HYDROGEN CHLORIDE GAS
This is the compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula HCl. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl has the chemical formula HCl. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl
Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas

Where
H2SO4 (aq) is concentrated sulphuric acid.
NaCl is table salt.
NaHSO4 is sodium bisulphate.
HCl is hydrogen chloride.
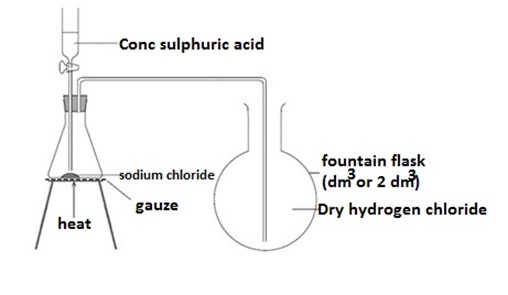
A balanced chemical equation for the reaction

The gas cannot be collected over water because it is soluble in water. Thus, it is collected by downward delivery method.
Test of hydrogen chloride gas
The gas forms white denser fumes of ammonium chloride with ammonium gas.
The physical properties of chlorine
-
It is soluble in water.

Where H3O+ Is oxonium ion
- It is colorless
- It has a pungent smell.
- It is denser than air.
- It turns blue litmus to red since it is acidic.
edu.uptymez.com
Uses of hydrogen chloride gas
These are some of the uses for hydrogen chloride gas:
- Most hydrogen chloride is used in the production of hydrochloric acid.
- Hydrochlorination of rubber
- Production of vinyl and alkyl chlorides
- Chemical intermediate in other chemical production
- Used in toilet bowl cleaner (The Works)
- Use as babbitting flux
-
Treatment of cotton
o Delinting
o Separation from wool
-
Used in semiconductor industry (in pure grade)
o Etching semiconductor crystals
o Converting silicon to SiHCl3 for purification of silicon
edu.uptymez.com
Sulphur and sulphur extraction
- Sulphur ( S= 2:8:6)
edu.uptymez.com
Sulphur is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is an abundant, multivalentnon-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Sulphur element is a bright yellow crystalline solid when at room temperature. Chemically, sulphur can react as either an oxidacing or a reducing agent. It oxidizes most metals and several nonmetals, including carbon, which leads to its negative charge in most organosulphur compounds, but it reduces several strong oxidants, such as oxygen and fluorine.
Sulphur is the solid yellow powdered non metal, yellowish in color. Sulphur is found within the soil in the place called Sulphur bed.
The following countries lead in the extraction of sulphur; Mexico, Italy, Japan, France and USA.
Sulphur can be found combined with ores such as;
- Galena – Pbs
- Iron Pyrite -FeS2
-
Zinc blend – ZnS
edu.uptymez.com
Some compounds of sulphur have unpleasant smell (odors). Sulphur compounds are responsible for the smell such as that of onion, cabbage. The substance which causes tears during cutting of onions, also the smell associated with rotten eggs is caused by the sulphur compounds.
Compounds of sulphur
They include;
- Sulphur dioxide. (SO2)
- Sulphuric acid.( H2SO4)
- Sulphur trioxide. (SO3)
- Hydrogen Sulphide( H2S)
edu.uptymez.com
Hydrogen sulphide gas – H2S have smell of the rotten eggs or cabbages. At the same time the gas is poisonous and toxic.
Allotropy and allotropes of sulphur
Allotropy is the existence of an element in various different forms with different physical properties but same chemical properties.
Allotropes are the different forms of the same element with the same chemical properties but different physical properties e.g. rhombic, monoclinic, plastic, amorphous are all allotropes of sulphur.
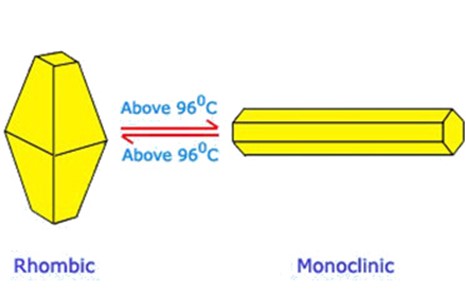
Rhombic sulphur
- Exists at 960C
- Transparent white crystal
- Stable at 960C
- Has shape of octahedral
- Prepared by heating sulphur
edu.uptymez.com
With methyl benzene (toluene)
Monoclinic sulphur
- exists above 960C
- yellow translucent
- stable above 960C
- has octahedral shape
- prepared by heating sulphur
edu.uptymez.com
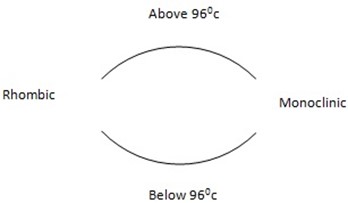
Relationship between rhombic and monoclinic sulphur (at transition temperature)
Transition temperature is the temperature which one allotrope can change to another allotrope either by raising or lowering the temperature.
Rhombic and monoclinic sulphur are related to the temperature.
Preparation of plastic sulphur
Plastic sulphur- is the allotrope of sulphur prepared by heating sulphur then cooling it and mixing it with cold water. Sulphur heated then melts and becomes molten after that mixed with cold water, sulphur contact becomes very hard than any allotrope.
