Accounts is a place in a ledger where all the transactions are relating to a particular asset, liabilities and capital, expenses,or revenue items were recorded.
Accounts is a wider concept with identifying measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgments and decisions by users of the information. The part of accounting that is concerned with recording data is known as book keeping.
Book keeping – is the art of recording financial business transactions on a set of books in terms of money or money‘s worth.
Why do we need to keep business records?
•To determine whether the business is making profit or loss.
To determine financial strength of the business.
•To enable the government to access reliable resources.
•To enable different stake holders to make reliable decisions about the business i.e. investors, bankers, customers etc.
THE DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM
Before looking at the system of double entry let us look at the meaning of business transactions. Transactions means movements of money,goods or services from one part/person to another. For example: Selling goods in cash Tshs 10,000/= or selling goods worth Tshs 10,000 on credit to Aisha.
The double entry system – Is the process of recording these business transactions twice.
LEDGERS
A ledger is a main principle book of accounts in which business transactions are recorded in double entry system.
The ledger contains section called “Accounts” which contain detail of transactions for specific items each account bears a title and a number called folio i.e. page of the ledger.
Each account should be shown on a separate page. The double entry system divides each page into two values;
a. The left hand side is called the debit side
b. The right hand side is called the credit side.
The title of each account is written across the top of the account at the center so double entry system needs every debit entry should have corresponding credit entry. An example of a ledger;
NAME OF THE ACCOUNTS
| Date | Particulars | folio | Amount | Date | particular | folio | Amount |
edu.uptymez.com
Each side of account should have four column i.e. date, particulars, folio and amount.
Use of columns;
i) Date column
For writing year, month and date.
ii) Particulars
For short descriptions of the transactions
iii) Folio column
For pages of reference
iv) Amount column
For writing amount of money
Worked examples on how to record transactions in double entry system;
1. Juma starts business with Tshs 20,000/= in cash on 1st January 2006. The transaction needs to debit cash account and credit capital account as follows.
