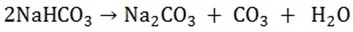A. METAL OXIDE
An oxide is a compound of oxygen with another element.
Preparation of oxides:
There are two ways of preparing metal oxides
a) DIRECT METHOD
It involves direct combination of metal with oxygen
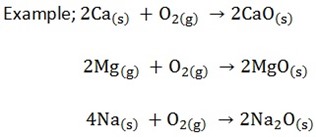
- INDIRECT METHOD
edu.uptymez.com
It involves thermal decomposition of a salt of carbonate, hydroxide (I) nitrates
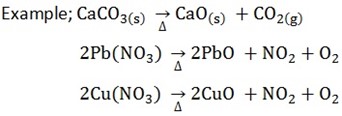
CLASSIFICATION OF METAL OXIDES
1. BASIC OXIDES
Are oxides of metal when reacts with acid forms salts
Examples are MgO, CaO, Na2O, K2O
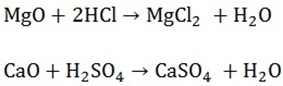
2. ACIDIC OXIDES
Are oxides of non metals and when dissolved in water form solution
Examples are CO2, NO2, SO2
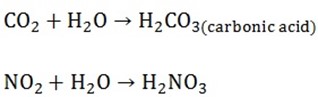
3. AMPHOTERIC OXIDES
These are oxides which have both basic and acidic properties
(H neutralize both acidic and Alkali to form salt)
Examples are ZnO, Al2O3 and PbO
4. NEUTRAL OXIDES
Are oxides which do not react with either acid or base (Have no basic/acidic properties)
Examples are H2O, CO, NO, N2Cl
5. PEROXIDES
When elements burn in excess air, peroxides are formed
Examples are N2O2, H2O2
6. MIXED OXIDES
These are oxides of two simple oxides
Examples are Fe3O4 – Tri iron tetra oxide
(Mixture of Fe O and Fe2O3)
SOLUBILITY.

USES OF OXIDES
I. Used in preparation of salts in the laboratory
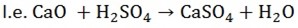
II. Used in formation of slag
III. Used as a drying agent
IV. Used in manufacture of motors
V. Oxides react with acid to form salt and water
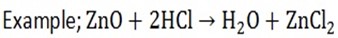
The following are the reaction equations when the following oxides react with hydroxides
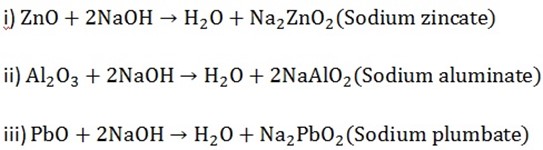
B. METAL HYDROXIDE
Very active metals (K, Na and Ca) dissolves in water forming hydroxide soluble oxides dissolves in water to form hydroxide (Alkali)
Soluble oxides dissolve in water to form hydroxide (alkali)
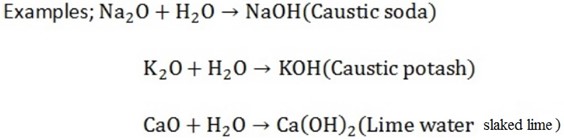
Caustic soda and caustic potash are used in the manufacture of SOAP.
Lime water is used to detect CO2 gas. The rest of the hydroxides are insoluble.
PREPARATION OF INSOLUBLE HYDROXIDES
i) Dissolve a soluble salt in water i.e. CU(N03)2
ii) Dissolve a soluble hydroxide in water i.e. Ca(OH)2
iii) Mix them together
Cu(NO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 → Cu(OH)2 + Ca(NO3)2
iv) Separate the two by filtration.
NB: The filtrate is Ca(NO3)2 and the residue is Cu(OH)2
PROPERTIES OF HYDROXIDE
i) Have bitter taste
ii) Neutralize acids to form salt and water
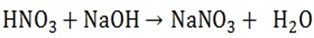
Solubility of hydroxide in water
- The nature of hydroxide of metals varies according to position of the metal in the reactivity series.
edu.uptymez.com

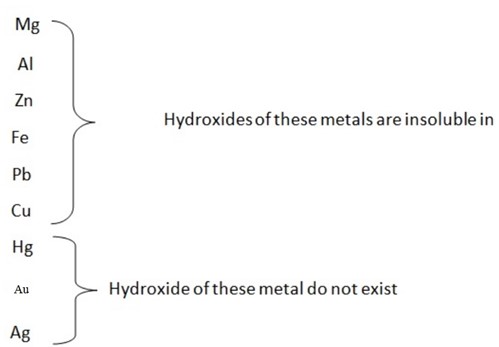
The hydroxide of sodium, calcium and potassium are the strongest because they dissociate completely in water
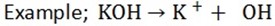
Ammonium hydroxide is weak base because it does not dissociate completely in water
Question:
By using diagram and details explain/ show how you would prepare
i) Zinc hydroxide
ii) Magnesium hydroxide
Solution:
i) Zinc hydroxide (Zn(OH)2)
– Dissolve soluble salt in water (Zn(N03)2).
