Every person or group of people who stay together (school) has daily routine or activity. This can be expressed by different works, everyday, often, usually, daily, every month.
Usually action is expressed in present simple tense or habitual aspect. The social area/ focus is on the following.
BREAK TIME
At 10:00 A.M break starts. We go out for a break of 30 minutes. During break time, I drink tea with some snacks. At 10:30 A.m. I go back to class. Classes end at 2:00 p.m.
After classes I go home at 2:45 P.M. I eat lunch.
Exercise
As a student’s what is your Daily Routine?
Vocabulary
Take a shower – wash the whole body
Attendance – counting people
Supper – food eaten at the right (a right meal)
Structure
Prepositions
“ON” – is used with days and dates
Examples
- I go to church on Sundays.
edu.uptymez.com
- I go to the Mosque on Friday
- I was born on 03rd May 1978
edu.uptymez.com
“AT” – is used with exact time Examples:
- He come at six o’clock
- We traveled at night
- The lesson starts at 8:00 am.
edu.uptymez.com
“IN” – is used with parts of the day, months and years
Examples:
- He came in the evening
- School will be closed in December
- He was born in 2009
edu.uptymez.com
Asking questions.
We can also ask questions using does, do
Note: Does – is for singular nouns and pronouns
Do – is for plural nouns and pronouns.
Examples:
- Does she speak English?
- Does he come to school late?
- Does she smoke?
- Do they speak English?
- Do they come to school late?
- Do we have to write our names?
edu.uptymez.com
Exercise
Make question using does and do
- Does …………………………..?
- Does …………………………..?
- Do ….…………………………..?
- Do ….…………………………..?
edu.uptymez.com

EXPRESSING ON GOING ACTIVITIES
This activity can be done by individual or somebody else. They refer to what is going on at a time of observation guessing, talking and so on. This is PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE or PROGRESSIVE ASPECT
– The verbs end with …ing
- Martha and Consolata are sweeping the floor
- It is looking at you
- They are eating rice
- You are playing nicely
edu.uptymez.com
– When you go to school in the morning there are a lot of activities going on, you will see
- Some students sweeping the compound
- Some students watering the flowers
- Some students parading
- Some teachers shouting to the students
- Parents paying fees.
edu.uptymez.com
Extra verbs
Flowering, watering, chasing, snoring, reading, shouting, waiting, glorying, drinking, ringing, banking, blowing, cutting, shrinking .
Note: present continuous tense
He
She is
It
I am + verb ……………ing
They
We are
You

