What is qualitative analysis?
Qualitative analysis is the analysis which deals with the determination or identification of the components of the unknown given chemical solid substance. The unknown chemical solid substance actually we talk about the solid salt which normally we are given but the name is unknown. The solid salt is placed into the watch-glass, then you are required to identify “cation” and “Anion” then chemical formula of the salt
SOLID SAMPLE [unknown salt]
This is the solid salt which contains the ions which you are required to identify.
Consider the solid salt in the watch glass below;

ION(S)
This is the positively or negatively charged particle formed by the Electron loss or gain by atom/element
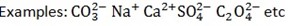
TYPES OF IONS
There are two types
Cation e.g. NH4+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Pb2+ etc
Anion e.g SO42-, HSO4–, CO32-, HCO3–, NO3–, CL– etc
NOTE;
CATION; is the positively charged particle formed by the Electron loss by an atom/Element. Example;
NH4+, Ca2+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Mg2+, K+ etc
ANION; is the negatively charged particle formed by the Electron gain by an atom/Element. Example;
SO42-, HSO4– – Bisulphate/ Hydrogen sulphate
Cl–, NO3–, HCO3– – Bicarbonate/ Hydrogen carbonate
CO32-, C2O42-, S2O32-, SO3– etc
QUALITATIVE GUIDE SHEET (QDS)
-This is the sheet which contains the information used or guiding in order to answer the Qualitative analysis questions. Normally in the Examinations room you are provided with this sheet. Consider how the sheet appears and it includes .experiment, observation and Inference.
|
S/N |
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
a) |
Appearance of the sample e.g. Take the sample then observe its appearance and texture |
Salt was ‘Blue’ crystalline solid |
Cu2+ may be present |
|
Salt was ‘Green’ crystalline solid |
Fe2+ may be present |
||
|
Salt was ‘White’ crystalline solid |
NH4+,Na+, K+, Al3+, Mg2+, Pb2+, Zn2+ may be present |
||
|
|
|
Salt was white powdered solid |
CO32- of Zn2+, Pb2+ may be present |
|
b) |
Solubility- take the solid salt put into the test tube then add distilled water |
Salt was soluble |
Soluble salt was present NO3–, Cl–, SO42-, CO32- etc |
edu.uptymez.com
EXPERIMENT
This is the practically done action by the experimenter.
An Experimenter can
(i)Take the salt sample from Watch glass then;-
Observe its colour
Salt solid sample observed on the hand by observer, the colour of the sample must be stated.
E.g. Blue- Cu2+, red- Cu+, green- Fe2+, Fe3+ – brown/yellow, White- NH4+, Na+, Zn2+, Pb2+, K+ etc
Check the texture of the salt.
Smell the salt or its odor
Dissolve it into the distilled water into the test then observe if soluble or not soluble (insoluble).
OBSERVATION
This is what an experimenter has seen due to the Experiment which he/she had performed.
The following are the common or possible observation which an experimenter can observe
- Powdered/crystalline solid sample
- The colour E.g. Green, yellow, white.
- Evolution of the gas e.g. O2, NH3, NO2,SO2
- Formation of the ppt( precipitation)/(precipitate)
- The colour of Residue formed after heating the solid sample.
- The smell of the solid sample E.g. Urine (NH3)smells irritating chocking smell
- Solubility of the salt if soluble/insoluble.
edu.uptymez.com
Note;
On doing the solubility leave the salt to stay for certain period of time, because some of the salt takes the time to dissolve completely. Don’t harry up to state that the salt is Insoluble.
INFERENCE (conclusion)
This is the stage which an experimenter is required to take the conclusion above the result observed after doing an experiment.
|
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
|
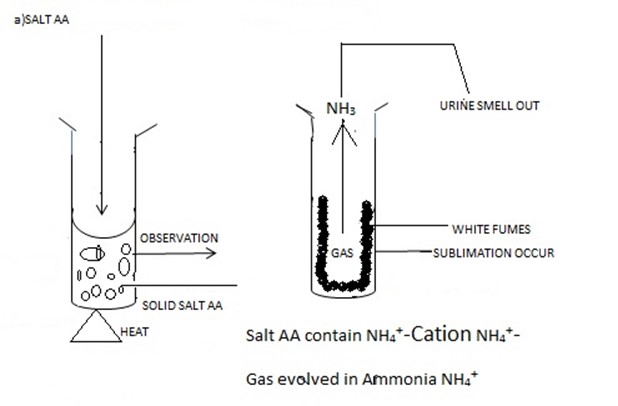
Action of heat of salt TT |
Gas with urine smell produced Gas – NH3 |
NH4+was confirmed |
|
|
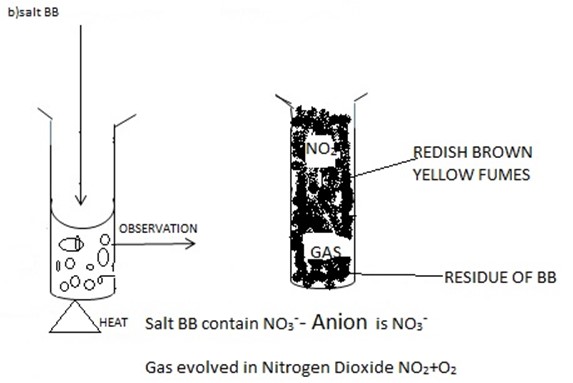
Action of con. H2SO4 on solid salt TT |
Reddish brown/yellow fumes was observed Gas –NO2 |
NO3– was confirmed.