Dr CASH ACCOUNT Cr
| Date | Particular | folio | Amount | Date | particular | folio | Amount |
| 1/1/2006 | capital | 20,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
Dr Capital account Cr
| Date | Particular | folio | Amount | Date | particular | folio | Amount |
| 1/1/2006 | Cash | 20,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
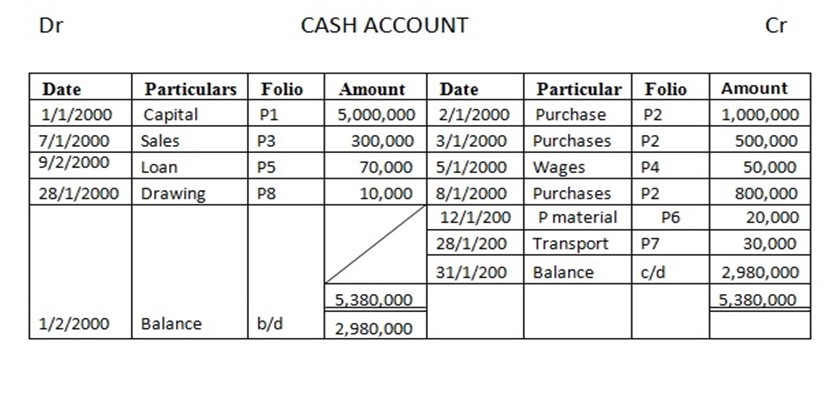
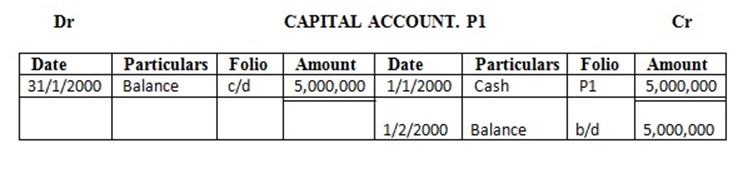
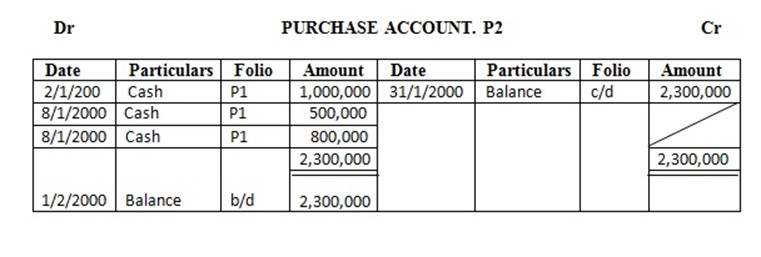
2. John started a business on 1st Jan 2000 with capital at Tshs 5,000,000 in cash
January
2) 2 purchased goods and paid in cash T.shs. ………… 1,000,000/=
3) 3 Brought goods for cash. ………………… 500,000/=
5 paid wages in cash …………… 50,000/=
7 sold goods in cash …………… 300,000/=
8 brought goods in cash ………. 800,000/=
9 received loan from C.R.D.B………….. 70,000/=
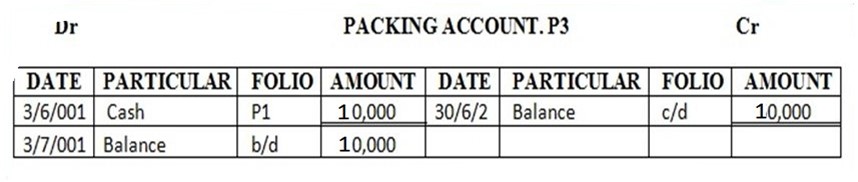
12 bought parking materials in cash…….. 20,000/=
28 paid transport charges ……… 30,000/=
28 drew cash for burial Tshs……….. 10,000/=
Enter the above transaction in the ledger and complete the double entry
Solution
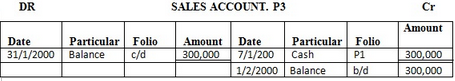
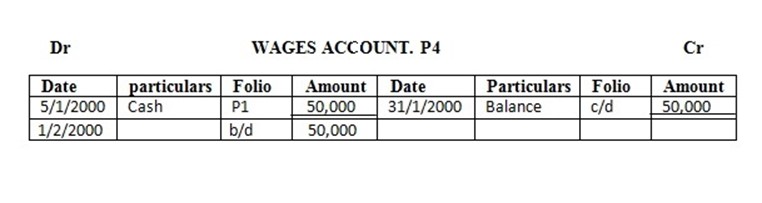
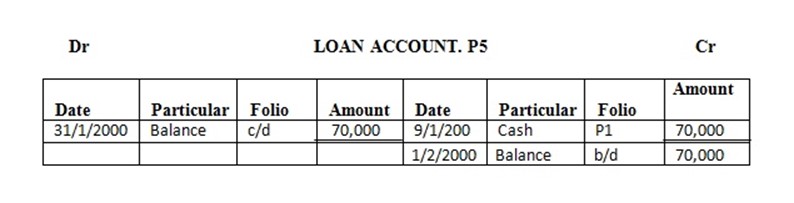
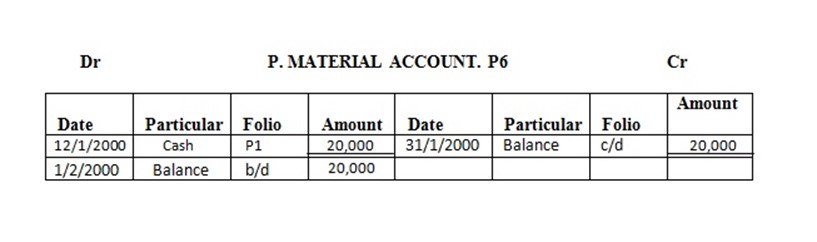
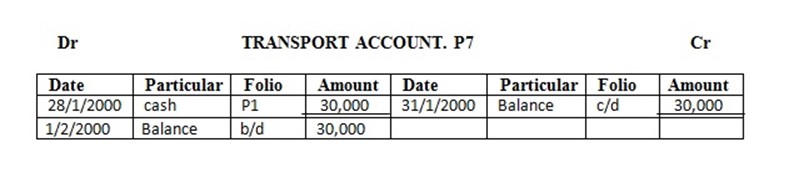
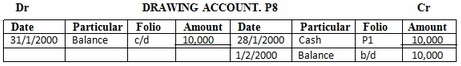
EXERCISE
1. Mark commenced business on 1st June 2001 with capital Tshs. 1,000,000.
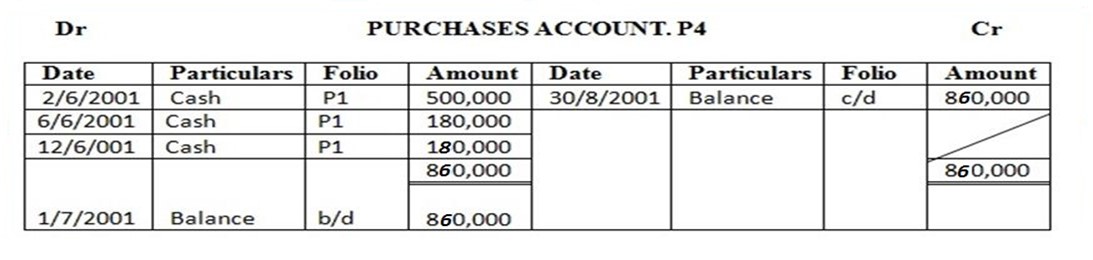
June 2 bought for cash……… 500,000/=
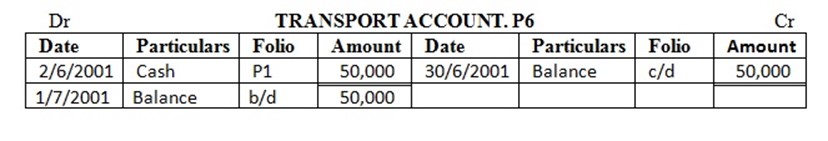
2 paid transport charges………….. 50,000/=
3 bought parking charges………….. 10,000/=
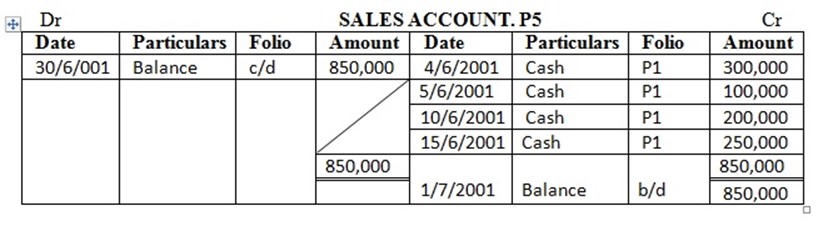
4 sold goods for cash …………. 300,000/=
5 sold goods for cash…………… 100,000/=
6 purchased goods and paid cash… 180,000/=
