A differential equation is a relationship between the rates of different variables (i.e an independent variables x, a dependent variable, y, and one or more differential coefficient of y with respect to x).
Eg 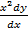 + y sin x = 0
+ y sin x = 0
xy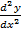 + y
+ y 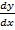 +
+ 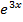 = 0
= 0
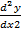 +
+ 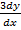 – 4y = 0
– 4y = 0
The order of a differential equation
The order of a differential equation is given by the highest derivative involved in the equation.
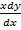 – y2 = 0 is an eqn of the 1st order
– y2 = 0 is an eqn of the 1st order
xy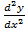 – y2 sin x = 0 is an eqn of the 2nd order
– y2 sin x = 0 is an eqn of the 2nd order
xy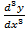 – y
– y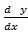 +
+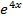 = 0 is an eqn of the 3rd order
= 0 is an eqn of the 3rd order
The degree of a differential equation
Eg 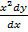 + y sin x = 0 the degree is 1b
+ y sin x = 0 the degree is 1b
Linear differential equation (L.D.E)
A linear differential equation should look in the form
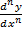 +
+ 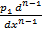 +
+ 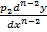 + ………
+ ……… 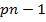
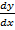 + pn y = Q
+ pn y = Q
Where P1, P2, P3 …Pn, Q are functions of x, or constant n = 1, 2, 3, 4…….
Examples
i) 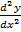 +
+ 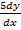 + 6y = 0
+ 6y = 0
ii) 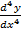 +
+ 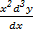 +
+ 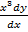 =
= 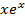
iii) 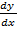 = 4
= 4
Examples of non L.D.E
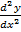 +
+ 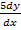 + 6y = 0
+ 6y = 0
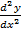 +
+ 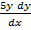 + 6y = 0
+ 6y = 0
Note
A D. E will be linear if
- Variable y and its derivatives occur at the first degree only
- No product of y and its derivatives
- No transcendental function of y or x
edu.uptymez.com
Exercise
Show which of the following differential equations is the L.D.E or N.L.D.E
i) 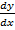 = y……………linear
= y……………linear
ii) (x2 – 1) 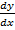 = y……linear
= y……linear
iii) 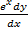 + y2 + 4 = 0…………..non – linear
+ y2 + 4 = 0…………..non – linear
iv) 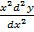 =
= 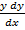 ……………non – linear
……………non – linear
v) 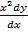 = 1 + xy………linear
= 1 + xy………linear
vi) (x2 – y2) 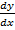 = 2xy……Non – linear
= 2xy……Non – linear
Formulation of a differential
Differential equation may be formed when arbitrary constant are eliminated from a given function.
Examples 1
Y = A sin x + B cos x, where A and B are two arbitrary constants
Solution
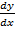 = A cos x – B sin x
= A cos x – B sin x
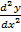 = -A sin x – B cos x
= -A sin x – B cos x
 his is identical to the original eqn with opposite signs
his is identical to the original eqn with opposite signs
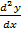 = -1(A cos x + B sin x)
= -1(A cos x + B sin x)
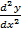 = -y
= -y
Form a DE whose solution is the form y = Ae2x + Be-3X Where A and B are constant.
Example 2
Form a different equation from the function y = x + 
Solution
y = x +  = x + Ax-1
= x + Ax-1
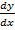 = 1 – Ax-2 = 1 –
= 1 – Ax-2 = 1 – 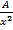
From the given equation
Y = x + 
yx = x + 
x(y – x) = A
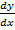 = 1- x (y – x) x-2
= 1- x (y – x) x-2
= 1 – 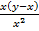
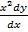 = x2 – x (y – x)
= x2 – x (y – x)
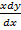 = x – (y – x)
= x – (y – x)
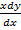 = 2x – y
= 2x – y
Example 3
Form the DE for y = Ax2 + Bx
Y = Ax2 + Bx…… (i)
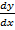 = 2Ax + B
= 2Ax + B
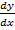 – 2Ax = B……. (ii)
– 2Ax = B……. (ii)
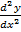 = 2A
= 2A
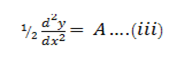
Substituting both (ii) and (iii) into (i) gives
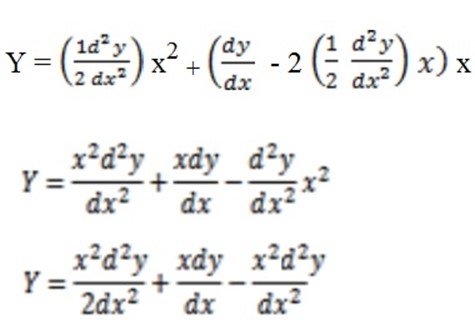
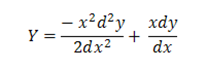
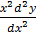 – 2x
– 2x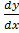 + 2y = 0
+ 2y = 0
Solution to a DE
This involves finding the function for which the equation is true (i.e manipulating the eqn so as to eliminate all the differential coefficients and have a relationship between x and y)
E.g. verify that the function
i) Y = 3e2x is a soln of DE = 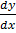 – 2y = 0 for all x
– 2y = 0 for all x
ii) y (x) = sin x – cos x + 1 is a soln of eqn 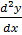 + y = 1 for all value of x
+ y = 1 for all value of x
Solution
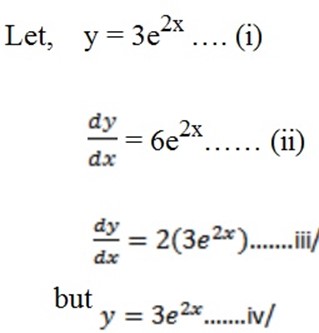
Substitute equation iv into iii.
