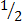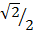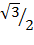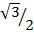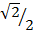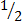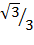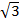Trigonometric ratio
Introduction: TRI – is the Greek word which means three.
-Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics which deals with measurement.
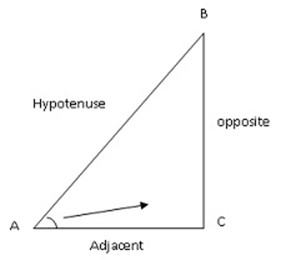
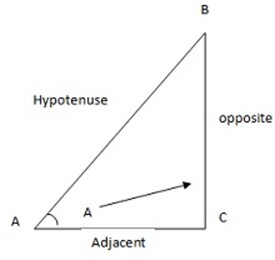
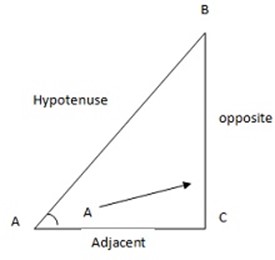
-A Trigonometric ratio consists of three parts that is – Hypotenuse, Adjacent and opposite.
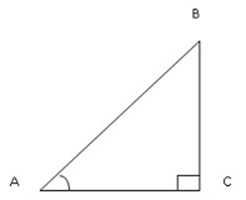
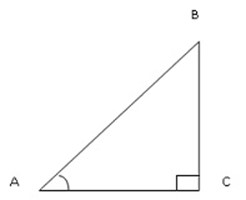
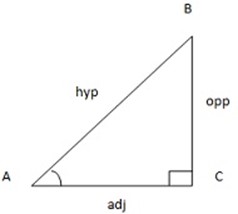
Consider the diagram below which is the right angled triangle
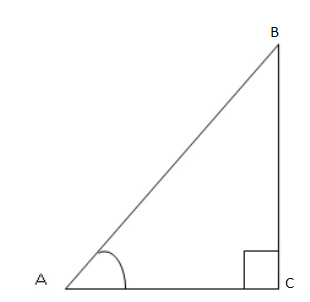
For example
Assume angle B
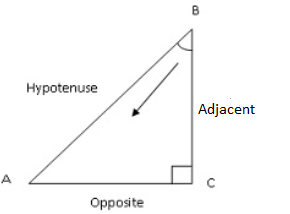
For trigonometrical ratios we have sine, cosine and tangents which used to find the length of any side and angles.
 Refer to the right angled triangle below:-
Refer to the right angled triangle below:-
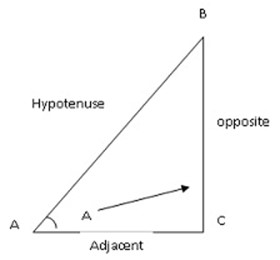
For sine(sin)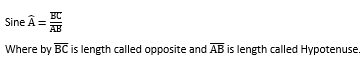
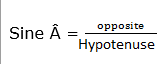
Sin  = 
For cosine (cos)
Consider the diagram


Cos  = 
For Tangents (tan)
Tan  =  where
where
AC is called Adjacent
BC is called Opposite
Tan  = 
In summary
|
SO |
TO |
CA |
|
H |
A |
H |
edu.uptymez.com
Where: S – sine, T – tan, C – cos, O –opposite, A – adjacent, H – opposite
Example 1.
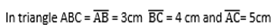
Find a) Sin Â
b) Cos  and (c) tan Â
Solution:

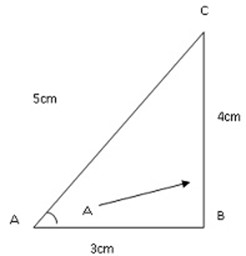
a) Sin  = 
Sin  = 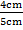
Sin  = 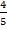
b) Cos  = 
Cos  = 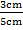
Cos  = 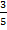
c) Tan  = 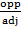
Tan  = 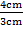
Tan  = 
Example 2
Find the value of sin Â, cos  and tan Â
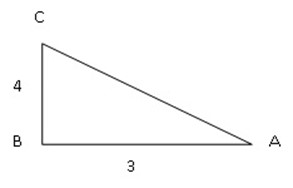
 Solution:
Solution:
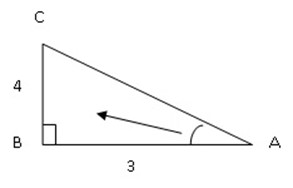
Where Opposite = 4, Adjacent = 3, Hypotenuse =?
Use Pythagoras theorem
a2 + b2 = c2
42 + 32 = c2
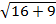 =
= 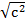
c = 5
Sin  = 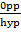 =
= 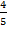
Cos  = 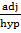 =
= 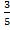
Tan  =  =
= 
Example 3
i) If the sin  = 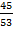 find the value of
find the value of
(a) Cos  , (b) Tan Â
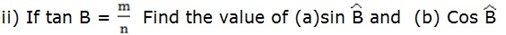
Solution:
given sin  = 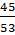 where sin  =
where sin  =
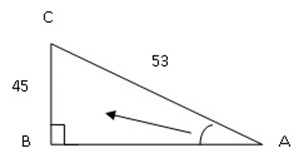
By using Pythagoras theorem
a2 + b2 = c2
(45)2 + b2 = (53)2
2025 + b2 = 2809
b2 = 2809 – 2055
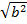 =
= 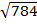
b = 28
a) Cos  = 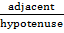 =
= 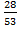
b) Tan  = 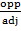 =
= 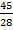
Solution:

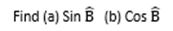
from Pythagoras theorem
a2 + b2 = c2
m2 + n2 = c2
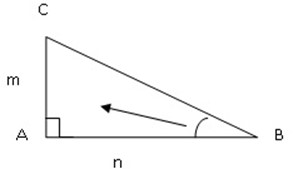
(m + n)2 – 2mn = c2
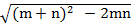 =
= 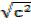
c = 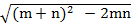
a. Sin B= 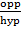 =
= 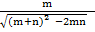
b. Cos  = 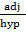 =
= 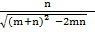
Example 4
If cos y = 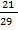 Find (a) sin y (b)tan y
Find (a) sin y (b)tan y
Solution:
Given that Cos y = 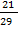
But cos y = 
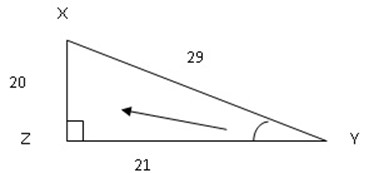
a2 + b2 = c2
a2 + (21)2 = (29)2
a2 + 441 = 841
a2 = 841 – 441
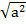 =
= 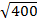
a = 20
a. Sin y = 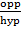 =
= 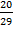
b. Tan y = 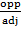 =
= 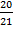
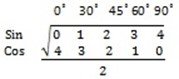
Special angles
The trigonometrical ratios has the special angles which are 0°, 30°,45°, 60°, and 90°.The special angles does not need table or calculator to find their ratios.
To prove the value of trigonometric ratio for special angles
 Consider the diagram below
Consider the diagram below
Note:
when the point B move toward the point c the angle of A = 0° and the length of AB = AC and BC = 0
Sin 0° = 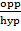
Sin = 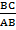
Sin 0° = 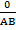
Sin 0°= 0
Tan 0°= 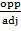
Tan 0° = 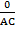
Tan 0°= 0
Cos 0° = 
Cos 0° = 
But AC = AB
Cos 0°= 1
 Consider the diagram
Consider the diagram
If the point A moves towards point C the difference from A to C becomes zero. The angle between A and C become 90°
Sin 90° = 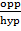 but opp = hyp
but opp = hyp
Sin 90° = 1
Cos 90° = 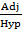
Cos 90° = 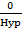
Cos 90° = 0
Tan 90° = 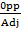
Tan 90° = 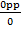
Tan 90° = 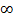 (undefined)
(undefined)
Example
 Find sin 45°, cos 45, and Tan 45° consider a right angled triangle ABC with 1 unit in length
Find sin 45°, cos 45, and Tan 45° consider a right angled triangle ABC with 1 unit in length
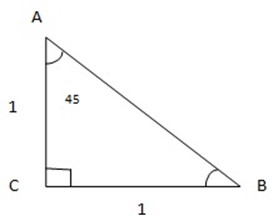
The length Of AC = CB = 1 unit But use Pythagoras theorem to find the length AB.
From Pythagoras theorem
a2 + b2 = c2
12 + 12 = c2
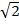 =
= 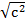
c=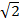
Sin 45 ° = 
Sin 45° = 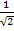
Rationalize the denominator
Sine 45° = 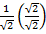
= 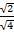 =
= 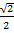
Cos 45° = 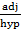
Cos 45° = 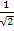
Cos 45° = 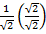
= 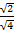 =
= 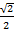
Tan 45° = 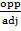
Tan 45° = 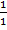
Tan 45°= 1
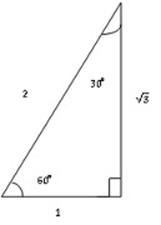
Find Sin, Cos and Tan of (30° and 60Ëš)
Consider the equilateral triangle ΔABC

