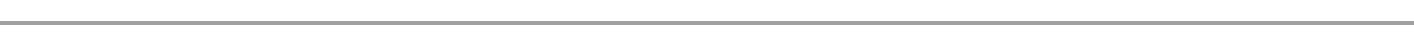Genetics is a branch of science which deals with the study of inheritance and variation.
Definition of terms
-
Heredity
Is a passing of features from parents to their young.
-
Variation
Possessing of characteristics which are different from these of the parents and other offsprings.
-
Genotype
Is the genetic constitution or make up of an organism
-
Phenotype
Is the outward or physical appearance of an organism
-
Dominant gene
Is a gene that prevents the expression of another gene.
-
Recessive gene
Is a gene that is masked by another gene.
-
Homozygous
Is a condition where by the two genes for a given trait are similar/ alike
-
Heterogeneous
Is a condition where the two genes for a trait are different.
-
Gene
Is a part of chromosome that carries the genetic material called DNA. Are also referred to as nucleotide chemical units of inheritance arranged along the chromosomes. They are called hereditary factors.
-
Trait
Are characteristics inherited by individual from their parents
-
Allele
Is an alternative form of a gene controlling the same characteristics but produce different effect
Example: T-tallness and t- shortness
-
MONOHYBRID CROSS
Are offspring produced by crossing two individual with different character
e.g. homozygous green podded plant (GG) and homozygous yellow podded plant (gg)
13. FIRST FILLIAL GENERATION (F1)
Is the first generation of offsprings produced after crossing the parental genotypes.
14. SECOND FILLIAL GENERATION (F2)
Are offsprings produced by selfing the F1 generation
15. MONOHYBRID INHERITANCE
edu.uptymez.com
This is inheritance of one pair of contrasting (different characteristics e.g height where an individual is either tall or short).
16. DIHYHIBRID INHERITANCE
This is inheritance of two pairs of characteristics
Example: – pure tall pea plant with colours flowers and dwarf pea plant prossesing white flowers.
17. EPISTASIS
It is the interaction between the two different known as allelic dominant genes
18. PEDIGREE
Is the historical or ancestral record of individuals shown in a chart ,table or diagram
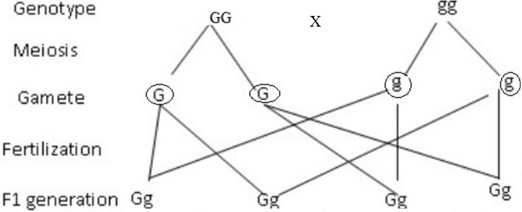
19. CHROMOSOMES
They are thread like structures found in the nucleus of the cell they are only visible when a cell nucleus is about to divide. Every nucleus of the cell of the same species has a constant number of chromosomes e.g.
Drosophila has 8 chromosomes, fruit fly pea plant has 40chromosomes sheep has 56 wheat has 14 chromosomes maize has 20 chromosomes.
Each member of the chromosome pair is known as homologous chromosome
Types of chromosomes
There are two types of chromosomes in the human body
- Autosomes
- Heterosomes
edu.uptymez.com
Autosomes
These are also known as autosomal chromosomes. They carry all genetic information except that of sex. In humans autosomes are 44 in numbers forming 22pairs
Heterosomes
These are also known as sex chromosomes these chromosomes determine the sex of the organism in humans. One pair is responsible for the determination of sex
Diploid and haploid nuclei
Diploid nucleus has the chromosomes occurring as homologous pair e.g 23 pairs in the human this is denas 2n diploid nuclei are found in the gametes
Haploid nuclei have only one set of unpaired chromosomes. In 23 chromosomes are there haploid nuclei are denoted as n diploid cells are formed after fertilization
GENETIC MATERIALS
Genes are nucleotide chemical units of inheritance arranged along the chromosome and are capable of being replicated and mutated.
Each gene occupies a specific location on a chromosome this location is known as locus (plural is loci) each chromosome contains many genes.
Homologous chromosomes when paired together will have similar or different genes called alleles.