|
|
edu.uptymez.com
Conclusion; cation NH4+ Anion –NO3– formula of TT –NH4NO3
TYPES OF QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
There are;-
i./Guided Qualitative Analysis
Ii./Systematic Qualitative Analysis (unguided)
GUIDED QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
-Is the type of Qualitative which the experiments to be done by an experimenter is guided or instructed or limited.
POSSIBLE QUESTION
The salt sample WW contains one cation and Anion in the tabular form of Experiment, Observation and Inference Identify cation and Anion in the salt solid sample WW.
|
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
a) Take the sample WW then observe it |
|
|
|
b) Take one spatula full of solid sample WW then smell it |
|
|
|
c) Take the salt WW put it into the clean test tube then add distilled water until half of test tube |
|
|
|
d) To the solid sample WW add
edu.uptymez.com |
|
|
edu.uptymez.com
Conclusion Cation – Anion- Formula of WW
SYSTEMATIC QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
-Is the type of the qualitative analysis which no instructions is given but an experimenter should follow the procedures/stages which can led to identification of solid sample
POSSIBLE QUESTION
The salt sample WW contains one cation and Anion in the tabular form below identifies cation, Anion and formula of WW.
SOLN/ ANS:
|
S/N |
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
a) |
Appearance of the sample WW |
Solid sample WW was white crystal solid |
NH4+, Na+, zn2+, Pb2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Al3+, may be present |
|
b) |
Smell of sample WW |
The sample gave smell of Ammonia gas (urine) ... Gas- NH3 |
NH4+ was present and confirmed |
|
c) |
Solubility of WW |
The sample was soluble and formed clear solution |
Soluble salt may be present NO3–, Cl–, SO42-, CO32-, HCO3–, except AgCl, Baso4, ZnCO3, PbCO3 |
|
d) |
Action of dil. H2SO4 to solid WW |
Gas with Urine smell detected |
NH4+ confirmed |
|
e) |
Action of dil. NAOH solution to WW solution |
Gas with urine system detected |
NH4+ confirmed |
|
f) |
Action of Bacl2 to WW solution |
White ppt was formed |
SO42- confirmed |
edu.uptymez.com
Conclusion: Cation NH4+ Anion SO42- formula (NH4)2SO4
STAGES OF SYSTEMATIC QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
They include;-
-Preliminary test
-Test in solution
-Confirmatory test
PRELIMINARY TEST
These are the tests which are done at the first stage such that preliminary information of the solid sample can be obtained;-
These Experiments includes;
1. Appearance of the sample (solid)
Here we talk about colour, Texture of sample,
2. Solubility of the sample (solid)
3. Smell of the solid sample
4. Action of heat on solid sample
5. Action of dil. HCl (Hydrochloric Acid) or concentrated sulphuric Acid (con.H2SO4)on the solid sample into test tube(TT)
6. Flame test of solid sample
7. Residue test of the solid sample
THE REQUIREMENTS;
a. Clean test tubes
b. Test tube holder

C. Heat source e.g. Bunsen burner
d. Distilled Water E.g.

e.) Acid E.g.

APPEARANCE OF SOLID SAMPLE

Rewind or Recall from periodic table.
POSSIBLE QUESTION
|
S/N |
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
a) |
Appearance of a solid sample |
Sample BB was white crystalline solid |
Transitional elements (Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+) absent |
|
Sample BB was light green crystalline solid |
Fe2+ or Cu2+ may be present |
||
|
b) |
Appearance of RR |
Sample RR was blue in color |
Cu2+ may be present |
|
|
|
Sample RR was yellow in color |
Fe3+ may be present |
edu.uptymez.com
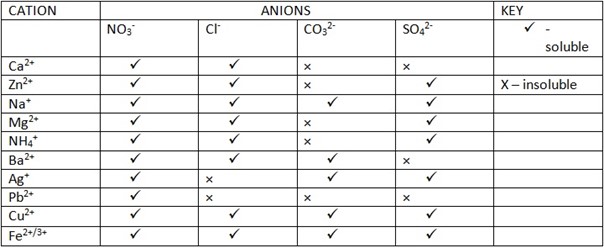
SOLUBILITY OF SOLID SAMPLE
Take solid sample put small (little) amount into clean test tube then Add distilled Water into the solid sample observe it if soluble or insoluble. Be careful on observing
E.g. salt -AA or CC or TT etc
Note;
Transition metals [Cu2+,Cu+, Fe3+] they tend to display [show] their colour if their salt dissolved into Water provided that they are soluble-salt.