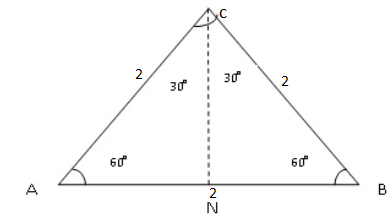
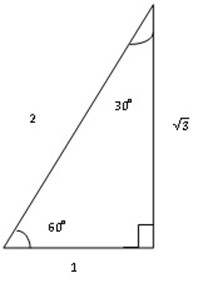
Use Pythagoras theorem
a2 + b2 = c2
12 + b2 = 22
b2 = 22 – 12
b2 = 4 – 1
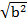 =
= 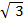
b = 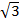

Sin 60 = 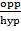
Sin 60° = 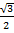
Sin 60° = 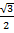
Cos 60 = 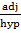
Cos 60° = 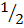 or 0.5
or 0.5
Cos 60° = 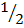 or 0.5
or 0.5
Tan 60° = 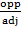
Tan 60° = 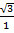
Tan 60° = 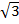
Sin 30° = 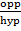
Sin 30° = 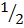 or 0.5
or 0.5
Tan 30° = 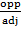
Tan 30°= 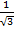
= 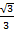
Tan 30° = 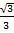
Cos 30° = 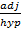
Cos 30° = 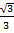
In summary:
Sin 0 = 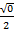
Sin 0 = 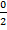
Sin 0 = 0
Example 1.
Find the value of 4 sin 45° + 2 tan 60 without using table
Solution:
4 sin 45° + 2 Tan 60°
= 4 (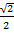 ) + 2
) + 2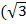 )
)
= 2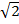 + 2
+ 2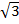
Note:
Trigonometry: Is the branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of angles and sides of right angled triangle
TRIGONOMETRICAL RATIONS FOR SPECIAL ANGLES
Trigonometrical rations for special angles deal with 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°.
|
A |
0° |
30° |
45° |
60° |
90° |
|
Sin A |
0 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
Cos A |
1 |
|
|
|
0 |
|
Tan A |
0 |
|
1 |
|
|
edu.uptymez.com
Example 1.
Without using mathematical table evaluate
(i) 4 sin 45° + cos 30°
(ii) 4 tan 60° – Sin 90°
Solution:
i) 4 sin 45° + Cos 30°
= 4 x 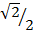 +
+ 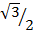
=2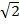 +
+ 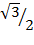
=4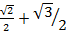
(ii) 4 tan 60° – sin 90
Solution:
4 tan 60° – sin 90 = 4
= 4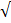 3 – 1
3 – 1
(iii) 3(cos60° + Tan 60°)
Solution:
= 3(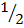 +
+ 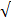 3)
3)
= 3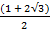
= 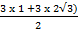
= 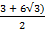
Example 2
Find the value of 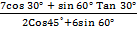 without using mathematical table
without using mathematical table
Solution:
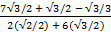
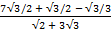
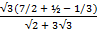