EXPRESSING LIKES AND DISLIKE
The word like (v) means to be sound as or pleased with from the verb we get the word like (vi) and dislike (Ti) opposite or antonym. Grammatically likes/ dislike are not nouns but only used in everyday talks (spoken English) whether like or dislike the force behind them are human feeling, taste experience traditions.
- Usually like and dislike are expressed in non-verbal forms of communication such as gesturers, social expressions movement nodding.
- Non- verbal – communication is also called body language
edu.uptymez.com
Examples:
Question : what game do you like most?
Answer : I like football and boxing
Question : what music do you like most?
Answer : I like bongo flava
Question : what drink do you like most?
Answer : I like orange Juice only
PREFERENCE
The most suitable is ……..to…………
Therefore
Example: I prefer——— to———-
- I prefer tea to coffee
- I prefer English to Kiswahili
- I prefer reading to writing
edu.uptymez.com
Exercise
Make ten (10) sentences using the following words below
TALKING ABOUT ONE’S FAMILY
– Expressing family relations:
A family is smallest social unit. The family consists of father, mother, children and relatives. This kind of a family is called Extended family
Vocabulary
- Uncle – The brother of your father or mother
- Cousin – The child of your uncle or aunt.
- Nephew – The son of you r brother or sister
- Niece – The daughter of your brother or sister
- Sister – in – law – The sister of your wife or husband
- Father in- law – the father of your wife or husband
- Grandfather – The father of your father or mother
- Brother in- law – The brother of your wife of husband
- Grandmother – The mother of your father or mother
- Aunt – The sister of your father or mother
edu.uptymez.com
A family tree
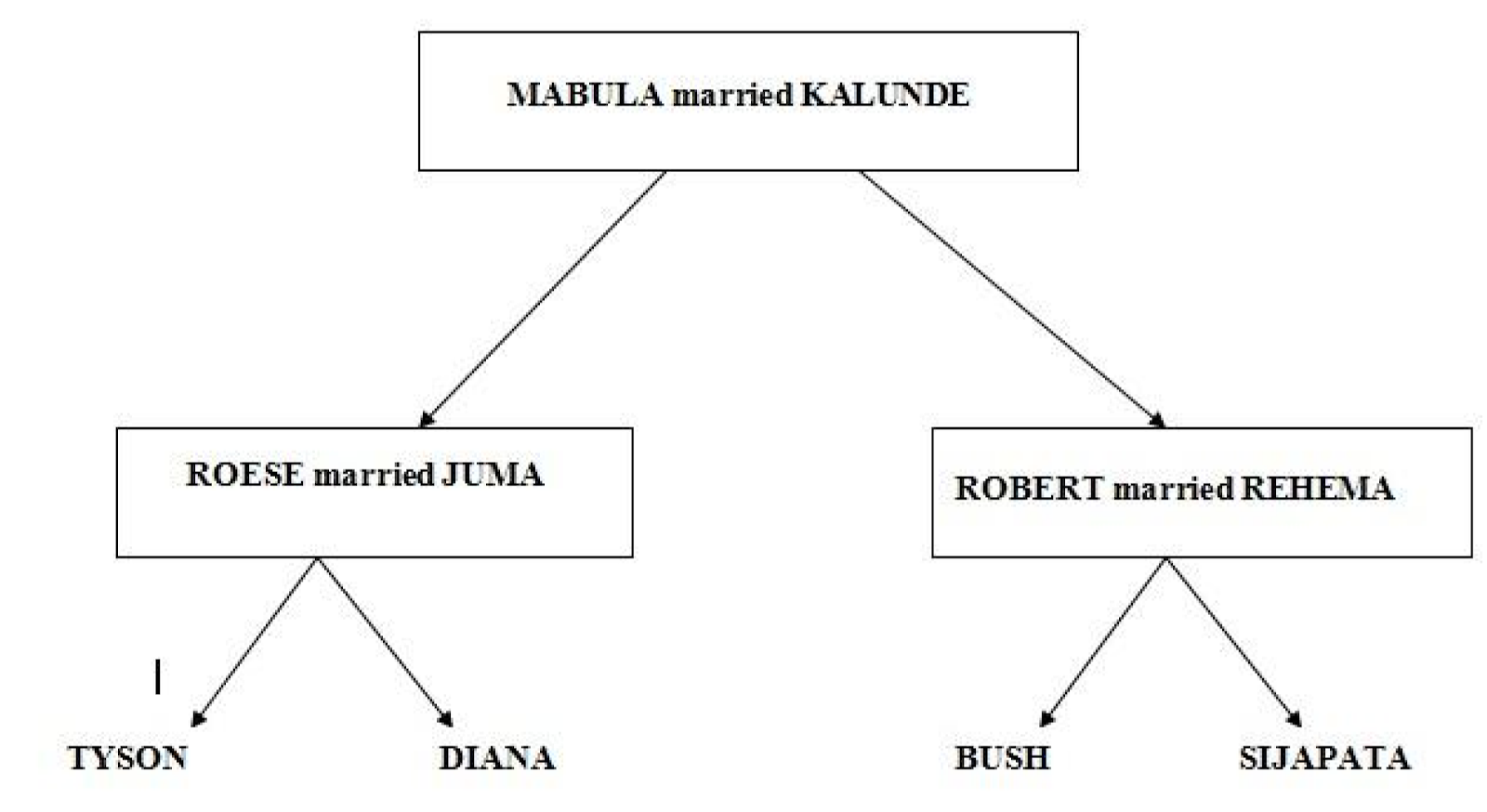
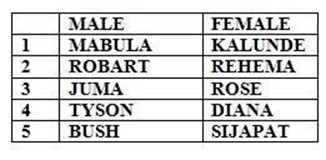
Mabula married Kalunde.They have two children ,Robert and Rose. Robert got married to Rehema and they have two children Tyson and Diana Rose at mrried to Juma and they have two children;Bush and Sijapata Study the following diagram:
Expressing occupations of family members
Members of a family usually has daily activity for production or social services
Vocabulary; Venders, Tailors, Sailors, Plumber, Nurse,Teacher.
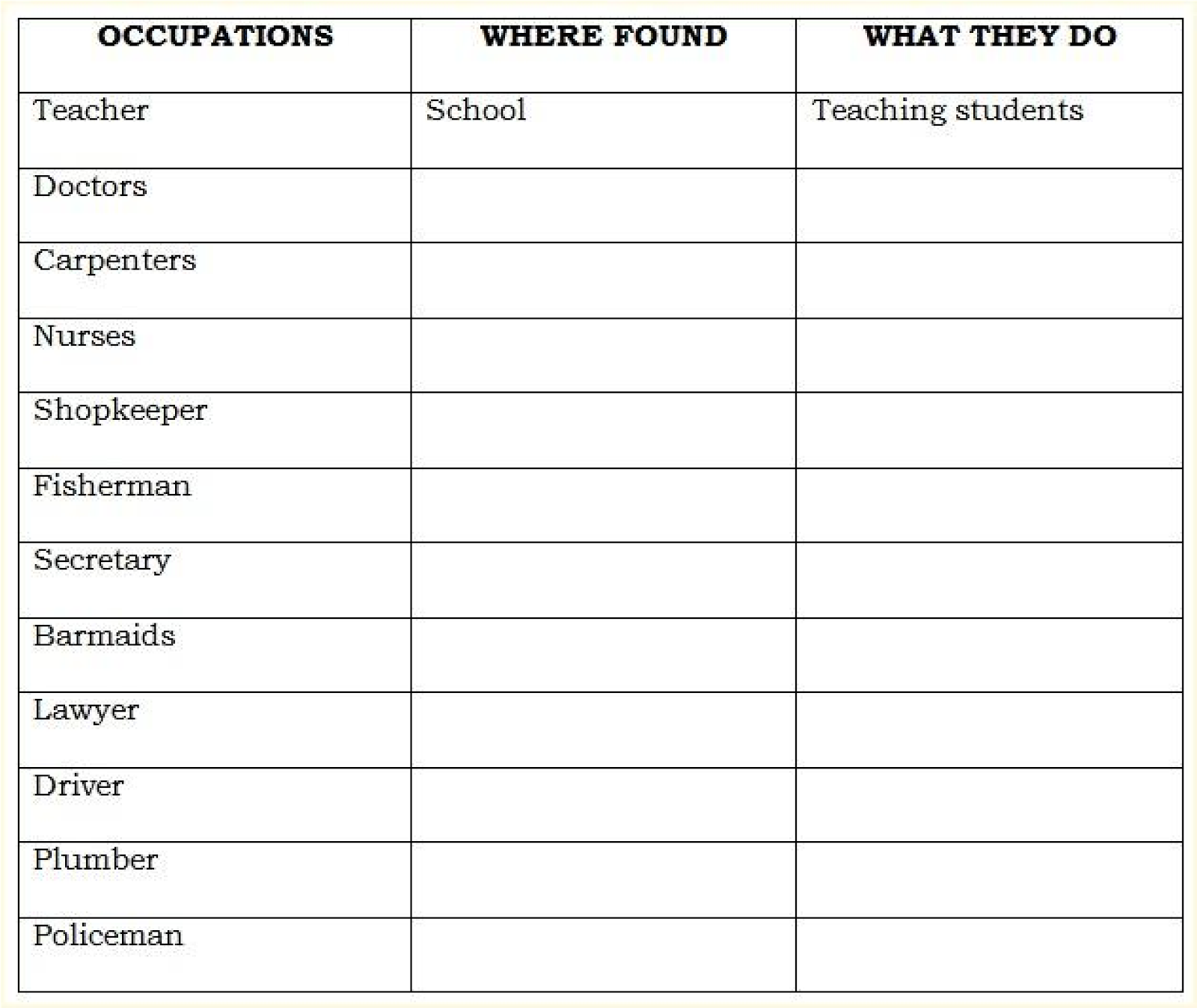
Exercise:
Fill in the following table with the right information. The first one has been done for you.
OWNERSHIP OR POSSESSION
Possession refers to one having his/her property such as school, pen, houses, car, home, and farm – Most occurring words
- Possessive pronouns: e.g. my, her, his, our, their
- Other terms: posses, belong, own, property of….
edu.uptymez.com
Examples
- My father owns a boat
- My sister own a big house
- I have a hen
- We possess a big library
- That bus belongs to my father
edu.uptymez.com
DESCRIBING PHYSICAL APPEARANCE
People differ in physical appearance in terms of height, size, colour,[complexion] morphology, hair, eyes, ears, nose, teeth, fingers, legs, toes, chest head.
Study the following text
Mr. Kibakaya is a light coloured skinned man in our street. He is baldheaded and his remaining hairs gray. Older people say that he has a fair complexion. His daughter is skinning, tall but tenders. She is beautiful and attracts attention whenever she passes. Her twisting eyes confuse young man. She puts on her-heals on every weekend. Her young brother is shot and fat, he looks handsome and magnetic to girls his chest is wide as well as frightening nose
DESCRIBING CHARACTER
Every person has a particular behavior that display his/her character: Example: cruel, greedily, rude, rough, carelessness, generous, gentle, sincere, open, lian
Examples:
- He is a rude boy at our school
- She is careless that her uniform is full of sports
- A sincere student is liked by teacher
- You’re a liar
edu.uptymez.com
Character changes because of age education and people around, character reflects moral and cultural value. People from broken families usually show bad character. Character can also be understood through a language that a person uses.
Structure
Asking questions
We can also ask questions using the words in the box

- Who is shouting?
- What are you doing?
- Which boo is yours?
- Whose pen is this?
- When do we go home?
edu.uptymez.com

EXPRESSING OPINIONS AND FEELINGS
What is your opinion?
Do you like city life or rural life?
There are some people who want to go to live in towns. They think that life is cheap and simple there. They think they can buy cars, houses, good clothes etc.
Giving opinions can be easily expressed during debates
Example: Motions
- Boarding schools provide better education than day school
- Co- education school are better than single sex school
- Special ability schools are not special in rolling students
- Students failure in examination is due to poor teaching.
edu.uptymez.com
Look at the following ways in which we can express opinions in English 
- Asking for opinion
edu.uptymez.com
- expressing an opinion
edu.uptymez.com
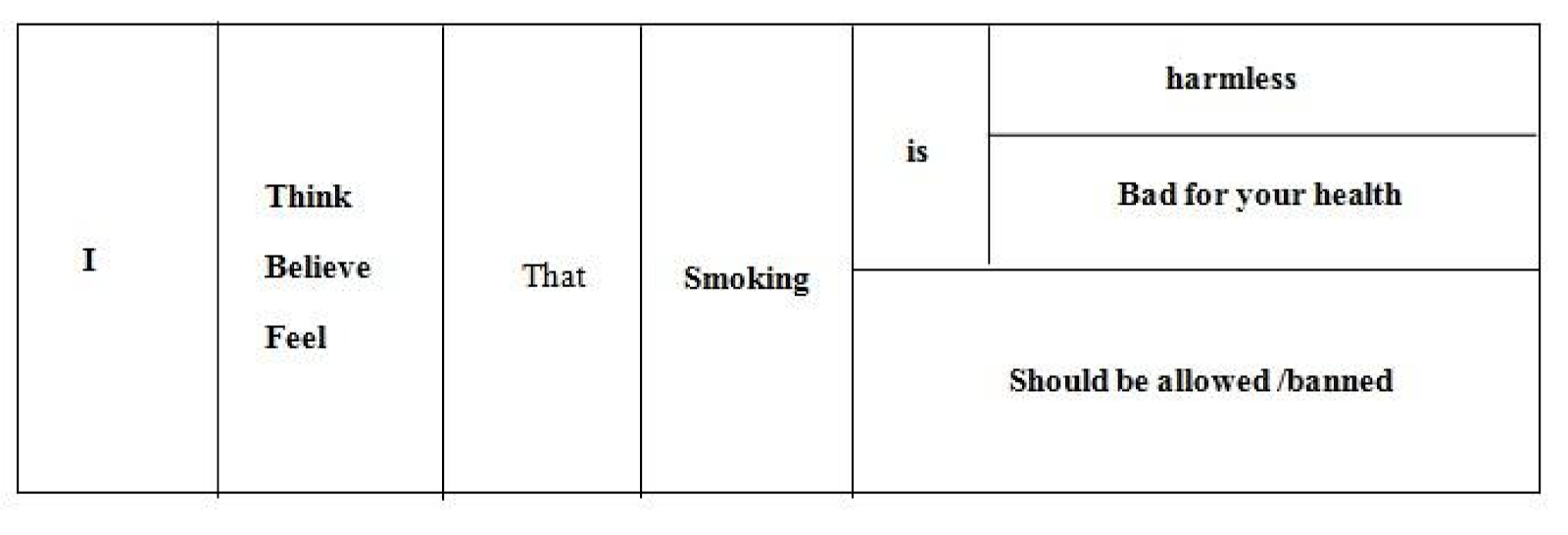
In my opinion,school rules are a waste of time