COLOR OF SOLUTION FORMED ON DISSOLVING SALT SAMPLE IN WATER.
-Consider the table below for more illustration;
E.g. SALT SAMPLE
POSSIBLE QUESTION
|
S/N |
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
a) |
Solubility of sample QQ |
edu.uptymez.com |
Cu2+ may be present |
|
b) |
2. |
Colored solution was formed |
Transition metals Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+may be present |
|
Colorless solution was formed |
Soluble salt of NH4+, Na+, Ca2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, K+, Al3+ may be present |
edu.uptymez.com
Fill (i) and (ii)
Answer
- Blue solution was formed
-
Solubility of a sample
edu.uptymez.com
SMELL OF THE SOLID SAMPLE
Take the solid sample then smell it. Normally Ammonium salt -NH4+ Even at the room-temperature they tend to give out the Urine smell (smell of Ammonia gas –NH3 or When they are Heated (∆). But other salts are (odorless) E.g. Don’t give out the smell , salt of Na+,Cu2+, Zn2+,Pb2+,Ba2+,Mg2+,K+ .etc.
TABLE OF RESULTS
|
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
Salt had the irritating chocking smell (Urine smell) or smell of Ammonia gas |
NH4+ is confirmed |
|
No specific smell detected or salt had no any smell |
NH4+ was absent or Na+, Ca2+, Al3+, Zn2+, Pb2+, Mg2+, K+ may be present |
edu.uptymez.com
POSSIBLE QUESTION
|
S/N |
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
a) |
On smelling the sample XX into a watch glass |
Ammonia gas smell was detected |
i) |
|
|
|
ii) |
NH4+ was absent |
|
b) |
|
Urine smell detected |
NH4+ confirmed |
edu.uptymez.com
Fill (i), (ii), (b)
Ans (i) NH4+ confirmed (ii) no specific smell detected (b) Smell of the sample
NATURE OF GASES, SMELL, ACTION OF LITMUS, COLOR, SOLUBILITY
- Some of the gases are Acidic, Basic (Alkaline), colorless, colored, soluble, insoluble have smell (odor), odorless.
edu.uptymez.com
|
GAS |
SMELL |
NATURE |
COLOR |
SOLUBILITY |
ACTION ON LITMUS |
|
NH3 |
Urine or |
Basic/alkaline |
colorless |
Highly soluble |
Blue |
|
NO2 |
Pungent |
Acidic |
Reddish |
soluble |
Red |
|
So2 |
smell |
|
Brown/yellow |
soluble |
Red |
|
Irritating |
Acidic |
colorless |
soluble |
|
|
|
cl2 |
Irritating |
Acidic |
Greenish |
soluble |
Red then |
|
|
|
|
yellow |
|
bleached |
|
CO2 |
odorless |
Acidic |
colorless |
soluble |
Red |
|
O2 |
odorless |
Neutral |
colorless |
insoluble |
No |
edu.uptymez.com
Note: We can try to know the nature of the gas by dissolving it into Water then resulting solution may be Acidic, Basic, or Neutral. E.g.
- NH3 + H2O →NH4OH – Base/Alkaline
- CO2 + H2O→H2CO3 – Acid
- NO2 + H2O→HNO3 – Acid
- Cl2 + H2O→ HClO + HCl – Acid
- SO3 +H2O→H2SO4 – Acid
- SO2 + H2O→H2SO3 – Acid
edu.uptymez.com
ACTION OF HEAT ON SOLID SAMPLE IN THE DRY AND CLEAN TEST TUBE
To the clean, dry test tube put the salt sample then heat it for few minutes and observe the changes which occur some of the salt are stable(under composes) but other decomposes(stable) During heating process you can observe the colour if gas Evolved, smell of the Gas Evolved. Normally each radical releases
Example
SALT RADICAL + HEAT → GAS EVOLVED + RESIDUE
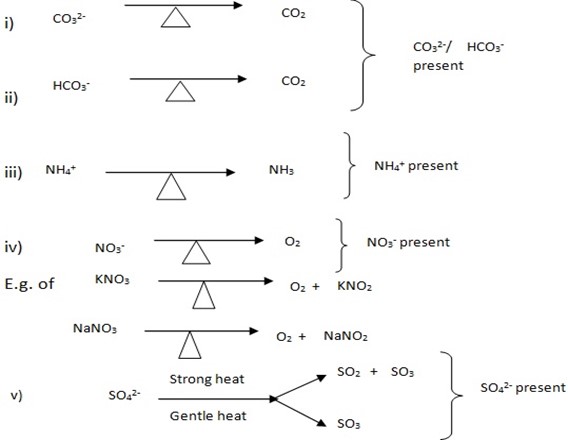
You have been given with salt sample AA, PP, QQ, NN, ZZ, and TT.
