MATERIALS OF THE EARTH’S CRUST.
The earth’s crust is composed of different materials ranging from elements, minerals and rocks. These materials differ in their physical and chemical composition.
ELEMENTS
They refer to the smallest particles of matter which can not be split into different forms by any means. Examples of elements are magnesium, potassium, sodium, iron, aluminum and silicon.
MINERALS
They are naturally occurring substances which have definite shape, colour and resistance formed due to combination of different elements. They are formed as a result of the combination of two or more elements. Some single elements like gold, silver and diamond may occur as minerals.
|
Mineral |
Element |
|
Quartz |
Silicon and oxygen |
|
Feldspar |
Potassium, sodium, calcium and aluminum |
edu.uptymez.com
ROCK
A rock is an aggregate of minerals in a solid state. On the other hand the term rock can include substances like clays, shells, sandstones and corals. Rocks which contain metallic compounds are called ores.
|
Rocks |
Minerals |
|
Lime stone |
Mica, feldspar, calcite, iron ore |
|
Granite |
Mica, iron ore, quarts and feldspar |
|
Basalt |
Calcite, dolomite |
|
Sand stone |
Quarts, calcite, feldspar and iron ore |
edu.uptymez.com
ROCK TYPES AND THEIR CLASSIFICATION
Rocks are aggregates of minerals in a solid state. Examples of rocks are such as lime stone, granite, basalt, sand stone and shale. Rocks can be classified depending on various criteria such as mode of formation, texture, structure, colour, permeability, age and the degree of resistance.
Rocks can be classified as follows:
1) A: ACCORDING TO THE MODE OF FORMATION (GENETIC)
Rocks can be classified into:-
Igneous rocks
Sedimentary rocks
Metamorphic rock
IGNEOUS ROCKS
These are rocks which are formed by the cooling and solidifying of the molten material from the interior of the earth. The molten materials can solidify either intrusively or extrusive. When molten materials are still in the earth’s crust are formed as magma but when they reach on the earth’s surface are called lava.
CLASSIFICATION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
Igneous rocks can be classified into two criteria;
1) According to the place of occurrence
2) According to chemical composition.
1.According to the place of occurrence, igneous rocks can be classified as;
a) Intrusive rocks
These are igneous rocks formed when the molten materials cool and solidify within the earth. The cooling and solidification of the molten materials can be near the surface or very deep in the crust. Igneous rocks formed when molten materials cool and solidify near the surface are called hypabyssal igneous rocks. Examples include granite, porphyries, and dolerite. These rocks can be exposed to the surface if there is severe erosion. Some rock masses like lopolith, laccolith, phacolith, sill and dykes are also hypabyssal igneous rocks.
When molten materials cool and solidify deep in the crust they form plutonic igneous rocks. These rocks consist of large grains and they are hard since they cool and solidify slowly. Examples include Granite, diorite, gabbro, pumice, and peridotite.
Extrusive rocks
These are igneous rocks formed when the molten material solidifies on the earth’s surface and form lava. These rocks have small grains because they cool and solidify fast due to low temperature on the earth’s surface.
Hypabyssal igneous rocks
These are rocks formed when the magma cools and solidifies closely or nearly to the earth’s surface. They have medium size particles, example dolerite.
Plutonic igneous rocks
These are formed when the molten material (magma) solidifies deep down in the crust. They are consisted of large grains and they are hard because of the slow cooling process for example granite, diorite, gabbro etc
2.According to Chemical composition, igneous rocks can be classified into;
i) Felsic (acidic) igneous rocks: These are igneous rocks which consist of great amount/content of silica and feldspar with a very little or no iron or any other metallic metal for example gramorphyte, granite etc
ii) Mafic (basic) igneous rocks: These are igneous rocks which consist of small amount of silica with large amount of magnesium, iron and other minerals like aluminum.
iii) Ultra mafic (ultra basic): These are rocks which consist of a very large amount of metallic minerals like iron, magnesium and little amount of silica less than 45% for example peridotite.
iv) Intermediate igneous rocks: These are igneous rocks with silica content between basic and acidic degree. That is both acidic and basic oxides are in equal proportions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
They are hard and non stratified.
They are formed by cooling and solidification of the molten materials.
They can be acidic ,basic, or intermediate depending on the amount of silica.
They are crystalline ( having a definite shape).
They can undergo metamorphism to form metamorphic rocks.
They can undergo weathering process and after sedimentation can form sedimentary rocks.
They contain minerals like iron, magnesium etc.
They don’t consist fossils.
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
These are rocks formed by the process of sedimentation that is deposition or accumulation and lithification of sediments and some weathered particles and other minerals. These sediments may be deposited by water, wind or moving ice.
The particles are either deposited by running water or by moving ice.
