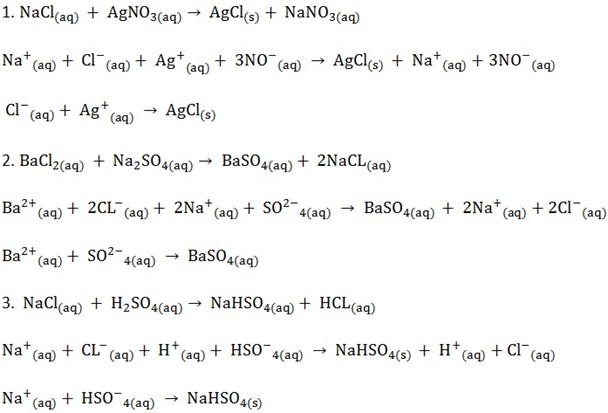A chemical equation is a short way of describing exactly what happens during a chemical reaction.
Chemical equations must;
1. Tell the truth or represent the facts
2. Show symbols of elements and formula of products and reactants
3. Be balanced
4. Bear state symbols (s), (l), (g) and (aq) for substances dissolved in water (aqueous – water).
A state symbols s, l, g and aq that appear in chemical equation described as;-
s – Solid state of chemical component.
l – Liquid state of chemical component.
g – gaseous state of chemical component.
aq – a dissolved chemical component in water.
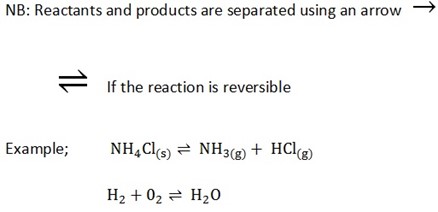
BALANCING OF CHEMICAL EQUATION
Balancing of the chemical equations is done so as to obey the law of conversation of matter which states;
“Matter can never be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction “.
When balancing the chemical equation, we change the coefficient only.
Examples;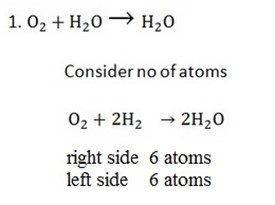
The coefficient of chemical symbol describe single molecule of component. A component of single molecule, its coefficient does not written on chemical symbol and considered as single molecule e.g O2 in the equation above. And all unit multiple coefficients are written on chemical symbol e.g 2H2 in equation above.
– When balancing don’t consider anything which is above or below the line
– When balancing statement or equations like this find the 1 cm of the two numbers 2, 3 to get 6
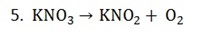
– If oxygen is alone then reduce the oxygen atoms
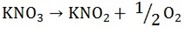
– Eliminate denominator by multiplying 2 throughout
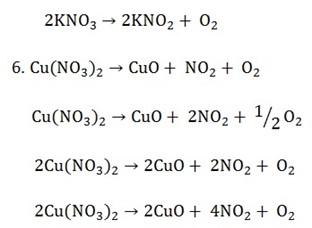

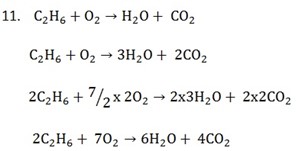
Types of chemical reactions include,
1. Decomposition reactions.
Decomposition reaction is that reaction, where by a giant molecules of chemical component break-up into simple molecules. Decomposition can be influenced by heating or catalysis.
Examples; By heating
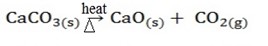
By catalyst
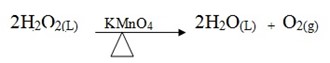
There are two types of decomposition by heating.
i) Thermal decomposition.
Is the type of decomposition reactions which are irreversible.
Example;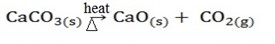
NOTE;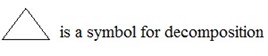
(ii) Thermal dissociation
Is a type of decomposition reaction which are reversible.
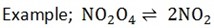
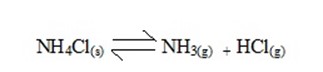
2. Synthesis (combination) reactions
Simpler compounds combine to form one compound (opposite of decomposition)
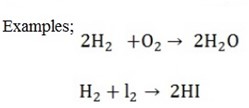
3.
Displacement reactions
In these reactions one element displaces another element from a compound
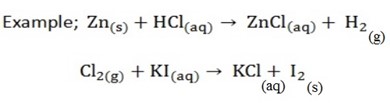
4. Double decomposition reactions
The compound exchange their radicals
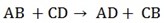
B and D are only to be interchanged. The reactants are always aqueous
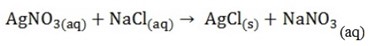
The reactant must be soluble in water and one of the product must be either solid or a gas or liquid
5. Neutralization.
This is the type of reaction which involves acid and base which react to produce salt and water only. All metal oxide is basic in nature.
Base + Water = Alkali. Not all bases are alkalis but all alkalis are bases because not all bases form alkalis.
Examples,
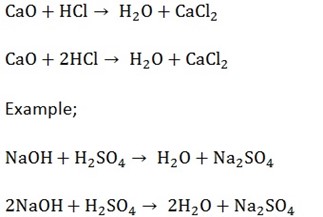
Question;
Complete and balance;
Classify the following chemical reactions;

Writing a balanced chemical equation for the following:

IONIC EQUATIONS
These are reactions equations written by omitting the spectator ions (ions remaining even after the reaction.
STEPS OF WRITING IONIC EQUATION
1. Balance the equation;

2. Split all solid and soluble ionic compound on the reactants side and only the soluble ionic compounds on the product side into individual ions
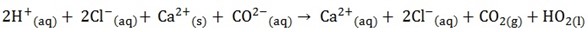
3. Omit the ions found on both side of the equation
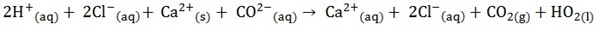
4. Write the equation for remaining species (ionic equation)
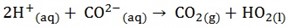
QUESTION;