POSSIBLE QUESTION
You have been given with salt sample ZZ, QQ, Which was the piece of the paper isolated in the Examination room by form IV students at Mtazamo secondary school.
|
|
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
|
|
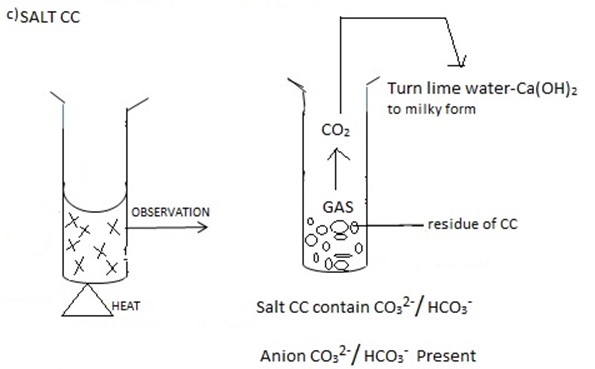
The salt ZZ gave the yellow residue- hot and White-Residual-GG cold and Reddish brown yellow fumes of the gas PP. The salt QQ gave the colorless gas – FF Which turn lime water – Ca(oH2) to milky form and Extinguishing the fire or burning candle the gas produced the Effervescence and turned damp litmus-Blue paper Red and yellow Residue HH.
|
|
|
edu.uptymez.com
a. Fill the inference column
b. Given cation – Anion and formula of salt ZZ including cation -Anion -in QQ
c. Name gas FF, PP, Residue HH, GG.
|
|
INFERENCE |
|
1 2. |
No3– confirmed Co32-/HCO3– May be was present |
edu.uptymez.com
b. Cation – Zn2+, Anion-No3– formula Zn (NO3)2 OF ZZ cation -Pb2+ Anion – CO32-/HCO3–
c. FF- Nitrogen dioxide – NO2
PP-Carbon dioxide – CO2
HH – Lead oxide (PbO),
GG- zinc oxide (ZnO)
HOW TO IDENTIFY THE GAS EVOLVED DURING EXPERIMENT [Heating using Acid]
The following methods can be used;-
- Through smelling
- By using the damp litmus paper
- By observing the colour of gas
-
Experiments
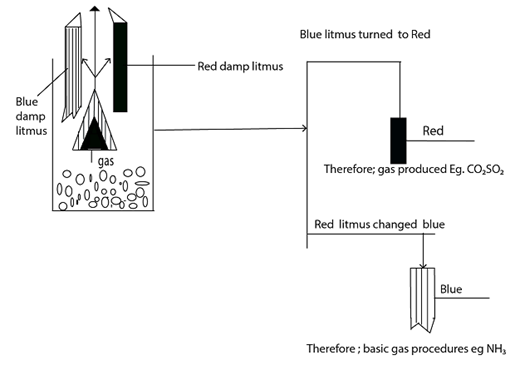
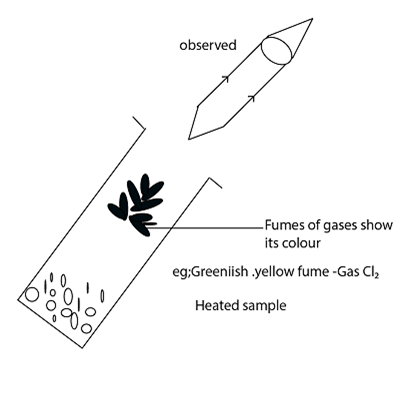
edu.uptymez.com
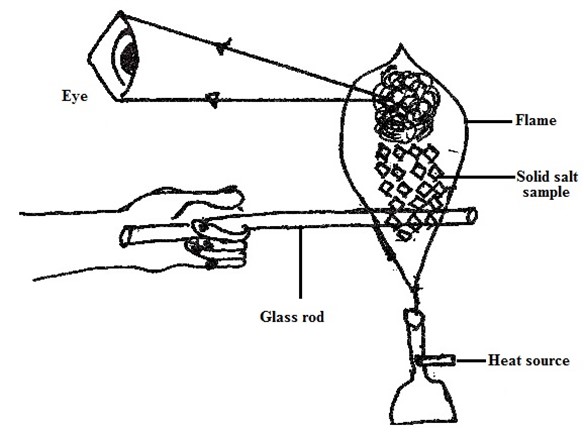
FLAME TEST [Give the cation E .g Pb2+ Cu2+,Na+etc
→The Nichrome wire or glass rod or Test tube then dip into the test-tube containing dil. HCl the reason; Is to provide White vapour on the flame on heating the salt. Take the Wet nichrome or glass rod or test tube dip into the salt sample, so the salt sample should stuck on the Wire. Transfer the salt on the flame burn it While observing the colour given by the flame.