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS CAN BE CLASSIFIED INTO THREE CATEGORIES
a) Originally formed sedimentary rocks.
b) Mechanically formed sedimentary rocks.
c) Chemically formed sedimentary rocks.
a)Organically formed sedimentary rocks.
These are formed from deposition of the remains of living organisms for example they include coral reefs, carbonaceous rocks and siliceous rocks formed as a result of remains of organisms. The remains of once living organisms may accumulate in layers to form sedimentary rocks. They can be classified into the following types;
1) Carbonaceous rocks
These are formed from deposition of plants remains only. They are formed from accumulation of plants which were rich in carbonates and being buried for many years ago. Example Coal
2) Calcareous rocks
These are formed from accumulation of remains of animals only. They are formed from lithification of skeletons and shells of animals. Examples are coral, chalk, limestone etc
3) Siliceous rocks
These are rocks formed from the remains of organisms like diatoms and radiolarians whose skeletons and shells are rich in silica/silicon. Example diatomic rocks
b)Mechanically formed sedimentary rocks.
These are rocks which have been formed by compaction and cementation of sediments which have laid down on sand or on the sea floor. They are formed through accumulation/deposition and lithification of weathered materials e.g.Igneous rock- weathering- sediments- deposition- lithification- sedimentary rocks.
A particular rock is disintegrated and the weathered materials formed are deposited in layers to form sedimentary rocks. These rocks can be classified into the following;
1) Arenaceous
These are formed through deposition of particles with medium size of sand e.g. Sand stone
2) Argillaceous
These are formed from deposition and lithification of weathered materials of very fine or small particles e.g. clay and silt. Argillaceous particles may include clay stone, salt stone, mud stone etc.
c)Chemically formed sedimentary rocks.
These are rocks formed through chemical process or decomposition. The basic chemical process includes carbonation which is the reaction between weak carbonic acid with rocks containing calcium carbonate.
Calcium carbonate + Water + Carbon dioxide → Calcium bicarbonate
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca (HCO3)2
Other processes include those of sulfates, chlorides, silicates, iron stone etc
|
Mechanically rocks |
Organically rocks |
Chemically rocks |
|
Shale |
Chalk |
Gypsum |
|
Mud stone |
Limestone |
Rock salt |
|
Silt stone |
Coal |
Flint |
|
Grit |
Coral reef |
Ironstone |
edu.uptymez.com
CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
They are stratified and young rock layers overlay the old rock layers.
They are non crystalline.
They contain fossils as a result of accumulation of skeletons and shells of once living organisms.
They can undergo changes to form metamorphic rocks when they are influenced by pressure and temperature.
They are consisted of some fragments which were deposited and then cemented to form a rock.
METAMORPHIC ROCKS
These are rocks which are formed when one type of rock change into another type of rock after being subjected under intense heat or pressure or both. Any rock can change to form metamorphic rock. For example :-
– Sedimentary rocks to metamorphic rock.
a) Sand stone to Quartzite.
b) Lime stone to Marble.
c) Coal to Graphite.
d) Clay/Shale to Slate.
e) Mud stone to Slate.
– Metamorphic rock to metamorphic rock,example slate to schist.
– Igneous rock to metamorphic rock.
a) Augite to Hornblende.
b) Granite to Gneiss.
The process which involves the change of one rock type to another rock type is called Metamorphism.
TYPES OF METAMORPHISM
There are three kinds of metamorphism;
(i)Dynamic metamorphism.
This is influenced by pressure because of the earth’s movement and brings about mountain formation. Examples;
Shale to Schist
Clay to Slate
Granite to Gneiss
(ii) Thermal or contact metamorphism.
This is caused by intense heat. This can take place when the rock comes into contact with hot molten material like magma or lava. Examples
⋅ Lime stone to Marble
⋅ Sand stone to Quartzite
(iii) Thermal dynamic metamorphism
This is the process that takes place as a result of a combination of heat and pressure. It is when the existing rocks are subjected to both pressure and heat to change their shape and appearance. Example Coal to Graphite
CHARACTERISTICS OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS
i) They are more hard and more resistant than the original rock.
ii) They are formed when any type of rock even the other metamorphic rock changes into other types of rocks
iii) It can undergo weathering to form sedimentary rock or after melting and cooling it can form igneous rock.