8 paid wages ……. 38,000/=
10 cash sales…… 200,000/=
12 cash purchases…………. 180,000/=
15 cash sales to date ……….. 250,000/=
20 paid rent …………. 50,000/=
Enter the above transactions in the cash account complete the double entry balance the accounts at the end of the month and extract a trial balance
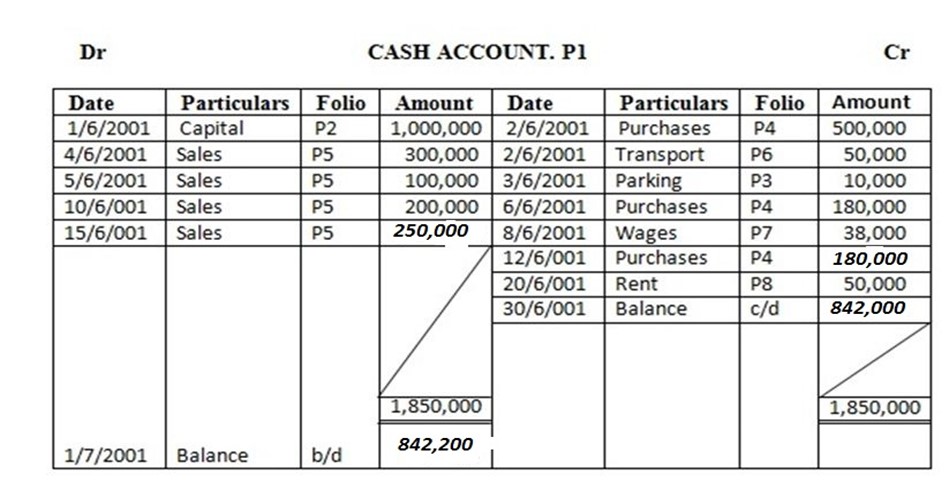
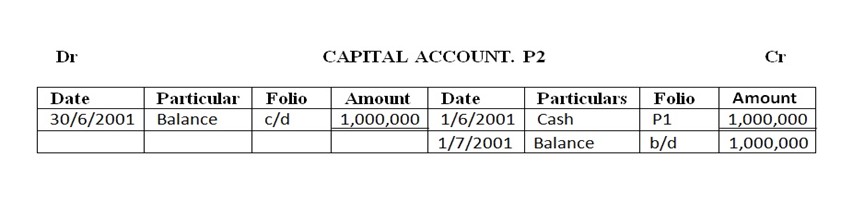
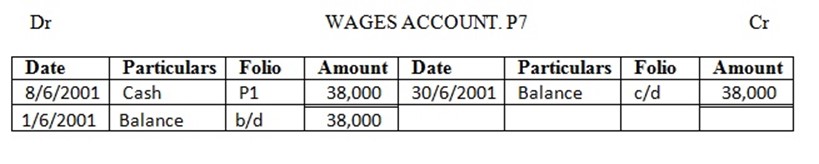
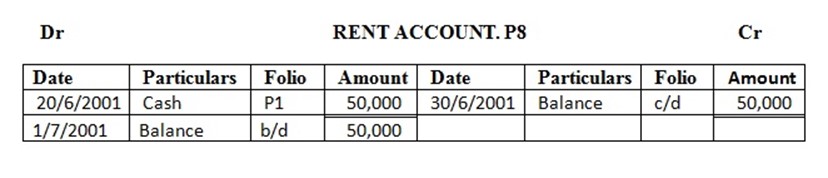
TRIAL BALANCE AT THE END OF THE MONTH 30TH JUNE 2001
| NO. | Details | Debit | Credit |
| 1 | Cash | 872,000 | |
| 2 | Capital | 1,000,000 | |
| 3 | Purchases | 830,000 | |
| 4 | Transport | 50,000 | |
| 5 | Packing | 10,000 | |
| 6 | Sales | 850,000 | |
| 7 | Wages | 38,000 | |
| 8 | Rent | 50,000 | |
| Total |
1,850,000 | 1,850,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
FIRMS NAME
DR Trading account for the year ended CR
| Opening stock xxx | Sales xxx |
| Add purchases xxx | Less. RIN xxx |
| Less outwards xxx | Net sales xxx |
| Net purchases xxx | |
| Cost of goods available | |
| For sale xxx | |
| Less : closing stock xxx | |
| Cost of goods sold xxx | |
| Gross profit c/d xxx | |
| Xxx | Xxx |
edu.uptymez.com
PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
This is an account prepared in order to ascertain the net profit and loss by the business. All expenses are debited to this account while gains or profits are credited to this account and debited with all incurred expenses.
Note
If the business has made profit it increases the capital and if it has suffered loss it reduces the capital.
It’s lay out;
FIRM’S NAME
DR PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT FOR THE YEAR ENDED CR
| Expense xxx
Net profit xxx |
edu.uptymez.com
xxx
Gross profit b/d from trading account xxx