An alleles is an alternative form of gene controlling the same character out producing different effects. The gene can control color of the skin
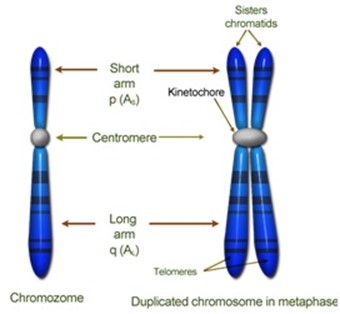
NUCLEIC ACID
Nucleic acids are polymericmacromolecules, or large biological molecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. If the sugar is deoxyribose, the polymer is DNA. If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA.
Together with proteins, nucleic acids are the most important biological macromolecules; each is found in abundance in all living things, where they function in encoding, transmitting and expressing genetic information—in other words, information is conveyed through the nucleic acid sequence, or the order of nucleotides within a DNA or RNA molecule. Strings of nucleotides strung together in a specific sequence are the mechanism for storing and transmitting hereditary, or genetic, information via protein synthesis.
DNA (deoxyribo nucleic acid)
– DNA has a double stranded shape or coil twisted like a ladder to form a double helix.
– DNA is the genetic material contained in the genes.
COMPONENTS OF DNA
- Deoxyribose sugar
- Phosphate group
- Organic base or Nitrogenous bases.
edu.uptymez.com
Nitrogenouse base
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Uracil (U)
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T)
edu.uptymez.com
Functions of DNA
- There are genetic material which are responsible for genetic characteristics
- They assemble the amino acids to form a protein molecule
edu.uptymez.com
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
The RNA molecule is responsible for carrying genetic information from the DNA molecule to the ribosome which is the sight of the protein synthesis
TYPES OF RNA
Messenger RNA – carries information from the nucleus in from of base triplets.
Transfer RNA – It transfers the appropriate amino acids to the ribosome.
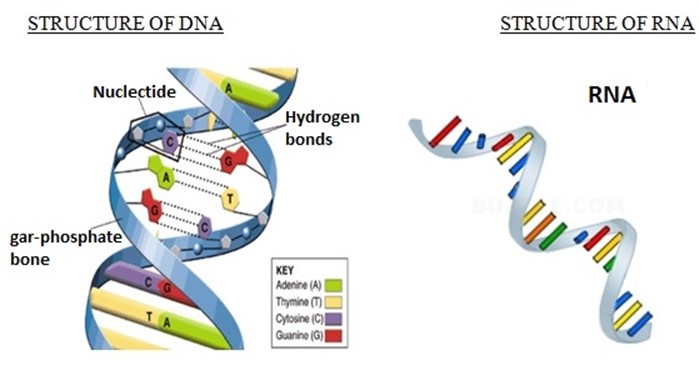
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DNA & RNA
|
DNA |
RNA |
|
Has a deoxyribose sugar |
Has a ribose sugar |
|
Has a double stand |
has a single stand |
|
Found in the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast |
Found in nucleus and cytoplasm. |
|
Has organic bases, cytosine, guanine adenine and thymine |
Has organic bases, cytosine guanine, adenine and uracil |
edu.uptymez.com
PRINCIPLES OF INHERITANCE.
Concept of inheritance.
Historical background of genetics
Father of genetics is Gregory Mendel
Mendel’s experiment
Mendel has selected garden pea plants [pisum sativa]
Reasons for selecting pisum sativa
- The garden pea has many contrasting and easily recognized characteristics.
- The hybrid obtained from the cross fertilization was fertile
- The flowers of a garden pea are bi sexual and naturally self pollinated
- The garden pea plant matures relatively fast producing many off springs (seeds)
edu.uptymez.com
MENDELIAN INHERITANCE.
-
LAW OF SEGREGATION
It states that “characteristics of an organism are controlled by internal factors (genes)occurring in a pair is carried in each gamete”
-
LAW OF INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT
” Each of the 2 alleles of one gene may combine randomly with either of the alleles of another gene independently”
PUNNET SQUARE
edu.uptymez.com
-
Is a chart showing the possible combination of factors among the offspring of a cross.