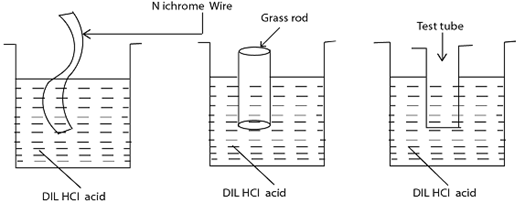
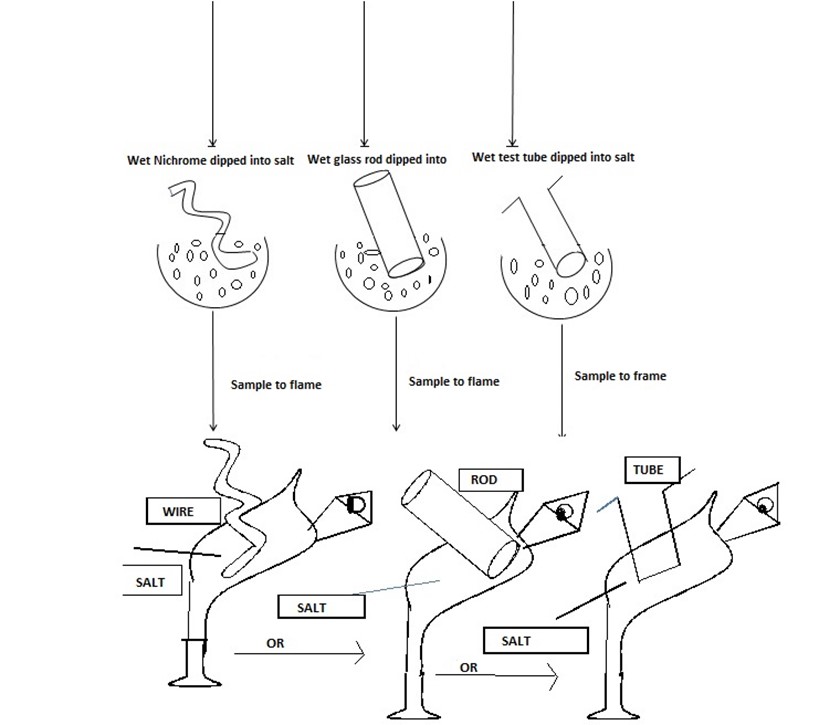
OBSERVATIONS;
Example Blue- Green flame – Cu2+, Green flame-Fe2+,yellow spark-Fe3+,Golden yellow flame-Na+, Lilac/Purple flame-K+, Blue flame – Pb2+,Brickred flame- Ca2+, No specific flame Zn2+,Al3+, Mg2+.
PROCEDURES OF THE FLAME TEST
Refer the diagram below

Consider the diagrams below showing how to perform Flame test
|
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
Green-Apple flame/colour action |
Ba2+ confirmed |
|
Green flame |
Fe2+ confirmed |
|
Blue- Green flame |
Cu2+confirmed |
|
Golden yellow flame |
Na2+ confirmed |
|
Yellow sparks |
Fe3+ confirmed |
|
Blue/Bluish flame |
Pb2+ confirmed |
edu.uptymez.com
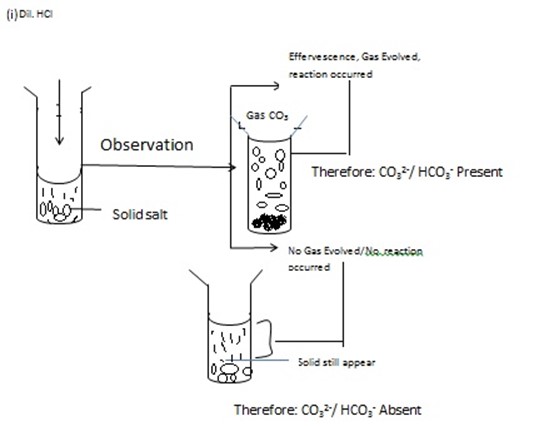
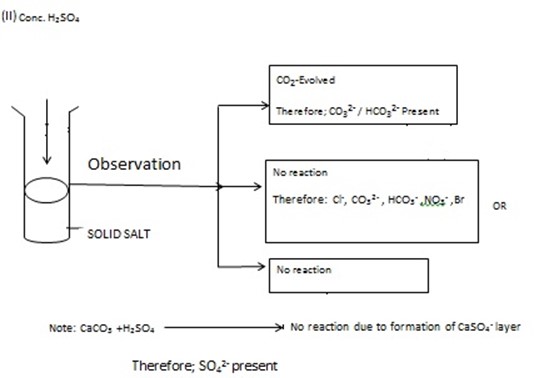
ACTION OF DILUTE HCl, HNO3 OR CONCENTRATED SULPHURIC ACID [con.H2SO4] ON SOLID SALT IN DRY AND CLEAN TEST TUBE
Take the solid salt put into the clean and dry test tube, and then Add either dilute HCl or con.H2SO4 or dil.HNO3 then observe what happened. Hydrochloric acid –HCl, Nitric Acid – HNO3 and
H2SO4have the tendency to break down radical such as CO32- OR HCO3– then form CO2– carbon dioxide which give off Effervescence. But on additional of con.H2SO4or HNO3 (dil) or dil. HCl to the salt which have no Co32-/HCO3– No Co2. Evolved probably other gas
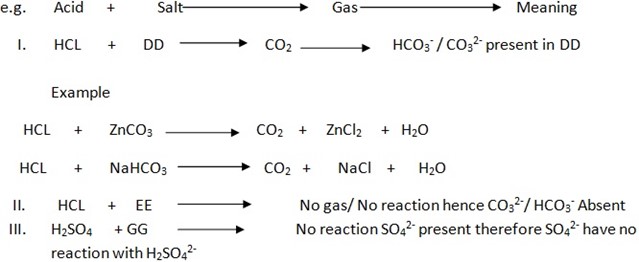
PROCEDURES DURING ACTION OF ACID ON SOLID SAMPLE [SALT] BY USING ACID
[Dil. HCL, H2SO4, dil.HNO3]