- supporting opinion
edu.uptymez.com
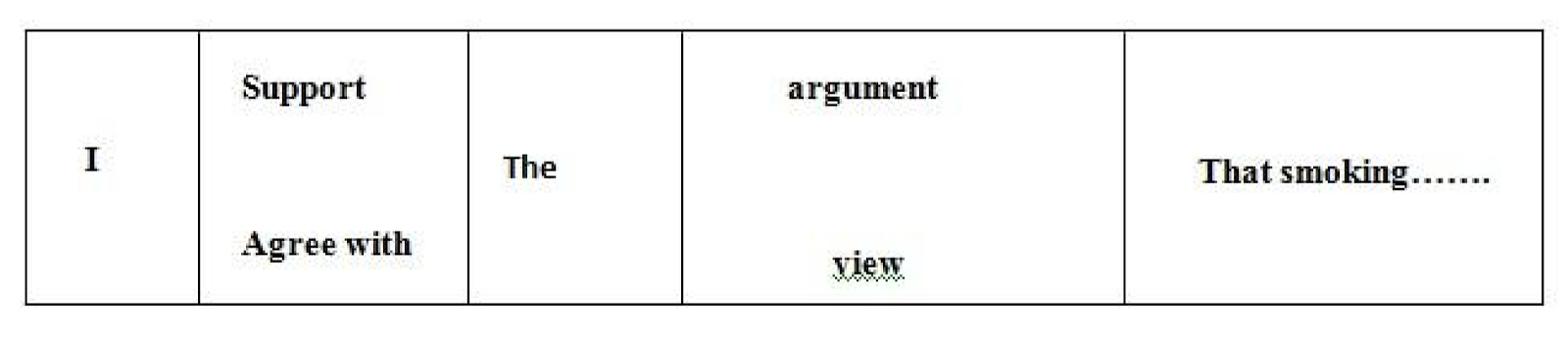
- opposing an opinion
edu.uptymez.com
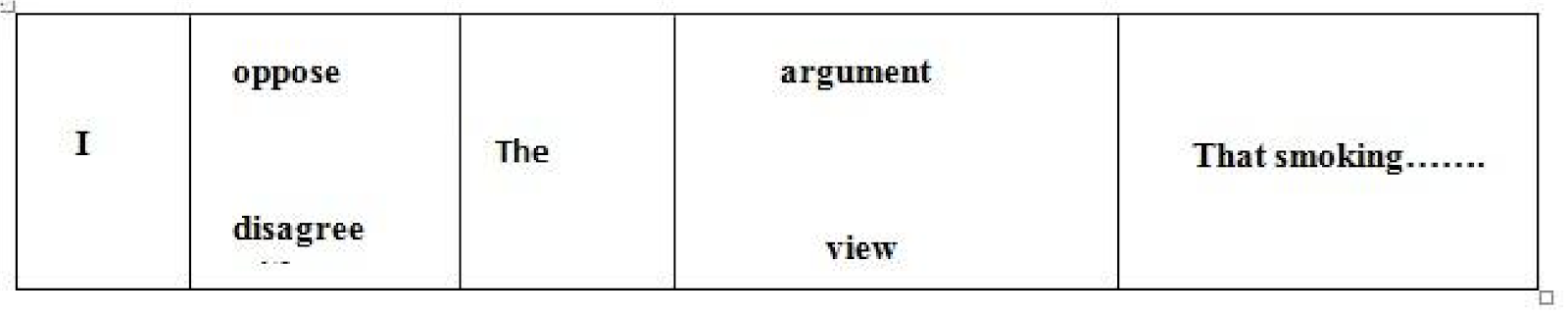
- Expression doubt
edu.uptymez.com
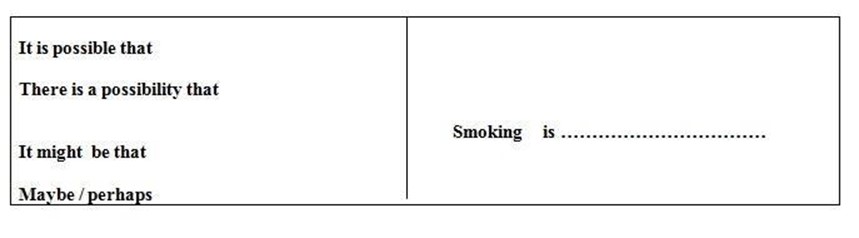
Participants
Chief proposer and opposes, audience, guest, speaker, secretary
Vocabulary :
Suggest, view, evaluate, propose, against, think, argue, advise, disagree, equally, feeling can be expressed.
Example
I feel hungry
You are happy
Expressing state of health
Examples
Are you sick ?
What are you suffering from?
Yesterday I had a headache
Exercise
Write conversations between a doctor and patient