– Dissolve soluble hydroxide in water (NaOH).
– Mix them together.
Zn(NO3)2 + 2NaOH  Zn(OH)2(s) + NaNO3(aq)
Zn(OH)2(s) + NaNO3(aq)
Separate by filtration
CARBONATE AND HYDROGEN CARBONATE
- Carbonates occur in many natural forms examples are chalk, limestone and marbles. Examples of carbonates that occur naturally are the carbonates of Zinc, iron, lead and Manganese.
- Sea animals have carbonates in their shells in the forms of calcium carbonates. The remains of these animals sink to the bottom of sea leading to chalk formation after thousands of years, through pressure the chalk hardens to form limestone
edu.uptymez.com
General properties of carbonates:
1. All carbonates are insoluble in water except those of sodium, potassium and ammonium.
2. All carbonates give carbon dioxide on heating except those of sodium and potassium
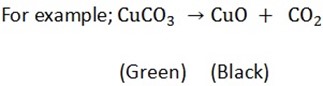
3. All carbonates give carbon dioxide with dilute acids
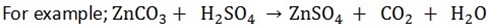
PREPARATION OF SODIUM/ POTASSIUM CARBONATES AND SODIUM/ POTASSIUM HYDROGEN CARBONATES:
a) A solution of sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) is saturated with carbon dioxide, giving a solution of sodium bicarbonates
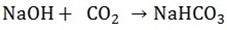
If a solution of potassium hydroxide (caustic potash) is saturated with carbon dioxide, a solution of potassium bicarbonate is formed
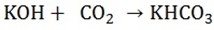
a) This solution is divided into two equal portions, one portion is allowed to evaporate at room temperature, when crystals of sodium hydrogen carbonate (sodium bicarbonate) or potassium hydrogen carbonate (potassium bicarbonate) are obtained which are be filtered and dried.
b) An equal volume of the original sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solution is added to the second portion. Sodium carbonate or potassium carbonate is formed
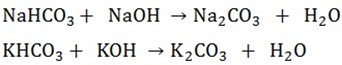
The solution is evaporated down and allowed to cool crystals of sodium carbonate is formed
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN SODIUM CARBONATE AND SODIUM BICARBONATE
(Na2CO3) (NaHCO3)
|
1 |
Have 2 crystalline forms Na2CO3.10H2O and Na2CO3 and anhydrous form sodium carbonate efflorescence. |
– Can only be made in the hydrous from sodium hydrogen carbonate does not efflorescence (NaHCO3) |
|
2 |
Is soluble in water |
Is much soluble in water |
|
3 |
Does not decompose on heating |
It decomposes on heating to form carbonate, carbon dioxide and water |
|
4 |
Is known as washing soda used in softening water and removing grease |
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used as a baking powder to make bread, rise CO2 given off causes the bread of cake to rise |
edu.uptymez.com
All carbonates and hydrogen carbonates react with acids to form carbon dioxide, water and salt.
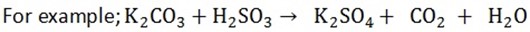
Dilute sulphuric acid react very little with calcium carbonate because the product calcium sulphate is insoluble, form a layer on the outside of the carbonates and stop further reaction.
Also dilute sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid react little with lead II Carbonate because the product, the lead sulphate and lead II Chloride are insoluble, they form layer on the outside of the carbonates which cause to stop further reaction
- Nitric acid react readily with all carbonates because all nitric are soluble.
edu.uptymez.com
TEST FOR CARBONATES AND HYDROGEN CARBONATE.
a) Add dilute nitric acid to a solution of a substance. Carbon dioxide gas is evolved, water and salts are formed.
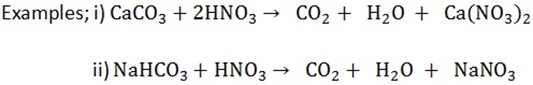
b) i) Add magnesium sulphate to a substance, if carbonates are present white precipitates are formed.