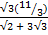
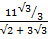
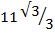
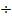
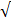 2 + 3
2 + 3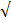 3
3
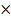
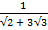
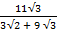
EXERCISE
1. Evaluate the following without using mathematical table
(a). 3 sin 45° + 7tan 30°
(b). 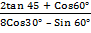
Solution:
3sin 45° + 7tan 30°
= 3 x 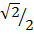 + 7 x
+ 7 x 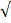 3
3
= 3 x 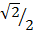 + 7 x
+ 7 x 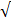 3
3
= 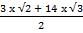
TRIGONOMETRIC TABLES
– Trigonometric tables deals with readings of the value of angles of sine, cosine and tangent from mathematical table when they are already prepared into four decimal
HOW TO READ THE VALUE OF TRIGONOMETRIC ANGLES FROM MATHEMATICAL TABLES
Example 1
Find the value of the following by using mathematical table
(i) Sin 43°= 0.6820
(ii) Sin 58º = 0.8480
(iii) Sin 24°42′ = 0.4179
(iv) Sin 52°26′ = 0.7923 + 4 = 0.7927
Example 2
By using mathematical tables evaluate the following
(a)Cos 37° =0.7986
(b)Cos82° =0.1392
(c)Cos 71°34′ =0.3162
(d)Tan 20° = 0.3640
(e)Tan 68° =2.4751
(f)Tan 54°22′ = 1.3950
Example3.
Find the value of the following letter from trigonometric rations
(i) Sin p = 0.6820
Sin p = 0.6820
P = Sin-1 (0.6820)
P = 43°
ii) Sin Q = 0.7291
Q = Sin-1 (0.7291)
Q = 46°48′
iii) Tan R = 5.42°45
R = 5. 42°45
R = tan-1 (5.42°45)
R = 79°33
APPLICATION OF SINE, COSINE AND TANGENT RATIOS IN SOLVING A TRIANGLE
Sine, cosine and triangle of angles are used to solve the length of unknown sides of triangles
Example

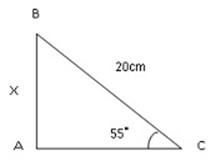
From
|
SO |
TO |
CA |
|
H |
A |
H |
edu.uptymez.com
Sine C = 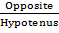
Sin 55Ëš= 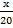
20 x Sin 55Ëš= x
20 x 0.8198 = x
x = 16.4 cm
The value of x = 16.4cm
Example 2
Find the length XY in a XYZ
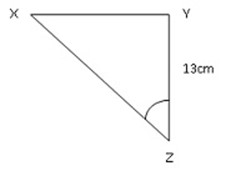
Solution:
From
|
SO |
TO |
CA |
|
H |
A |
H |
edu.uptymez.com
tan 62Ëš = 
tan 62° = 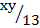
13 x tan 62° = xy
13 x 1.8807 = xy
24.4cm = xy
xy = 24.4cm
Example
Evaluate the value of m and give your answer into 3 decimal places
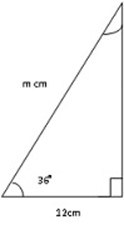
From
|
SO |
TO |
CA |
|
H |
A |
H |
edu.uptymez.com
Cos R =
Cos 36° = 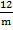
m = 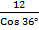
m = 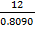
m = 14.833 cm
The value of m is 14.833 cm
EXERCISE

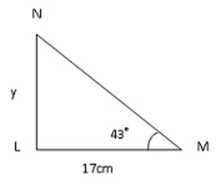
Solution:
From
|
SO |
TO |
CA |
|
H |
A |
H |
edu.uptymez.com
tan 43° = 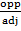
tan 43°=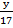
17 x tan 43° = y
y = 17 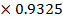
y =15.85cm