TALKING ABOUT PAST EVENTS/ ACTIVITIES
This give a particular form of verb endings it is sometimes called PAST TENSE
Note: common adverb Last week, yesterday etc.
Example:
My brother got married last Friday
Last week they closed the school
Expressing past activities
Tense is expressed by verbs. These verbs in the past tense be have with regular ending with-ed,ed, and others behave with irregular ending. Example see-saw, get-got, cut-cut.
Adverbs that show past tense
- Yesterday – I saw him yesterday
- Last – we were at club last Friday
- Ago – they met two years ago
- Previous – she experienced this problem from the previous.
edu.uptymez.com
– Such characteristics of irregular verb also apply to helping or modal verbs
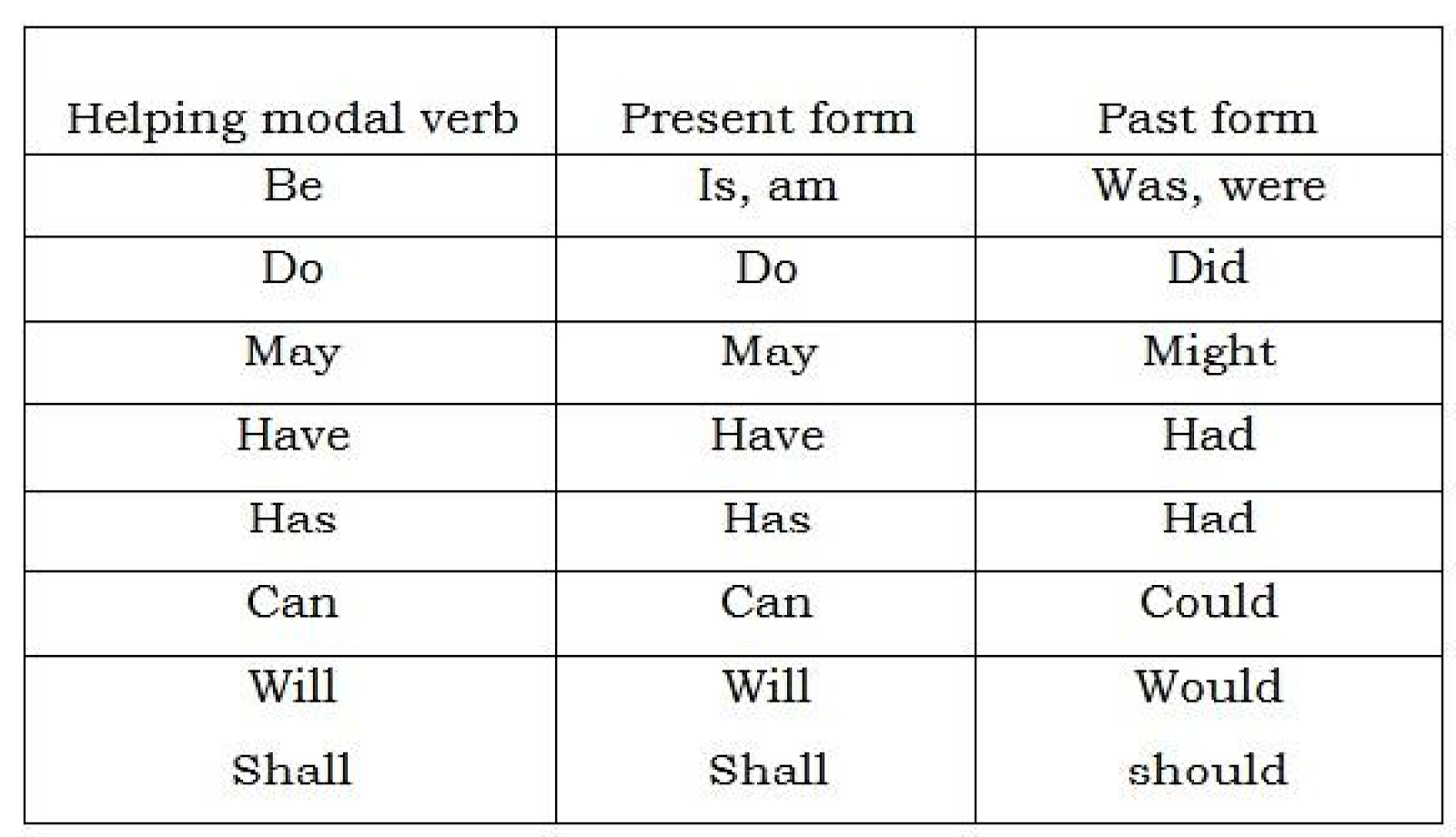
Note: the past tense of the above modal helping verbs are common in conditional clauses that is if……… then…………..
Structure
Past perfect tense
Format
Subject + had + verb in participle
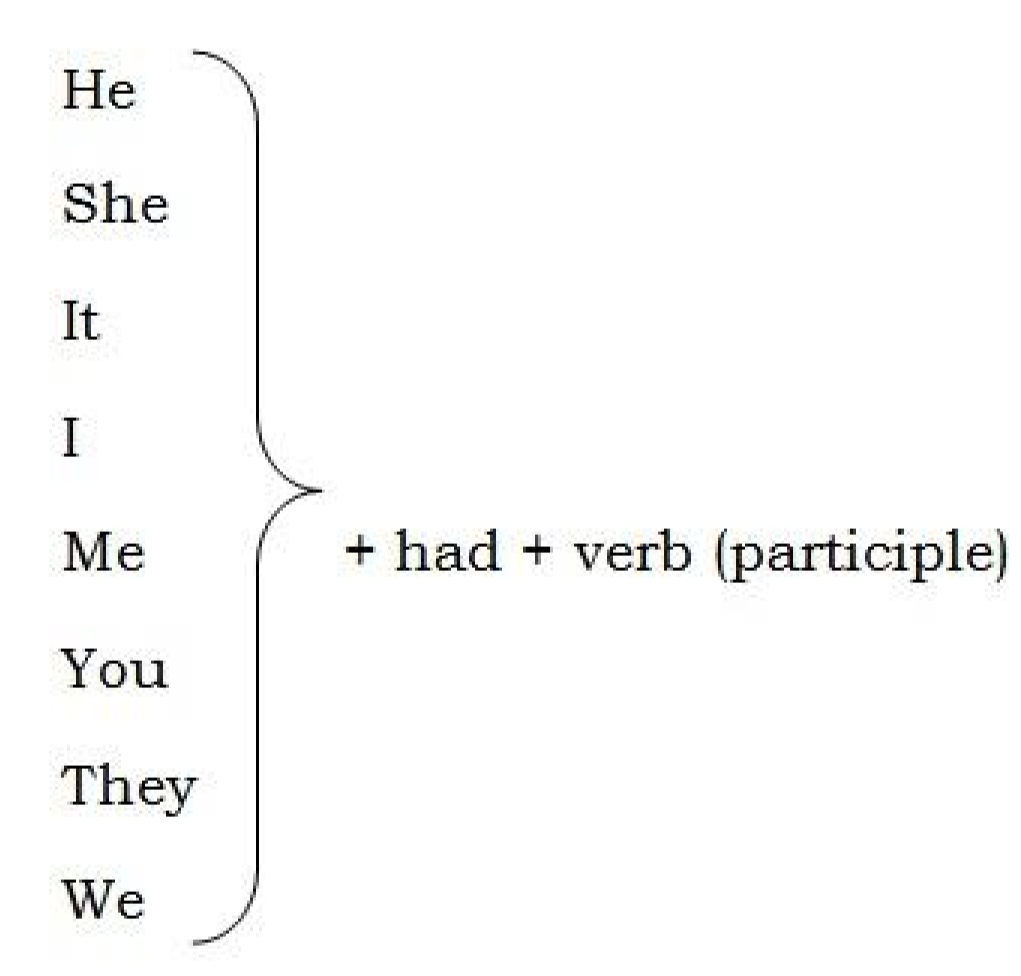
Examples:
I had seen several football games
I had done the job
Structure
Adjective: is a word that is used to describe a noun or a pronoun
General classification of Adjectives
- Adjectives of colour
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. black, yellow, green, purple, orange, red
- Adjectives of size and shape
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. small, giant, round, etc
- Adjectives of quantity
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. many, few, little, much
- Adjectives of age
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. old, new, middle, young.
- Proper adjectives or adjectives of origin
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. African, Kenyan, French (vi) Adjective of use
e.g. useful, useless
ORDER OF ADJECTIVE
Where there is more than one adjective before a noun in a sentence, the order of adjectives is as follows:
- 1st adjective – Describes the number (Quantity)
- 2nd adjective – Describes the general size and shape
- 3rd adjective – Describes age
- 4th adjective – Describes colour
- 5th adjective – Describes where it comes from (origin)
- 6th adjective – Describes what is made up of
- 7th adjective – Noun
edu.uptymez.com
Examples:

EXPRESSING FUTURE PLANS AND ACTIVITIES 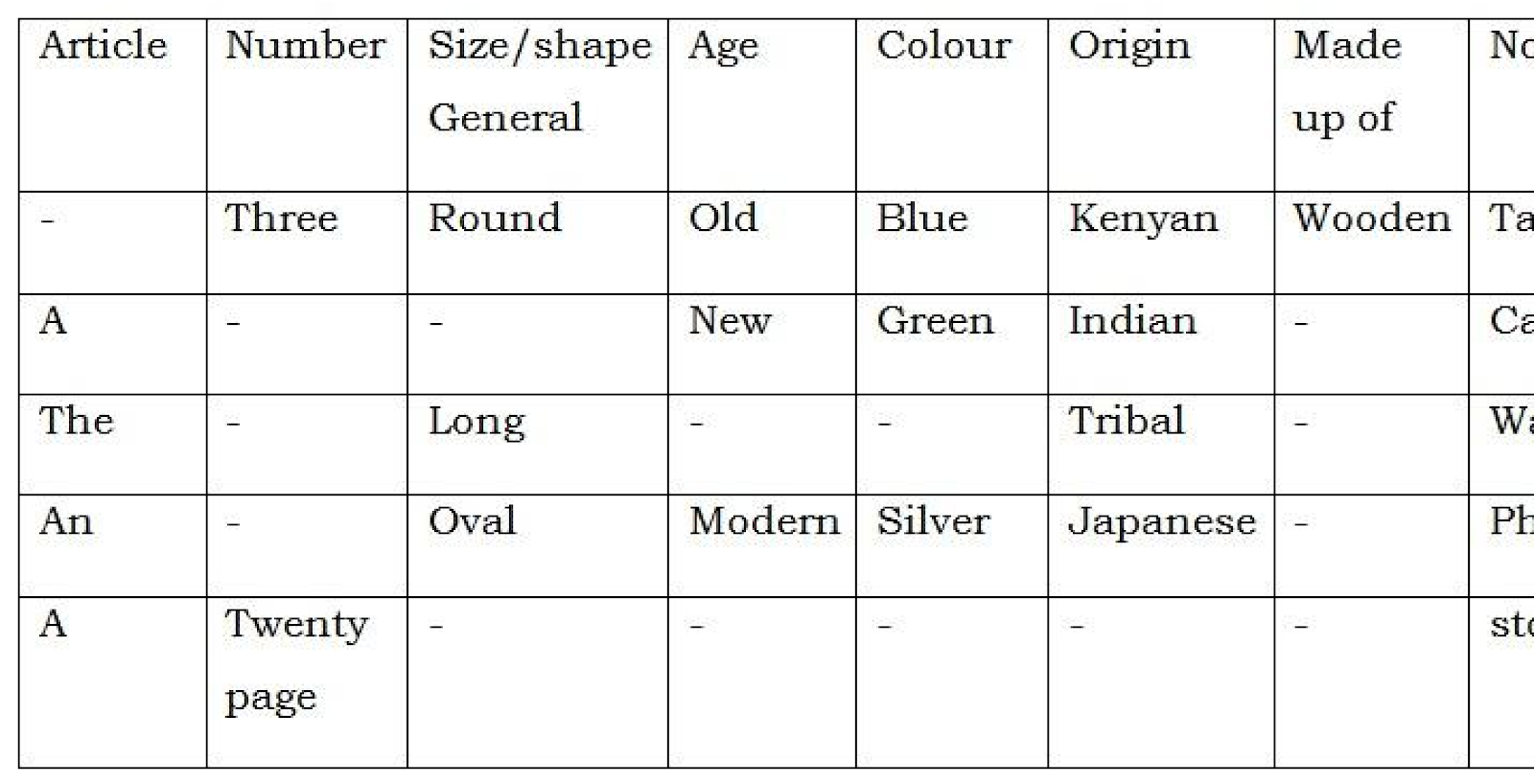
Future exists in different forms
- Intention – necessity – shall
- Probability – possibility – will
edu.uptymez.com
Common adverb
Tomorrow, next
How to form future?
Subject + shall/will + be + main clause
Examples:
It will be there tomorrow
Subject + will + be + clause
When we want to talk about things what we shall do tomorrow, next week, next month we use words like
- Going to
- Shall
- Will
edu.uptymez.com
Examples:
Tomorrow I’m going to write my mother a letter.
She will tell you something good tomorrow
We shall visit you next month
Going to, will and shall show future tense.
Future continues activities
Subject + will or shall + (be) + verb ……..ing + clause
Examples
You will be leaving the school at 4:30pm
We shall be singing in the church choir
Exercise
Mention 4 things that you are going to do after you have finished form four
- ……………………..
- ……………………..
- ……………………..
- ……………………..
- ……………………..
edu.uptymez.com
1. Mention three (3) things which will happen to someone who has HIV/ AIDS
- ……………………..
- ……………………..
- ……………………..
edu.uptymez.com
Note:
will is used all persons in the singular and plural for example
i) you will be wait ii) I will go to the market tomorrow
Shall is sometimes use instead of will, It is used in statement in the fist personal singular or plural, It shows determination or promise about future activities for example
i) We shall play hard and we shall win the game: (determination) ii) I shall write to you as soon as i arrive in Mpwapwa (promise)

READING A VARIETY OF TEXTS (INTENSIVE READING)
A FOOLISH CUSTOMER
One day Mr. Juha seat in a hotel drinking some coffee. A boy come to him that he was selling afternoon papers. “Which papers do you have? Juha asked. “I have the Daily news and The Guardian”, the boy said. “Well, give me both. How much do they cost?” Mr. Juha asked. “One thousand two hundred for both. The Guardian sells at seven hundred” the boy said, “Oh, that is very expensive; just give, The Daily News”
Mr. Juha gave the boy ton thousand shillings note. The boy said he had no change. “Let me go for the change sir”, the boy said “No! No! No!” you will run away with my money! Leave your papers here with me” Mr. Juha said. The boy left happily leaving Juha with the papers after two hours Mr. Juha counted the papers that the boy had left. They were only three! Juha laughed Kwe! Kwe! Kwe! Of course the boy never came back
Questions
Write True (T) or false (F) to the following sentences
- Juha sat in a hotel reading the Daily news
- The Guardian costs five hundred shillings
- Juha change was 8,800/=
- Juha counted his change
edu.uptymez.com
VOCABULARY
Customer – someone who buys things from the seller, buyer, client
Expensive – an item whose price is very high
Cost – The price of something
e.g. my shoes cost me five thousand shilling only
Change – Money left buying something
EXERCISE
Make two sentences using the words expensive and cost
- ……………………………………..
- ……………………………………..
edu.uptymez.com