You have been given with salt JJ, KK, and LL . examples ACIDS ADDED TO SOLID SALT
RESIDUE TEST [Identify cation Example Zn2+, Cu2+ etc.
Take the given salt sample put it into the test tube then heat until no changes occurs. The test tube should be clean and dry on doing the residue test. Note that some of the salt doesn’t decompose.
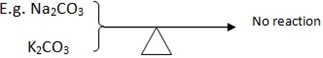
- These salt – CO32- of group I (alkaline metal) are stable on heating so they don’t decompose at all
edu.uptymez.com
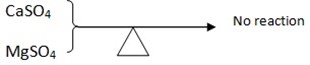
- These salt of group II (Alkaline metal) their Sulphates – SO42- are very stable
edu.uptymez.com
Illustration
OBSERVATION;
- Blue- Residue turn black- CuO cation- Cu2+
-
No colour E.g. MgO , Al2O3 etc
edu.uptymez.com
PROCEDURES FOR THE RESIDUE TEST
You have been given with salt sample solid WW, MM and TT.
|
|
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
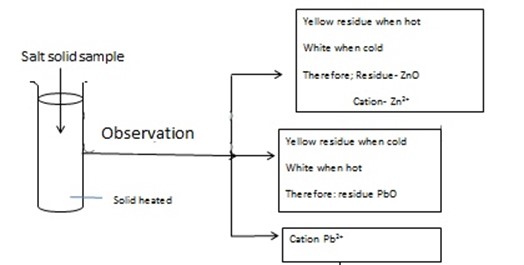
|
Residue was;-WW Yellow -hot but on cooling (cold) – turn white Residue WW – ZnO ↓ Cation → Zn2+ |
Zn2+ confirmed |
|
|
Residue MM was ;- Yellow-cold and white-hot Residue MM- PbO ↓ Pb2+
|
Pb2+ confirmed |
edu.uptymez.com
POSSIBLE QUESTION
Solid PP was White on heating gave yellow ─ Residue When hot on cooling become White PP was;-
- ZnCO3
- ZnO
- ZnCl2
edu.uptymez.com
TEST IN THE SOLUTION
This is the second stage of the Qualitative analysis which the test is done in the solution form.
Example –Take the salt given then put iit into the beaker or Test tube then add distilled water in order to obtain the solution.