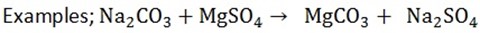
ii) If hydrogen carbonates are present no precipitates are formed
c) Action of heat
Potassium carbonate and sodium carbonate do not decompose when heated. Other carbonate decompose to form an oxide and carbon dioxide
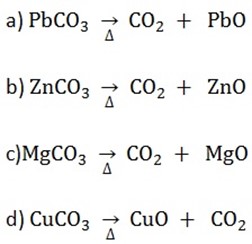
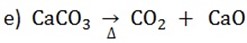
Preparation of sodium carbonate by SOLVARY PROCESS
1. Calcium carbonate is heated in a limekiln
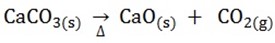
2. The calcium oxide is dissolved in water
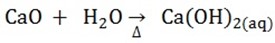
3. The carbon dioxide is reacted with ammonia brine
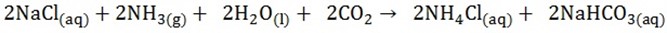
As the solution cools, sodium hydrogen carbonates the least soluble combination of ions, precipitates out and removed
4. The sodium hydrogen carbonate is heated
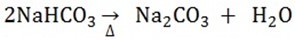
5. The Ammonium chloride and calcium hydroxide are reacted

NITRATES
Nitrates are important chemicals for industries purpose
Examples;
- potassium nitrate is used in gun powder
- Sodium nitrates occur in nature as salt petres
- Aluminium nitrate is useful in the manufacture of sulphuric acid as a fertilizer.
edu.uptymez.com
PREPARATION OF NITRATES
1. By neutralizing nitric acid with an alkali or base
2. by the action of nitric acid on a carbonate
3. by the action of metal on nitric acid copper
(Only for magnesium, zinc, lead and copper)
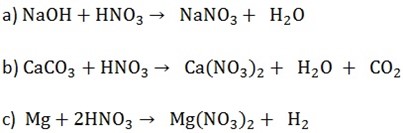
PREPARATION OF NITRATES
1. All nitrates are soluble and form crystalline solids
2. Action of heat on nitrates
a) Sodium and potassium nitrates give nitrites
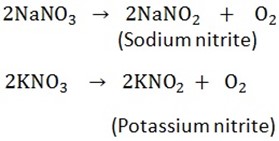
b) Many metal nitrates give the oxide
Example; i) Effect of heat on copper nitrate crystals when the blue crystals of copper nitrates are heated in a boiling tube they dissolve in their water of crystallization, prolonged heating gives brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide and the residue, copper oxide is a black.

ii) Effect of heat on lead nitric crystals
- When heated they decrepitate (expand with a crackling noise) and melt. Prolonged heating gives brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide and a yellow residue of lead monoxide (litharge)
edu.uptymez.com

c) Silver and mercury nitrates give the metal
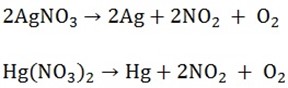
d) Ammonium nitrates give nitrous oxide
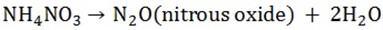
3. The action of concentrated sulphuric acid
– Concentrated sulphuric acid, heated with a nitrate liberates nitric acid
4. All nitrates except those of sodium and potassium are hydrated, sodium nitrate and calcium nitrates are deliquescent, and other nitrates are not.
Summary of chemical properties of Nitrates

TEST FOR NITRATES
1. Add concentrated sulphuric acid to the solid nitrate and warm Acid fumes (nitric acid) are involved. Add 3 – 4 copper turning and arm the mixture, the colour of the gas turns to deep brown.
2. The brown ring test is normally used to confirm the nitrates.
To a solution of nitrates are added a few drops of freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution.
A few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid are added carefully and brown ring obtained at the junction between the liquid.
It is nitrate ferrous sulphate (FeSO4NO) formed that
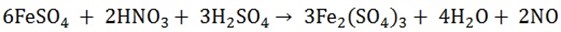
The nitrogen monoxide then reacts with more iron (II) sulphate to give the brown compound, which appears as a brown ring
USES OF NITRATES
1. Potassium nitrate is used as a food preservative; it is also used to make slow burning fuses.
2. Sodium nitrate is mainly used as a fertilizer
3. Ammonium nitrate is mixed with chalk, the mixture is known as NITROCHALK, widely used as fertilizer.
It is also used in manufacturing explosives.
4. Silver nitrate is used to make silver bromide and silver iodides chemicals used to make photographic film.
CHLORIDES
Chlorine can react with all metals to form chloride. Most common metals are attacked by dil. Hydrochloric acid to form chlorides
Example is Mg, Ca, Al, Zn, and Fe.