Other gains [income] xxx
xxx
Note
The excess of expenses over incomes is formed as net profit.
Example
1. From the following trail balance you are required to prepare a trading profit and loss account. For the year ended 30th June 2006 B Samanga.
Trial balance as at 30th June 2006
| s/n | NAME OF THE ACCOUNT | DEBIT | CREDIT |
| 1 | Sales | 3,850 | |
| 2 | purchases | 2,900 | |
| 3 | Rent | 240 | |
| 4 | Lighting expenses and general expenses | 150 | |
| 5 | Fixtures and fittings | 60 | |
| 6 | Debtors | 300 | |
| 7 | Salaries | 680 | |
| 8 | creditors | 910 | |
| 9 | Cash in hand | 1,710 | |
| 10 | Bank | 20 | |
| 11 | Drawings | 700 | |
| 12 | Capital | 2000 |
edu.uptymez.com
Note
Closing stock was valued at Tshs 300. B Samanga and profit account.
DR TRADING ACCOUNT B SAMANGA AS AT 30TH JUNE 2006 CR
| Opening stock 0000 | Sales 3,850 |
| Add purchases 2,900 | R.Inward 0000 |
| Less R outwards – 0000 | Net sales 3,850 |
| Net purchases 2,900 | Add all receivables |
| Cost of goods available for sale 2900 | |
| Less closing stock -300 | |
| Cost of goods sold 2,600 | |
| Gross profit c/d 1,250 | |
| 3,850 | 3,850 |
| Balance b/d 1,250 | |
| Expenses |
|
| Rent 240 | Gross profit 1,250 |
| L and G 150 | |
| Salaries 680 | |
| Total expenses 1,070 | |
| Net profit/balance c/d 180 | |
| 1,250 | 1,250 |
Balance b/d net profit 180 |
|
edu.uptymez.com
BALANCE SHEET FOR THE YEAR ENDED 30TH JUNE 2006
| ASSETS | LIABILITIES |
| Fixed assets | Long term liabilities |
| Fixture and fittings 60 | Capital 2,000 |
| Current assets | Creditor 910 |
| Stock 300 | Net profit 180 |
| Debtors 300 | 3,090 |
| Less drawing – 700 | |
| Bank 20 | |
| Cash hand 1,710 | |
| Total current assets 2,330 | |
| Total fixed asset 2,390 | 2,390 |
edu.uptymez.com