INTERPRETING LITERARY WORKS
Intensive reading: Involves comprehension and summary while reading a class reader (books) its chapters, the following activities should be done.
- Understanding the writing and pictures on the front cover, usually they summarize or give a piece of information of what is in the class reader (book)
- Title of the class reader (book)
edu.uptymez.com
– A name or topic which is discussed in the chapters
- Author: A person writes a book must be memorized.
- Main or chief character(s) he/ she is the main actor
- Minor character persons or animals in the story
- Setting (venue – A particular place in which the story take place Example, Dar es salaam, Nairobi, Kampala etc
- Difficult words should be selected and their meaning understood either by using a dictionary (decretive memory) or according how they are used in the book.
- To summarize each chapter in one or two sentences and finally the whole book into one to five sentences.
- The lesson one can learn from the book.
- The importance or significance or relevant of the book in society
edu.uptymez.com
It is still useful or not
Intensive reading therefore means reading deeply while extensive reading refers to reading widely (a lot of book)
Skimming – Narrow information into one sentences or passage
Scanning – Reading intensively for specific information
Definition of teams
- Author – A person who write a book or storing
- Plot – The main sequence of events in a play, novel
- Theme – Subject of a taller, piece of writing
- Chapter – main division of a book
- Character – Particular nature of someone
- Setting – way of place in which something is setting
- Summary – A brief statement of the main point
- Comprehension- The ability to understand
- Publisher – A company or person that Publisher, book, News,
edu.uptymez.com
Paper, Journal
CLASS READER I. Who is the author?
The author is Richard S. Mabala
II. List of what you see in front
- Hawa the bus driver
- The bus
- Ubungo plaza (the weather building)
- 114 (the number route of the car)
- UDA (the name of a car)
- Isuzu (the name of the company of the car)
- T 140 ADS (the plate number of the car)
edu.uptymez.com
(h)Coconut tree
(i) Route of the bus K/Koo
- Mention the name of the publish. The publisher is Ben and company Ltd.
- Who is the main character of the whole book why? Hawa is the main character of the book because she is the one who the whole story is taking about her being a bus driver.
- Names of the character
- Selemani
- Hawa
- Mzee Athumani
- Saada
- Hassani
edu.uptymez.com
Hawa the bus driver
CHAPTER I
HAWA’S DESCRIPTION
- Famous in Dar es salaam
- Very strong woman, tall, tough
- Weight 82kgs
- Bus driver
- The lioness
edu.uptymez.com
SELEMANI
- Husband of Hawa
- Worker at Urafiki Texttile Mill
- A medicine operator
- Tall, strong
- Smilling, cool
edu.uptymez.com
CHAPTER II, HAWA’S DAY
- Hawa lives in Manzese, suburb of Dar es Salaam.
- Two children Hassan and Sauda
- Primary school teacher George
- A nurse Chausiku, best friend of Hawa
edu.uptymez.com
CHAPTER III HAWA AND THE DRUNKED
- Hawa focus trouble from a drunkard
- The conductor, Meshack co-operates with passengers to help Hawa comfort the drunkard – The drunkard is taken to police station.
edu.uptymez.com
CHAPTER IV HAWA AND THE THIEVES
- During the night shift, A man with a pistol pointed at Hawa
- Hawa hijacked and ordered to drive to Mbezi
- Made attack with a passenger who was in a blue overall
- Hawa stopped the bus abruptly
- The thief was overcome by grabbing the pistol
- The passengers helped
- The thief was taken to the police station
- Hawa becomes the Heroine with mind that arms are like baobab trees.
edu.uptymez.com
CHAPTER V
Accidents are common in Dar es salaam due to drivers negligence, driving to fast disobey traffic lights, ignore other cars
Changu ni changu chota chako kwingine
Bus coach hit a primary school boy
- Hawa takes troubles to take him to hosp[ital
- Passengers are angry as well as police officers her hart is as sweet as ripe mango
edu.uptymez.com
CHAPTER VI SELEMAN IS JEALOUS
- Seleman is jealous because his wife is more famous
edu.uptymez.com
Hawa the great
- Some of Selemani’s friends advised him that it is wrong for a wife to be famous and bad to drive a bus
- Selemani orders his wife a stop driving and stay at home.
- Unwilling Hawa decides to resign
- Before submitting a resignation letter her fellow drivers advice her not to do so until they take with her husband
- After a long discussion selemani changes his mind and allow Hawa to drive after seeking his opinion to.
- Hawa and Seleman, continued to live happy together.
edu.uptymez.com
Lesson or significance or importance
Generally, Hawa the bus driver is still relevant in society.
- Heroine drivers
- Role of women to prepare breakfast/ meal for the family
- Mockery against women who exceed in society above men has no place anymore.
- Hijackers of business and planes
- Accidents in urban areas/ cities and highways
- Healous of husband who do not like to hear their wife.
edu.uptymez.com
Structure Articles a, an, the, are called articles
A: uses of article “a and an” (Indefinite Articles)
- “a” is used for countable singular Nouns
edu.uptymez.com
Example: a book, a boy
“an” is also used for countable singular Nouns but those which start with a pronunciation of a vowel a, e, I, o, u etc.
Example: an elephant, an egg
But we can also say an honest man because although the word honest start with “h” yet “h” is not pronounced. In pronunciation the word starts with a vowel “O” /Onist/
- a/an are used to refer to things which are not clear to us (indefinite)
edu.uptymez.com
Example
- A national party (which one?)
- A man is outside (who?)
edu.uptymez.com
(i) a/an are used to introduce something or a person for the first time.
Example:
I bought a radio.
The radio was stolen after two weeks
(ii) an/a are used with illness
Example
I have a cold/ a headache
I have a stomachache
Note: we don’t use articles with plurals
Example: measles, mumps
We also don’t use articles with: blood pressure, flu, gout or hepatitis
You cannot say
I have a blood pressure but you can say
I have blood pressure
(iii) an/a are used when describing someone‘s nationality.
Example:
She is an American
He is an African She is a Tanzanian
Note:
Do not put a if the Noun is plural
Example: I saw a boys (No!)
But: I saw boys (Yes)
Exercise
Put in the space below article a or an or put a dash (-) if no article is needed
- I can repair __________ car
- I can write__________ letters
- I can eat______________ onion
- Use_______ ruler to draw ___________lines
- I am ________Tanzania
edu.uptymez.com
DEFINITE ARTICLE “The”
Uses of “the” is used with the following things:
- Organizations
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. the OAU, the UNO
- ships
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. The M.V Express
- before certain expressions of time
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. – in the afternoon
– on the previous day
- On public bodies
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. the police, the RTD
- HISTORICAL EVENTS:
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. The Arusha declaration The majimaji war (vi)Political parties
e.g. The UMD party
The NPP
- The press
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. The Daily News
- River
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. The Ganges, The Nile
(ix)Before musical instruments e.g. He plays the guitar
(x) Mountains e.g. The Alps The Kilimanjaro (xi)Ocean
e.g. The Atlantic
- Things mentioned for the second time
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. I bought a shirt and an umbrella, The shirt is now old
- Used before the name of a country which consist of an Adjective!
edu.uptymez.com
Example:
The United Kingdom
The Soviet Union
The United Arab
But not;
The West German
The Great Britain
The New Zealand
- Things which are unique (the only one) e.g. The stars,
edu.uptymez.com
The moon,
The God,
The Angles,
The Kilimanjaro hotel,
The Hilton
(xv)Used before superlative e.g. The biggest boy The most beautiful girl
(xvi) The only thing found in the house e.g. The wall
The window
The roof
The kitchen The floor
Note: Do not use articles
- In front of uncountable Nouns
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. I like butter
- With languages
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. English is a world language
- In front proper Nouns
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. Mwamsiku is our Headmaster
INTERPRETING POEMS
POETRY
Definition: is an art which uses imaginative language in a pattern of lines and sounds to express deep thought, feeling or human experience.
However there are different definitions of the term poetry depending on the author, we can generally define poetry as the art of composing or writing poems.
Note: poems are meant for singing
Structure of poetry
- What is a poem?
edu.uptymez.com
It is a piece of writing arranged in patterns of lines and sounds.
- What is poet?It is an artist of writer who composes poems
edu.uptymez.com
- What is stanza?It is a group of lines divisions in a poem
edu.uptymez.com
- What is a verse?
edu.uptymez.com
It is a single line in a poem
- What is simile?
edu.uptymez.com
It is a way of comparing things using words like……………as…………or like……………………….
- What is metaphor?
edu.uptymez.com
It is a way of comparing things without words of comparison
- What is imaginary?
edu.uptymez.com
It is an art of drawing word picture by comparing the reality of what is talked about to different but relevant aspect of reality.
- What is rhyme?
edu.uptymez.com
Words with some sound at the end of the verse e.g. fly, tie, pie.
- What is alliteration?
edu.uptymez.com
Words with some sound at the beginning of words in verse reinforce the meaning.
Example: pixpox , pax pox etc.
1. What is reiteration?
It is repetition of a word, a verse or even a stanza for a particular effect
e.g. You are dead and dead and dead indeed
POETRY ANALYSIS
- Content – What the poem is about or what to describes
- Themes/ Message – Lessons we learn from the poem or novels message
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. ignorance, exploitation, friendship
3. Form – how the poem is arranged (stanza and verses) 4. Mood – attitude of the poet
e.g. happiness, anger, seriousness, etc.
5. Symbolism – using a person or object /animals as if they re people
Example:
EAT MORE GRASS (JOE CORRIE)
“Eat more grass” the slogan says more fish, more beef, more bread but I’m on unemploymentpay my third year now and weed.
Read the following poem very fast
Katai is a Masai
Katai can tie and untie a tie If katai can tie and untie a tie
Why can’t I tie a tie?
Like katai, cantie
And untie a tie?
Questions
- Which tribe is katai?……………………..
- What can katai do?……………………….
edu.uptymez.com
Structure
BETWEEN/AMONG
Between – is used with two things
Among – is used with more than two things
Examples:
- Kibile is standing between two girls
- Riwa Kariwa is standing among four girls
- The car is between two buses
- Ruth is among ten girls who failed the exams.
edu.uptymez.com