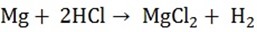
Those elements (metals) which are not attached by dilute carbonates or oxides of these metals react with dil.HCl hydrochloric acid to produce chloride
PREPARATION OF CHLORIDE
- Metallic chlorides can be prepared by direct or indirect or indirect methods.
edu.uptymez.com
1. BY DIRECT METHOD
– Chloride can be prepared by direct action of chlorine on metals
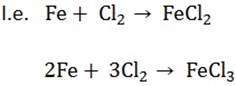
Iron (iii) chloride can be prepared by passing Cl2 over a heated metal.
An iron wire is placed in hand glass tube and a steam of dry Cl2 passes over it.
The reaction continues without further application of heat source and iron (iii) chlorides collect in a bottle as shown.
PREPARATION OF SOLUBLE CHLORIDE:
Soluble chlorides can be prepared by mixing dilute hydrochloric acid (Dil.HCL)
i) Oxides
ii) Hydroxides
iii) Carbonates
iv) Metals
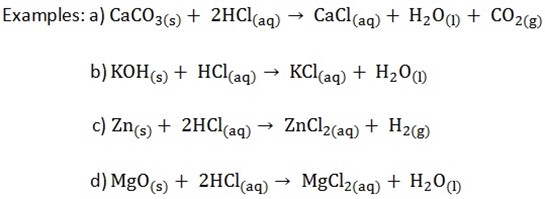
Methods for preparation of soluble chloride are summarized below
K prepared by action of the oxide, hydroxide or carbonate
Na dilute hydrochloric acid
Ca
Mg Prepared by Action of the metal, oxide or carbonate on
Al Dilute hydrochloric acid
Zn
Fe
NB: Lead and silver chloride are only common insoluble chlorides
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CHLORIDES
-
To identify a chlorine in a liquid mixture add nitrates or silver nitrate (A white precipitate formed)
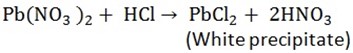
-
To identify a chloride from solid mixture, add concentrated sulphuric acid
The gas that produces thick white fumes with ammonium solution is produced
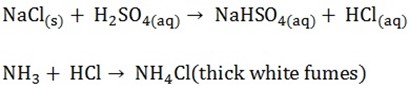
- Mix chloride with oxidizing agent (MnO2)
edu.uptymez.com
A green wish yellow gas is involved
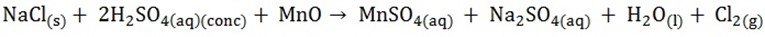
METAL SULPHATES
i) Preparation of soluble metal sulphates
Soluble sulphates can be prepared in the laboratory by dissolving a metal, a carbonate, a hydroxide or an oxide in dilute H2SO4
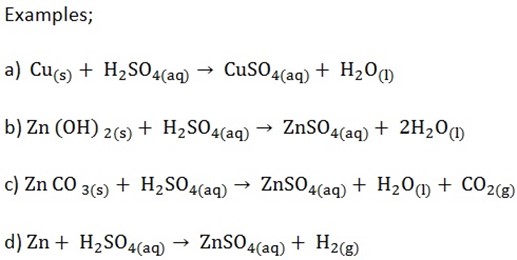
2. Preparation of insoluble sulphates
Insoluble sulphates can be prepared by adding dilute sulphuric acid to lead or barium ions
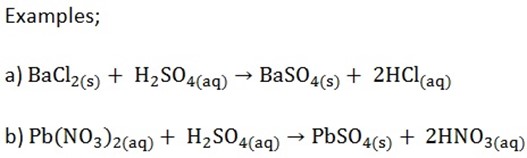
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
1. All sulphates react with barium chloride to give a white precipitate which is insoluble in dilute HCl
Note. Sulphites and carbonates give precipitate which is soluble in dilute HCl.
2. The sulphates or iron (II), copper (II) and zinc (called green, blue and white vitriol respectively) decompose when heated strongly to give the oxide of the metal, sulphur dioxide, sulphur trioxide and water
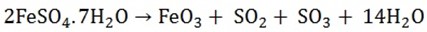
Note. In case of copper (II) and Zinc Sulphates, no sulphur dioxide is produced
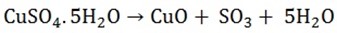
3. The sulphates of sodium, potassium, magnesium and calcium don’t decompose on heating
USES OF SULPHATES
1. Sodium sulphate
Is used to treat wood pulp in the manufacture of paper
2. Anhydrous (CaSO4) is used as a source of sulphur dioxide for the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
3. Ammonium sulphate is an important fertilizer
4. Aluminium sulphate
Is used in the purification of sewage as it precipitates proteins
5. CuSO4 (copper (II) sulphate) is used as fungicide i.e. destroyer of fungi on plants
Also it is used as an electrolyte for electroplating copper.