NB: plastic sulphur is not considered to be actual allotrope of sulphur because it is harder than others.
Amorphous sulphur prepared from chemical compound
Amorphous sulphur is the sulphur allotrope of sulphur produced from the chemical reaction of compounds containing sulphur.
Commercial uses of plastic sulphur
Used in the synthesis of plastic materials such as jars, trough, plastic water pipes, basin, pen- tubes containing ink.
EXTRACTION OF SULPHUR BY FRASCH PROCESS
The Frasch process is a method to extract sulphur from underground deposits. It is the only economic method of recovering sulphur from elemental deposits.[1] Most of the world’s sulphur was obtained in this way until the late 20thcentury, when sulphur was recovered from petroleum and gas sources (recovered sulphur) became more commonplace (see Claus process).
In the Frasch process, superheated water is pumped into the sulphur deposit; the sulphur melts and is extracted. The Frasch process is able to produce high purity sulphur.
As from 2011, the only operating Frasch mines worldwide are in Poland and since 2010 in Mexico. The last mine operating in the United States was closed in 2000. A Frasch mine in Iraq was closed in 2003 due to the U.S. invasion of Iraq.
Process
In the Frasch process, three concentric tubes are introduced into the sulphur deposit. Superheated water (165 °C, 2.5-3 MPa) is injected into the deposit via the outermost tube. Sulphur (melting point 115 °C) melts and flows into the middle tube. Water pressure alone is unable to force the sulphur into the surface due to the molten sulphur’s greater density, so hot air is introduced via the innermost tube to froth the sulphur, making it less dense, and pushing it to the surface.
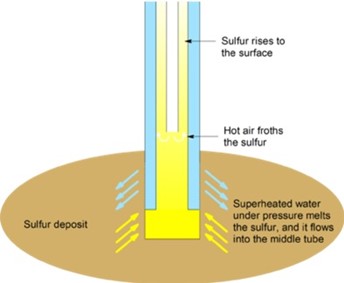
The sulfur obtained can be very pure (99.7 – 99.8%). In this form, it is light yellow in color. If contaminated by organic compounds, it can be dark-colored; further purification is not economic, and usually unnecessary. Using this method, the United States produced 3.89 million tonnes of sulfur in 1989, and Mexico produced 1.02 million tonnes of sulfur in 1991.
The Frasch process can be used for deposits 50–800 meters deep. 3-38 cubic meters of superheated water are required to produce every tonne of sulfur, and the associated energy cost is significant. A working demonstration model of the Frasch process suitable for the classroom has been described.
CHANGES WHICH OCCUR WHEN SULPHUR IS HEATED IN THE ABSENCE OF AIR
When sulphur is heated in the absence of air, it undergoes changes as shown below.
(a) Sulphur at 1600C
Sulphur melts and becomes mobile yellow liquid.
(b) Sulphur at 2000C
Sulphur becomes dark, viscous and the mobility of sulphur increases more.
(c) Sulphur at 4440C
Sulphur boils to become into vapour or gaseous form.
-
Chemical properties of sulphur
Consider the reactions below.
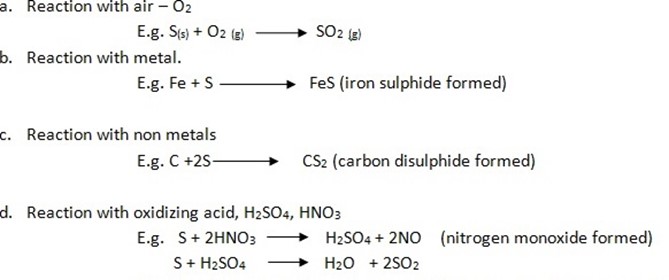
(Sulphur dioxide gas formed turning yellow potassium dichromate to green)
edu.uptymez.com
Commercial uses of sulphur
- Manufacture of gun powder.
- Manufacture of sulphuric acid through contact process.
- Manufacture of matches.
- Manufacture of plastic flower.
- Manufacture of detergents e.g. powder soap, puff.
- Manufacture of rubber through vulcanization.
edu.uptymez.com
Vulcanization is the hardening of rubber or is the process of heating sulphur with rubber to make it hard.
7. Manufacture of drugs and skin ointment.
8. Production of bleaching compound
Sulphuric acid and contact process
The contact process is the process used to manufacture concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4)in large scale in the industries.
E.g. concentrated sulphuric acid – is the acid containing few (small) amounts of water molecules.
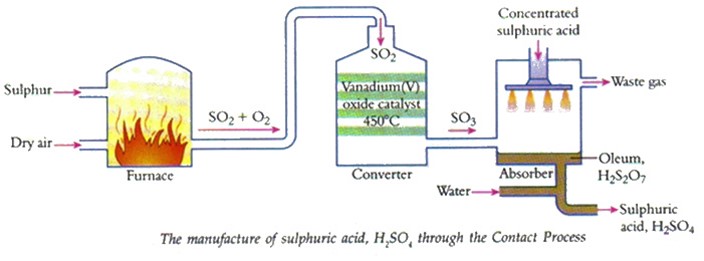
Sulphuric acid, its industrial manufacture, uses and reactions
Sulphuric acid is made in large quantity industrial because it has many important uses. The production of sulphuric acid takes place in four stages.
Stage 1
Production of sulphur dioxide
Sulphur dioxide gas can be produced by three methods.
-
Burning sulphur in air. The sulphur from Frasch process is burned in air. The equation is