iv) Most of them are foliated (they are composed of thin layers)
ROCK CYCLE
It is the relationship into which rocks tend to change from one type to another type of rock . For example the rock can change from igneous rock to sedimentary to metamorphic and go back to igneous. In the rock cycle, any type of rock can form another type of rock through different processes
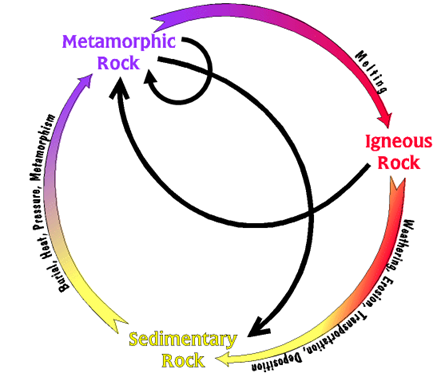
Processes in the rock cycle
i) At first igneous rock may be formed due to cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
ii) Then igneous rock can be attacked by weathering agents to form sediments which can be deposited and compacted or cemented together to form a sedimentary rock.
iii) It is the igneous rock or sedimentary rock can undergo metamorphism due to the influence of pressure and heat to form metamorphic rocks.
iv) Likewise metamorphic rocks can undergo further metamorphism to form either another or more metamorphic rock like Slate which is changed to form slate.
v) Lastly only rock that is either sedimentary or metamorphic when subjected to heat under high temperature can melt and cool to form an igneous rock.
1) B. CLASSIFICATION OF ROCKS ACCORDING TO AGE
Rocks can be classified according to age. The age of each rock can be indicated on the geological time scale. Geological time scale is a chat used for dating the history of the earth including rocks. This chart attempts to describe different periods and eras which rocks can be formed. The geological time scale divides geological time extending to about 600 million years.
According to the ages rocks can be classified into;
i) Pre Cambrian era
ii) Paleozoic era – ancient life
iii) Mesozoic era – middle life
iv) Cenozoic era – recent life
The last three eras are described as primary, secondary and tertiary eras respectively. The quaternary era represents rocks aged 1-2 million years ago. Each era is divided into period/system which in turn may be divided into series of formation.
GEOLOGICAL TIME SCALE
| Era |
Period |
Years in Million |
Major Geological event in Africa |
Ages |
|
Cenozoic |
Neocene Miocene Oligocene Eocene
|
|
Main period of volcanic activity in E.A began Main period of faulting in E.A, Alpine earth movement formed Atlas mountains and lava flow in Ethiopia.
|
|
|
Mesozoic |
Cretaceous |
135 |
Deposition of Marine sediments in Sahara and S. Nigeria. Formation of Enugu Coal Fields. |
|
|
Jurassic |
180 |
Break up Pangaea into Gondwanaland and Laurasia; Marine invasion in E.A and separation of Madagascar from mainland. |
||
|
Triassic |
225 |
Drankesberg lava formation of upper Karroo and volcanic activity in W. Africa |
||
|
Paleozoic |
Permian |
230 |
Formation of lower Karroo beds; Formation of Coal deposits in TZ, Zimbabwe, and South Africa; Ice ages in C. Africa and S. Africa |
|
|
Carboniferous |
|
Formation of Cape fields |
||
|
Devonian |
345 |
Marine invasion in Libya, Sahara and West Sudan, Continental basins formed by warping. |
Ages of Fishes |
|
|
Silurian |
405 |
Continental sedimentation in Zaire, Tanzania, and S.Africa followed by folding. |
||
|
Ordivian |
425 |
Deposition of sediments, formation of sandstones in Guinea, Volta basin and North-West Ethiopia. | ||
|
Cambrian |
|
Marine invasion of West Sahara and Kalahari basin. |
|
|
|
Pr-Cambrian |
Upper Middle Lower Azoic |
600 |
Ancient mountains building and ancient glaciation in south of equator Oldest recorded rocks of 3500millions years from S. Africa. |
Age of Algae |
edu.uptymez.com
Advantages of the geological time scale
i) It shows the ages of the rocks when they were formed i.e. other rocks were formed by deposition of igneous rocks etc
ii) It helps to understand when and how various land forms were formed for example the mountains of different types like the volcanic and the Fold Mountains have been accounted for.
iii) It can help one to know and predict the occurrence of crustal development likely to take place.
iv) It helps in the recording of plant and animals by so doing this helps to understand the relationship between living things and the geological process.
Disadvantages of the geological scale
i) The method used in determining the age of rocks were largely based on estimation
ii) Crustal deformation like over folding and gaps caused by denudation.
iii) It is not certain.
VALUES / IMPORTANCE OF ROCKS
i) They help in soil formation which can be good for agricultural activities.
ii) Storing underground water. Water is stored in the water holding stratum and can come out as a spring.
iii) Some rocks are used for fuels like coal and mineral oil.
iv) Rocks are used for building. A wide range of rocks like limestone are used for building houses and for manufacturing of cement.
v) Salt extraction, various salts are obtained from rocks occurring in some places.
vi) Manufacturing of some chemicals. Some rocks have salt such as nitrate or phosphate.
vii) Mineral deposits. Mineral ores occur in veins of some rocks such as igneous rocks.
viii) Some rocks are so impressive such that they attract some tourists to come and view them.