ANALYSING INFORMATION FROM THE MEDIA
Use of Factual information (F.I) and Non Factual information (N.F.I)
Example
- HIV/AIDS is mainly transmitted through sexual inter course F.I
- Violence against women increase their discipline (N.F.I)
- The sun doesn’t move (F.I)
- (2×3) – 5 (4-1) = -9 (N.F.I)
- Nairobi is the capital city of Kenya (F.I)
edu.uptymez.com
A WORLD OF COMPUTERS
– Do you know what a compute is?
Have you ever seen a computer
A computer is a machinery which uses electricity or batteries to do many things.
I. What can a computer do?
- Can write letter
- Can draw picture
- Can show diseases
- Can play games
- Can do calculations
- Can teach lessons
- Can count money
- A computer store many names.
edu.uptymez.com
II. Where do we find computers?
We can find computers
- At home
- In office
- At air port – In hospitals at school
- In internet cafes.
edu.uptymez.com
(Show the picture of the computer and its parts)
- Parts of the computer
edu.uptymez.com
A computer has five main parts
1. Central processing Unit (CPU)
- This is the brain of a computer. The CPU think and keeps record
edu.uptymez.com
- Display (Monitor)
edu.uptymez.com
- This is where you can see all the information it is like the screen of a T.V.
edu.uptymez.com
- Key board
edu.uptymez.com
- This is where you type things. It is just like a typewriter
edu.uptymez.com
- Mouse
edu.uptymez.com
- This point to the screen showing what you want to do
edu.uptymez.com
- Printer
edu.uptymez.com
- This prints (writes) things like the words you are reading in this book
edu.uptymez.com
Questions
1. Mention three things you think a computer cannot do
(i) ……………………… (ii) ………………………
(iii) ………………………
Question
Complete the computer words in the table below
Complete the crossword puzzle below 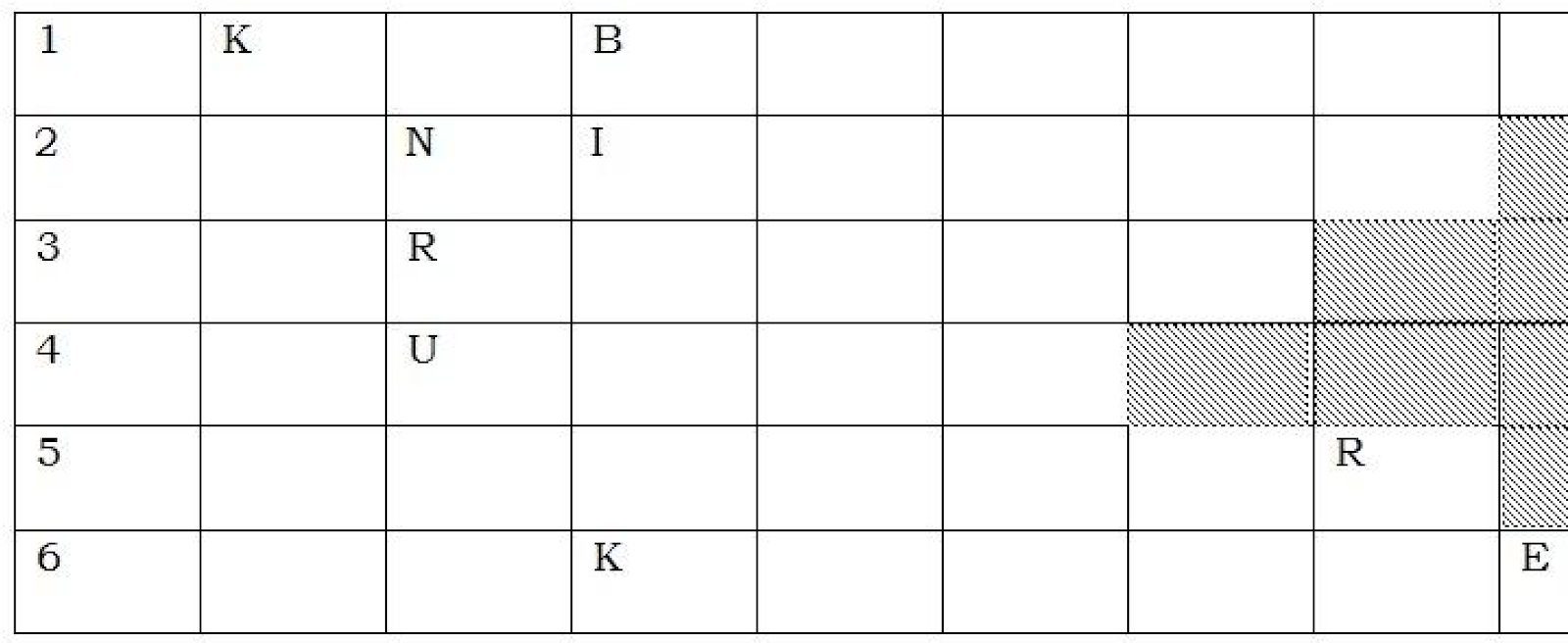
A cross
- What are get a school
- The past tens of lose
- What do we do at the door when we ask to get in?
- a type of greetings
- The short form of United Nation Organization
- What does a watch tell?
- A type of colour
- One of the countries in Africa
- A country whose capital is Khartoum
edu.uptymez.com
Down
- The biggest animal in Tanzania
- The past tense of take
- What we put in vegetables
- What we put in the pen
- How we pronounce “sick”
- The past tense of sit
- A short form of mistress
- It gives us light and heat.
edu.uptymez.com

WRITING PERSONAL LETTER
Friendly letters
Use to express your thought and feelings to get something done both the content and the form of a letter say something for you and about you.
The content is what you write in a letter, form is how it look There are two main kinds of letter o Personal /friendly letter and o Business/ official letters
Personal /friendly letters must have the following.
- The letter must have a date
- An address of whom you send the letter is unimportant.
- We start the letters with, Dear mother, Dear father, Dear friend, Hello Jack, Hi Marry ect 4. You can start the letter the way you feel No rules!
- You can put in the letter as many topics as you wish
- You can more from one topic to the other.
- You can make jokes, write funny things, ask questions, give short stories.
- The ending can be; bye bye, please write, take care, your love, lots of love, your friend
edu.uptymez.com
SAMPLE LETTER
AZANIA SEC SCHOOL
P. O. BOX 9074
DAR ES SALAAM
12TH FEB,2015
Dear Queen,
Many thanks for your letter. You certainly deserved, this result as I know you walked very hard.
I have been waiting so eagerly for the results of the examinations I did too. I must admit that I have not done half the things I planned to do during this holiday.
However, I have been doing a lot of revision. I have read two books of Geography and novels.
I will certainly let you know my examination result as soon as possible
Your sincerely/love
EXERCISE
Rearrange the Sentence and write the letter correctly
- But I’m now fit
- Will you go home during holidays
- Our school closest next month
- Hallow Upendo
- Your friend
- I hope your enjoy lessons (vii) When are you closing school?
- Please write to me soon
- I had Maralia
- How is school
- Jackline
edu.uptymez.com

LISTENING SKILLS AND NOTE TAKING
TAKING NOTES
Hearing is the natural ability of receiving sound waves/message
This is normally involuntary e.g. Noise
Sometimes we hear even if we don’t want to since we care not deaf
Listening is conscious or international attempt to hoar to receive the message deliberately listening involves some skills which can be taught and learn e.g. to get knowledge to carry out Instructions or write notes
LISTENING STRATEGIES
-It involves physical and mental alert/awareness
This brings you mind back when your mind can never concentrate
Sit in a manner that you will see the speaker
-Have desire to listen
This is a person paying attention on what the speaker is talking about tell the mind that you want to concentrate
-Develop willingness
Be ready to receive new information do not ask too much when you are listening
Give a speaker time to speak so as to avoid misinterpretation
-Postponed judgments
Don’t judge a speaker based on the appearance, dress, language, reputation or speaking style concentrate on what he/she is talking
-Observe
Careful look at the speaker to identity the corbels dues which will help you to identity important point emphasized force
Focus on speakers points view
Understand and listen what speaker believes in e.g. Empathy sympathy or tolerant. Predict and ask questions keep you after all the time and ask questions and predict speaker’s next words In cooperation of some stories that are relevant.
LOOK AS IF YOUR ARE LISTENING
Sit straight uncross your legs
AVOID BARRIERS/DESTRUCTION
Don’t sit with a person who is talkative. Temperature should be hot or too cold. There should not be too much noise
NOTE TAKING
A good listener is a good note taker.
STRATEGIES ON NOTES TAKING
Be brief
Speaker speaks many things at a time so one cannot be equivalent observe speakers facial and gestures expression, Write only enough to represent the idea,
Use abbreviation and symbols
≥ Greater than
≤ Less than
No. Number
? Important point
+ Positive
- Negative
edu.uptymez.com
Use point form when writing points