- It is used to show the formation of zygotes.
edu.uptymez.com
Female gametes are placed on the right while male gametes are placed on the left side.
 Male
Male
 Female
Female
Example:
A cross between homozygous tall (TT) and homozygous dwarf (tt) plant can be illustrated as follows:
Let assume tall is male and dwarf is female
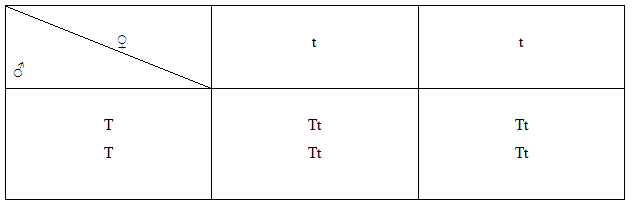
Test cross
A cross used to cross an individual of unknown genotype with a homozygous recessive individual
Example:- A homozygous dominant individual (TT) will phenotypically appear the same.
BACK CROSS
In the crossing of individual of unknown genotype with the homozygous parent.
This is another form of test cross, but the difference is that in test cross, it is crossed with any individual while in back cross with a parent.g: if the individual is homozygous (bb)
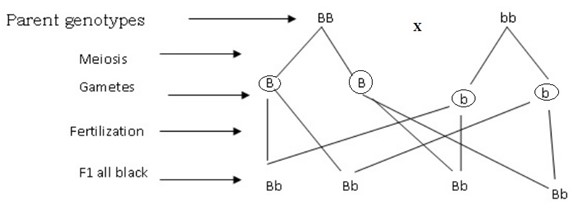
DOMINANCE
Dominance is a state of one character /gene from one parent masking the corresponding character from another parent.
Types of dominance
- Mendelian inheritance – Complete dominance
-
Non-Mendelian inheritance – Incomplete dominance
– Co-dominance
edu.uptymez.com
- COMPLETE DOMINANCE
edu.uptymez.com
- Is the dominance where by one gene masks the expression of the other gene.
-
A dominant gene always masks a recessive gene when the two occur together.
EXAMPLE:
edu.uptymez.com
-
A man homo zygote for brown iris marries a women who has blue iris. Show the results of F1. What colour would the iris of the cross between 2 members of F1?
Solution: –
The gene for brown iris is completely dominant over gene for blue iris in woman.
Let gene for brown be B and b for blue
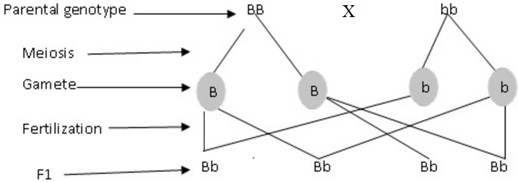
edu.uptymez.com
Genotypes – All are Bb.
Phenotype – All have brown iris.
Selfing F1
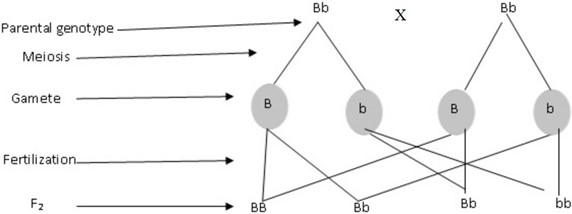
Genotypes – BB,Bb,bb
Phenotypes – 3 Brown iris, 1 brown iris
Genotypic ration – 1 : 2 : 1
Phenotypic ratio – 3:1
BB Bb bb
2. A pure purple flowered pea plant was crossed with pure white pea plant. Offsprings for F1 were phenotypically all purple flowered plants when F1 was selved a mixture of purple pea flowered and white pea plant were produced at an approximate ratio of 3:1
Solution: –
Let gene for purple be P and white be p
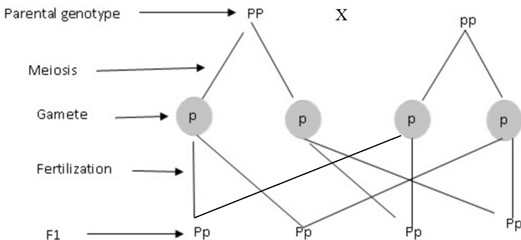
Genotypes : all are Pp
Phenotypes : all have purple flower
Self F1
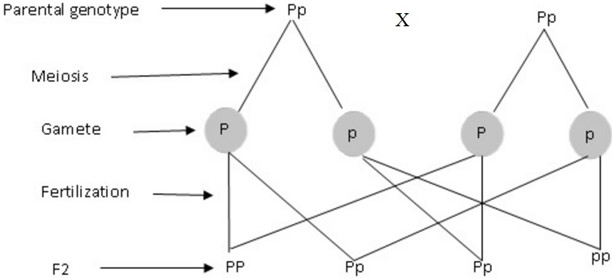
Genotype – PP, Pp, pp
Phenotypic ratio – 3 : 1
Genotypic ratio – 1 : 2 : 1
2. INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE
In incomplete dominance there is no dominant or recessive gene, but both express themselves equally. It results in a heterozygous individual which does not resemble any of the heterozygous individual which does not resemble any.
