymez.com
Production and nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of certain goods such as money and ammunition is done specifically by the government.
- Promotion of political ideologies .
edu.uptymez.com
Political consideration may influence the government to own business enterprise.
- Attract foreign capital.
edu.uptymez.com
Government enterprises attract more foreign capital and technology than the private sector. Thus government participates and runs business with an aim of getting foreign capital which if acquired,
facilitates development in the country.
ADVANTAGES OF STATE CORPORATIONS
(1) Provision essential facilities.
They are suitable for unprofitable enterprises in which the private sectors may not want to invest e.g dam construction, road construction, education , garbage collection, etc.
(2) Large initial capital
Some business enterprises require large capital which cannot be raised by private sector enterprise e.g provision of educational materials, electricity, etc.
(3) Risk ventures
Some sectors of the country are very risk and too confidential for the private sector to get involved e.g production of weapons, police and maintenance
(4) Relatively cheap
They provide goods and services to the public at lower prices than the private sector.
(5) Elimination of duplication of services
They help in elimination of duplication of services, which reduces wastage and inefficiency
(6) Source of government revenue
They create revenue to the government through their aim is not to make profits. The money obtained is used to run development projects.
DISADVANTAGES OF STATE CORPORATIONS
Lack of competition.
Because there is a little or no competition .this may lead to the production of goods and service, which are of poor quality. This reduces standard of living within the country.
(ii) Un economical.
The in profit ability and cost of production are passed on the public in the form of higher taxes .the government tries hard to get fund to finance unprofitable business.
(iii) No personal interest.
People who work in state corporations may have no interest in the business.
This result in the provision of poor quality goods and service.
(iv) Bureaucratic tendencies there is too much red tape in state corporations .This leads to delay in the supply of certain goods and services for decision to be made , it has to go through many channels .
(v) Monopoly some state corporations have there monopoly of supply for providing certain service e.g National water and sewerage corporations .This corporations has power to set prince at a higher rate because there are no competitors
(vi) Lack of capital . Some of the businesses require large capital, which cannot be raised by the government. This result in inefficiency in the production of goods and service
(vii) Un profitability .Some business under takings are unprofitable and costly to run. The government increases price and taxes to the consumers’ price and taxes to the consumers on order to be able to manage them.
(viii) Limited skills the management and administration of the state corporations is often influenced by sectarianism which is based either on tribal or political grounds and the workers many lack the skills needed. In many cases the skills of the employees are not considered which promotes inefficiency in the business.
PRIVATIZATION
Meaning
It is a transfer of government ownership of state enterprises from the government to the private sector.
REASONS/ADVANTAGES OF PRIVATIZATION
1. To increase government revenue.
The government earns income by taxing private enterprises. These taxes enable the government to get enough money to fund other development projects
This enhances economic growth and development.
2. To earn foreign exchange.
The privatized enterprises bring in foreign currency, especially if they are foreign owned.
This improves the balance of payments position of the country.
3. To reduce bureaucratic delays
In private enterprises, decision making is much quicker than in public enterprises because of bureaucratic tendencies in public enterprises.
4. To private quality, goods and service.
Privatization brings about competition among producers and providers of goods and services. Enterprises need to provide better quality products in order to capture the market. Consumers benefit from
privatization.
5. To promote efficiency
Private enterprises are often more efficiency than state enterprises.
The owners of private enterprises carefully supervise them to ensure efficiency and reduce the wastage of resources.
6. To reduce excessive government expenditure.
Most of the state – owned enterprises do not make profit the government spends a lot of money on them . To avoid such expenditure, the government sells off such enterprises.
7. To create employment opportunities
Many jobs are created in the private sector because the owners are interested in the companies and are keen to bring in new ideas, enabling the companies to expand.
DISADVANTAGES OF PRIVATIZATION
1. Exploitation of the public
Private investors tend to exploit the public by own over changing and provision of poor quality goods and services, especially if monopoly exist.
2. Limitation for expansion
Private firm may not have adequate bargaining power for fund international financial institutions like IMF and the World Bank, thus expansion may be difficult.
3. Profit caparatriation.
There are is capital out flow from the country that privatized the enterprises if the private sector is dominated n by the foreigners.
This retard the level of economic growth and development.
4. Limited supply of essential but unprofitable services.
The private sector is reluctant to supply the essential but unprofitable services like street cleaning garbage collection and road maintenance.
5. Continuity of business.
The existence of private enterprises largely depends on the life of the owner. If he /she dies the business also dies.
6. Difficult to control the production of dangerous goods .
It is dangerous for the private sector to deal in the production of dangerous commodities, eg making firearms.