Paying attention to signal words
These are words which show various points they are useful squad you to take your notes properly.
- They show contrast e.g. But, however otherwise, yet, despite, in spite, of, although, still, even though, never the less.
- They show results hence, thus, therefore
- To show additional – Again, another, more even, furthermore, also, too
- To summarize – conclude, finally, in short, to sum up, to conclude in brief.
- To give / show example – for example, for instance
- To show condition – if, unless, when
- To show similar – equally, as, like, seems, resemble
- To show amount – many, most, several and few
- To show strength – intensively, exactly, indeed, totally, extremely.
- To show – basically, without, doubt,
- To show place – beside, near, adjacent, opposite, over, below, beyond, across.
edu.uptymez.com

WRITING A VARIETY OF TEXTS
WRITING TEXTS
AT THE BANK COUNTER
DEPOSITION MONEY
Now imaging that you are at the bank counter and you want to keep your money there. This is called depositing.
In the bank you will be giving PAY-IN-SLIP you must fill in the form correctly.
The following are instruction and information, which will help you to fill in the form.
Write your name
Your bank brunch is Ubungo. Your account number is 002233445566. Write the date of today write your address. You have the following money
- Five notes of ten thousand each
- Seven notes of five thousand
- Thirty notes of two thousand each
edu.uptymez.com
At the bank
If you have a lot of money you must take it to the bank and keep it there.
Exercise:
What bad things may happen if you keep your money at home or in the dormitory?
i. The house may catch fire and the money will be burnt.
ii.
_______________________________________________
iii. iv.
At the bank counters Depositing money.
Now imagine that you are at the bank counter and you want to keep your money there. This is called depositing.
In the bank you will give pay-in-slip. You must fill in the form correctly.
The following are instructions and information, which will help you to fill the form.
Write your name.
Your bank branch is Ubungo. Your account number is 002233445566. Write the date of today. Write your address. You have the following money.
i. Five notes of ten thousand each. ii. Seven notes of five thousand each. iii. Thirty notes of two thousand each.
- Twenty eight notes of one thousand each.
- Nine notes of five hundred each.
- Eighteen coins of twenty shilling each. vii. Nine coins of one shilling each
edu.uptymez.com
Now fill in the pay-in-slip below:
Don’t forget to write the total amount you deposited in both numbers and words.
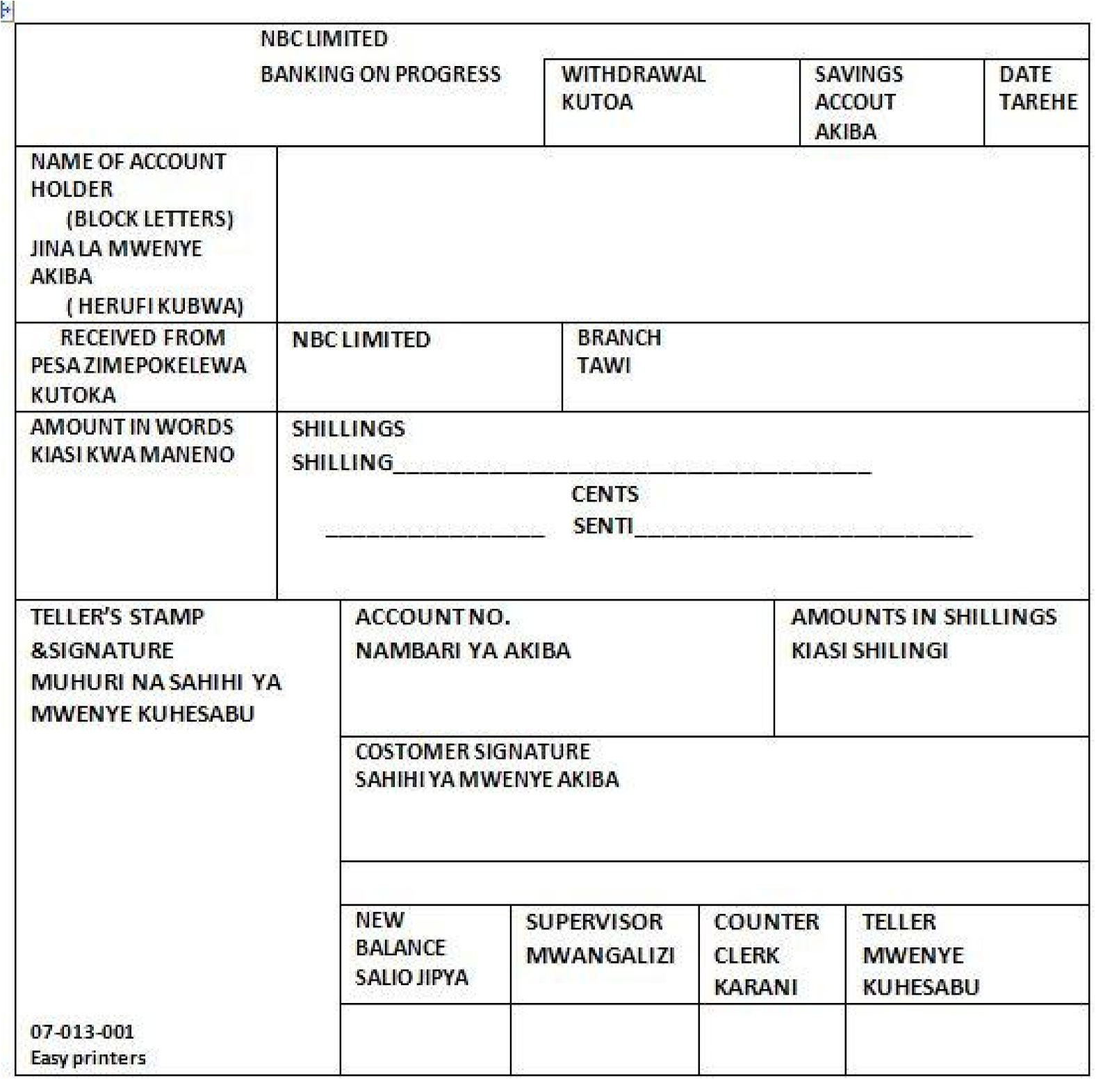
Withdrawal
Sometimes you have to go to the bank and take some of the money you deposited. This is called withdrawal.
You don’t have to take the whole amount of money you deposited. So you have to fill in the withdrawal form(voucher).
Now fill in the following form so as to withdraw 112,00/

Bank balance
It is very important to know how much money is left in your account in the bank. This is called bank balance.
Exercise
- Now fill the following slip so that you can know your balance
edu.uptymez.com

- I think you still remember how much you deposited and how much you withdrew. Now fill in the present balance.
edu.uptymez.com
A Diary
A diary is a book of records showing things which you may do in the future.
It also show things that you did today, previous days, weeks or months ago. In the diary you should only write important things. We use diaries so that we may not forget important events.
Exercise
The following is a page of diary
(i)fill in 5 important things you did yesterday in diary 1.
(ii) fill in important 5 things you will do tomorrow in diary 2.
(iii)prepare a month diary and fill in all the important things you will do in that month. Show it to your teacher .
Diary 1