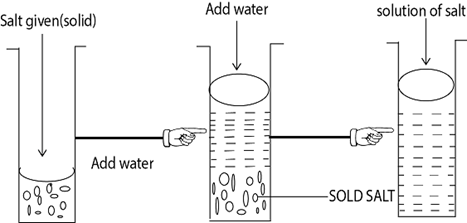
Note; AA – Known as mother solution (M.s) or stock solution/original solution
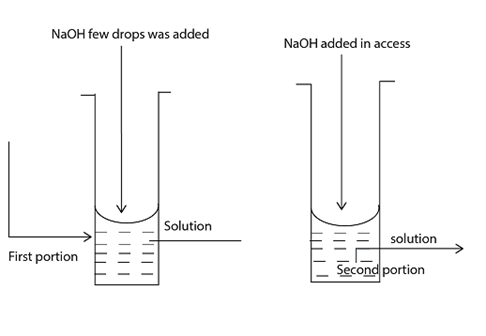
Then you can divide the solution into the different solutions E.g. First solution, second solution Third solution, then you can add given reagent such as NaOH, NH4OH etc
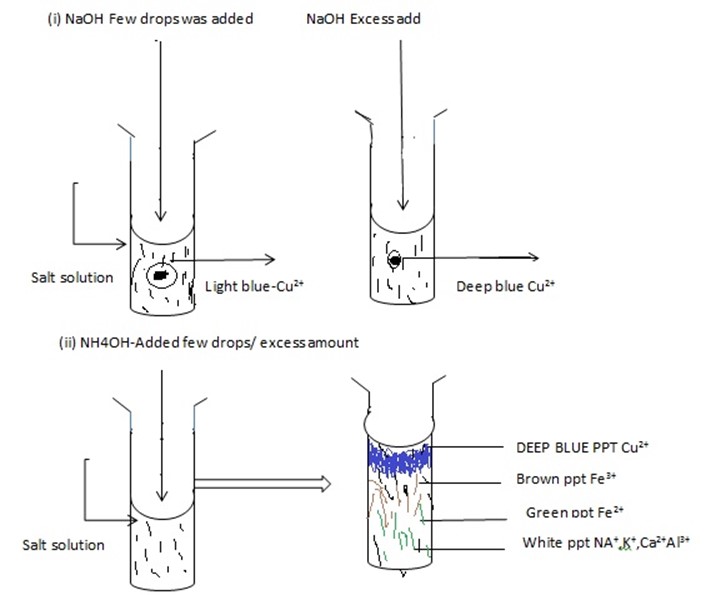
NaOH +CuCl2→CU (OH) 2 + Nacl
- NH4OH + Cuso4→ Deep – Blue ppt
edu.uptymez.com
NH4OH + Cuso4→ Cu (OH )2 + (NH4)2SO4
- NaOH + solution → Green ppt -Fe2+
edu.uptymez.com
NaOH + Fe (NO3)2 → Fe (OH)2 + HNO3
OBSERVATION;
Brown ppt -Fe3, Na+, Ca2+, NH4+, K+ White ppt
PROCEDURES DURING THE TEST IN SOLUTION
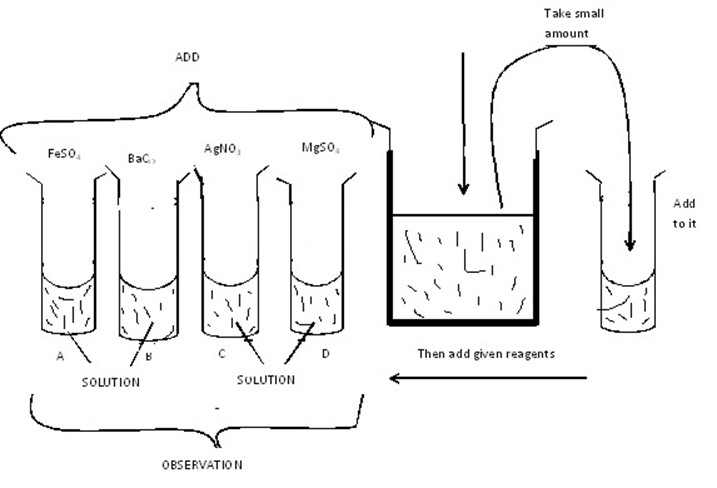
You have been given with the salt RR, FF.
Take the salt dissolve into the given distilled water in order to obtain the solution. This solution can be divided into the different solution named first, second, third etc.
The following solution, solution (reagent) can be Added to the prepared solution;-
- Sodium hydroxide – NaOH
- Ammonium hydroxide / Aqueous solution – NH4OH
-
Potassium hexaferrocynide
edu.uptymez.com
|
S/N |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
|
Deep blue ppt |
Cu2+ confirmed |
|
|
Green ppt |
Fe2+ confirmed |
|
|
||
|
|
Brown ppt |
Fe3+ confirmed |
|
|
White ppt |
Na+, Ca2+, Al3+, K+ confirmed |
edu.uptymez.com
THE MAIN AIM OF THE ADDITIONAL OF SODIUM HYDROXIDE ─NaOH or NH4OH TO THE ORIGINAL SOLUTION (O.S) or STOCK SOLUTION (S.S) OR MOTHER SOLUTION (M.S)
The aim is to identify the cation in the solution given, and then observe what occurred into the solution you make.
CONFIRMATORY TEST
This is the third stage and lastly stage of the Qualitative analysis which can be used to determine or identify the specific cation or Anion present in the unknown given salt. Each cation or Anion has the specific confirmatory reagent used to identify them.