-
Hydrogen sulphide from crude oil is burned in air. The equation is;

-
Sulphide ores are roasted in air to extract metals from the ores. Sulphur dioxide is also produced, the equation is ;

edu.uptymez.com
Stage 2
The contact process
The sulphur dioxide gas produced in stage 1 is mixed with air. The air and sulphur dioxide pass through a dust precipitate to remove any dust impurities and then the gases are passed through a drier. It is essential that this purification process takes place because impure gases will poison the vanadium (V) oxide catalyst.
The sulphur dioxide gas produced in stage one is mixed with air. Sulphur dioxide is converted into sulphur trioxide in a converter. Like the Haber process, this is an equilibrium reaction and goes in both directions. A yield of 95% is obtained by using the following conditions.
- Catalyst vanadium (V) oxide(vanadium pentaoxide)
- Temperature – 4500C
- Pressure 1 atmosphere
edu.uptymez.com

This reaction is exothermic, which means that as sulphur trioxide is formed energy is released. If the temperature rises above 4500C, the yield of sulphur trioxide decreases. The heat exchanger maintains the temperature at 4500C.
Stage 3
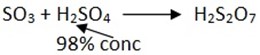
Production of oleum
If sulphur trioxide is dissolved in water, sulphuric acid is formed.

Oleum: H2S2O7 – yellow heavy chemical.
Definition; is the heavy yellow liquid formed when sulphur trioxide gas – SO3 reacts with acid H2SO4
NOTE: Oleum have strong affinity to water, so absorbs a lot of water than concentrated sulphuric acid formed.
Diagrammatic representation of the contact process
NB:
Do not add water to an acid but acid to water for safe dilution.
Because heat absorbed from the surrounding environment which cause water spray to boil which scatter. Then it can burn at the same time with denser fumes that will be formed. Normally acids have strong affinity to water. Reaction with water is endothermic.
Reactions of dilute sulphuric acid
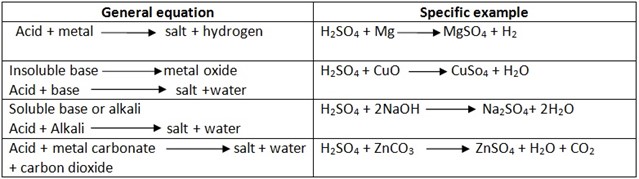
Reaction of sulphuric acid with marblechips – CaCO3 (egg shell)

Insoluble calcium sulphate formed, this cover acid to the top hence prevent further (more) reaction to occur or continue, then the reaction stops. This is why we can’t prepare CO2 by reacting marble chips and acid.
Commercial uses of sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
- Used to make detergents for washing.
- Used to make paints for house painting.
- Used to make dyes for making clothes
- Used in the synthesis of solvents. E.g. thinner for diluting paints.
- Used in pickling – the removal of the oxide layer on the metal surface e.g. before galvanization.
- Used in the lead accumulator battery as the electrolyte.
-
Used to manufacture fertilizers e.g. SA ( ammonium sulphate)

edu.uptymez.com
8. Used to make plastic materials.