Example: –
1. A red flowered rose was crossed with white rose and all members of F1 were pink. When pink were selfed, a mixture of red, pink and white flowered plants were obtained.
Solution:-
Let, R – Red , G – White
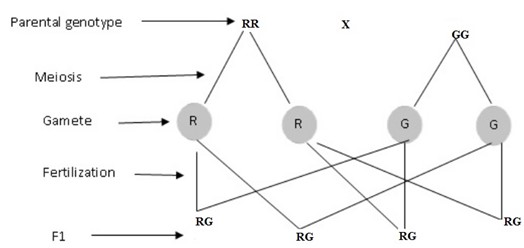
Genotypes : all are RG
Phenotype : all are pink
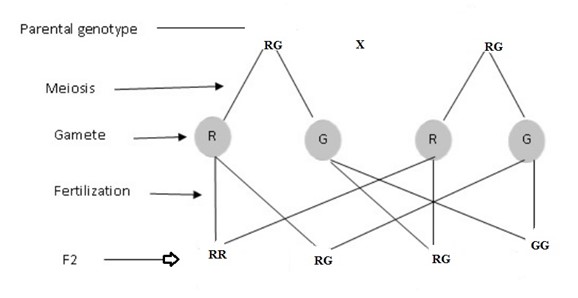
Genotypes – RR, RG, GG
Genotypic ratio – RR : RG : GG
1 : 2 : 1
Phenotypic ratio – 1 red : 2 pink : 1green
3. CO-DOMINANCE
In co- dominance genes from both parents are dominant and are phenotypically expressed in the offspring.
Example: A red cow is mated with white bull. In F1 generation all of offsprings have equal patches of red and white fur. Therefore neither red or white gene is dominant over the other such cattle and called Roan.
When a roan cow is mated with roan bull, offsprings may be red, roan or white mated in the ratio of 1 : 2 : 1
Let;
W – white bull
R – Red cow
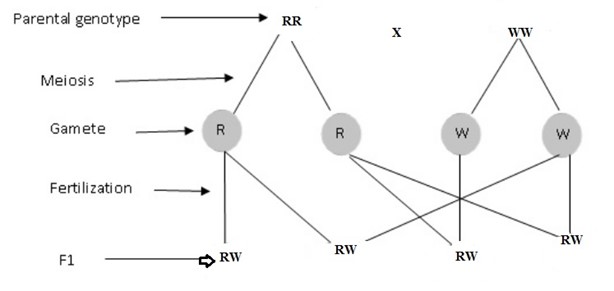
Genotypes – all are RW
Phenotype – all are Roan
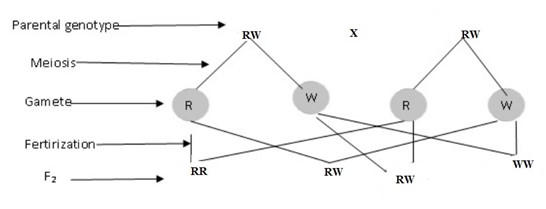
Phenotypes ratio – 1 Red : 2 Roan : 1 White
Genotypic ratio – RR : RW : WW
1 : 2 : 1