E.g. IDENTIFICATION OF ANION
|
EXPERIMENT |
OBSERVATION |
INFERENCE |
|
To a sample solution AgNO3 is added followed by dil. HNO3 solution then excess ammonia solution |
White ppt insoluble in HNO3 but soluble in ammonia solution |
Cl– present and confirmed |
|
A sample solid is mixed with manganese dioxide and conc. H2SO4 added and warmed |
Greenish yellow gas with a pungent smell is (Cl2) is given out which turn a moist Kl– starch paper blue |
Cl– present and confirmed |
|
To a solution of sample dil. HCl is added followed by BaCl2 solution |
White ppt insoluble dil. HCl is formed |
SO4-2 present and confirmed |
|
To a sample solution add fresh prepared ferrous sulphate solution followed by carefully addition of conc. H2SO4 along the side of the test tube |
Brown ring is formed |
NO-3 present and confirmed |
|
For insoluble carbonate add dil. HCl |
colourless gas forming lime water milky effervescence evolved |
CO3-2 present and confirmed |
|
To a sample solution in water MgSO4 is added, boiled if ppt not formed |
White ppt in cold |
CO3-2 present and confirmed |
|
White ppt after warming |
HCO3– present and confirmed |
edu.uptymez.com
(i)In-A-Solution
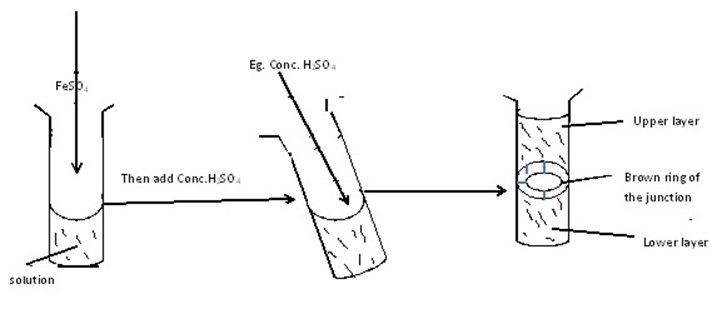

(ii)In-D-Solution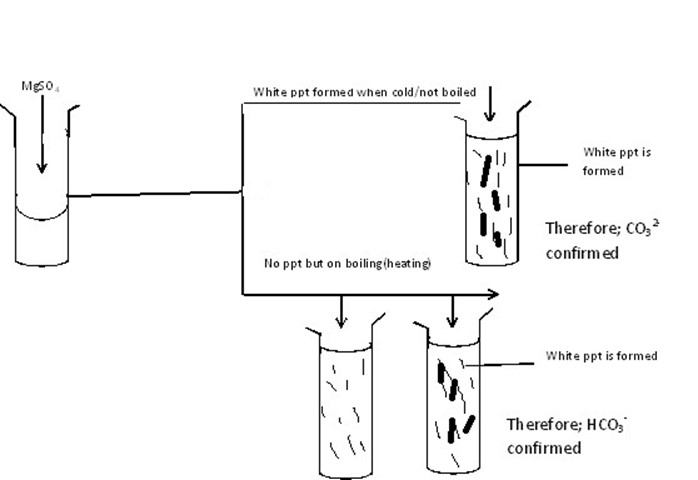
COMMON SALTS IN THE QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
You must be familiar with the following salts
(a)Ammonium salts
Example;
- Ammonium chloride – NH4Cl
- Ammonium Nitrate – NH4NO3
- Ammonium sulphate – (NH4)2SO4 etc
edu.uptymez.com
(b) Iron salts
Example;
- Iron II chloride – FeCl2
- Iron III chloride – FeCl3
- Iron II sulphate – FeSO4
edu.uptymez.com
(c) Calcium salts
Example;
- Calcium chloride -CaCl2
- Calcium carbonate – CaCO3
edu.uptymez.com
(d)Sodium salts
Example;
- Sodium carbonate – Na2CO3
- Sodium bicarbonate – NaHCO3
- Sodium sulphate – Na2SO4
- Sodium Nitrate – NaNO3
- Sodium chloride – NaCl
edu.uptymez.com
(e)Zinc salts
Example;
- Zinc carbonate – ZnCO3
- Zinc sulphate – ZnSO4
edu.uptymez.com
(f)Copper salts
Example;
- Copper II sulphate -CuSO4
- Copper II chloride -CuCl2
- Copper II Nitrate -Cu(NO3)2
- Copper I sulphate – Cu2SO4
edu.uptymez.com
(g) Lead salts
- Lead chloride – PbCl2
- Lead Nitrate – Pb(NO3)2
- Lead sulphate – PbSO4
edu.uptymez.com
(h) Potassium salts
- Potassium chloride – KCl
- Potassium carbonate – K2CO3
edu.uptymez.com
NOTE
You should be able to;-
-Use the qualitative Analysis sheet
-Know the Appearance of the salt
-Know the flame test
-Identify the cation, Anion
-Know how to write down the chemical formula of the compound.
-Write down the balanced chemical Equation Which take place or occur during practical
-Prepare the solution of the salt etc