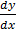 = 2y
= 2y
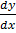 – 2y = 0
– 2y = 0
Direct integration
Direct integration is used to solve equation which is arranged in the form 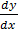 = f (x)
= f (x)
Examples
1. Solves 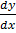 = 3x2 – 6x + 5
= 3x2 – 6x + 5
Solution
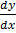 = 3x2 – 6x + 5
= 3x2 – 6x + 5
Then 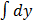 =
= 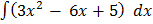
= x3 – 3x2 + 5x + c
Y = x3 – 3x2 + 5x + c
2. Solve 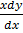 = 5x3 + 4
= 5x3 + 4
Solution
Rearranging in the form 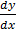 = f (x)
= f (x)
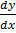 = 5x2 +
= 5x2 + 
Then 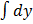 =
= 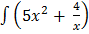 dx
dx
Y = 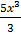 + 4ln x + c
+ 4ln x + c
Y = 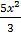 + 4ln x + c
+ 4ln x + c
The solution is a called general solution since it consist a constant C (i.e. unknown constant)
3. Find the solution of the eqn ex
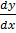 = 4 given that y = 3
= 4 given that y = 3
When x = 0
Soln: rearrange the given equation
= 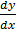 = 4e-x + 7
= 4e-x + 7
This is called a particular soln since it contains a non – unknown variable.
First order D.E
Separating the variables
This is a method used to solve the D.E when is in the form 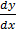 = f (x, y)
= f (x, y)
The variables y on the right hand-side prevents solving by direct integration
Example
1. Solve 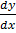 =
= 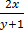
Solution 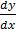 =
= 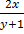
= (y + 1) 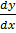 = 2x
= 2x
Integrating both sides with respect to x
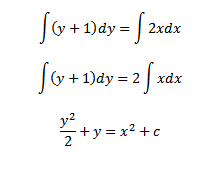
2. Solve 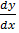 =
= 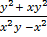
Solution
 =
= 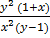
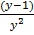
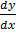 =
= 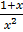
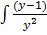 dy =
dy = 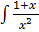 dx
dx
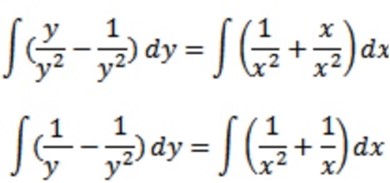
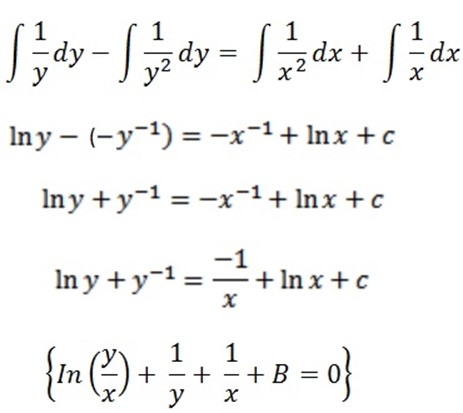
3. By separating variables solve the differential equation (xy + x) dx =(x2y2 + y2 + x2 + 1) dy
Solution
Given Equation;
(xy + x) dx = (x2y2 + y2 + x2 + 1) dy
X (y + 1) dx = (y2 (x2 + 1) + (x2 +1)) dy
X (y + 1) dx = (x2 + 1) (y2 + 1) dy
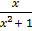 dx =
dx = 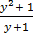 dy
dy
Integrating both sides
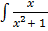 dx =
dx = 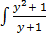 dy
dy
R.H.S =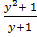 = y-1+
= y-1+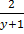
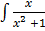 dx =
dx =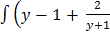 ) dy
) dy
½ ln (x2 + 1) = 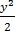 – y + 2 ln (y + 1) + C
– y + 2 ln (y + 1) + C