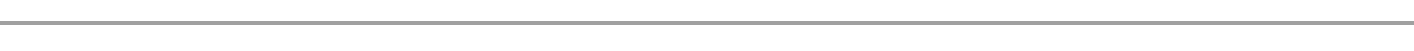INTRODUCTION
Soil is a top layer of earth’s surface. It is made up of broken down rock particles, rotted plant materials, water and air. It is a medium in which plant grow and derive moisture and nutrient.
Soil chemistry– is the study of various chemical nutrient present in soil and their influence on the properties of soil such as alkalinity or acidity
OR
Is the study of the soil to show its physical and chemical properties and components of the soil including biological and fertility property.
SOIL FORMATION
This is evolution of soil from parent material. The formation of the soil particle is regarded to the result from the combination of the waste products, or dead organic matter, water, and air which combines to form the soil.
These processes are continuously and take place through the action of weathering on the parental rock.
Mineral matters
These are substances which are considered to result from the weathering process.
With an exception of nitrates, all salts originate from the mineral. Nitrates originate from the humus.
Mineral matter in the soil are said to be derived from the weathering process – breaking of the rocks which form the earth’s crust.
Weathering
This is the process which the parent rocks undergo disintegration (breaking) down to form the fragments or small particles. Weathering process is a combination of disintegration and synthesis (building up process).
It involves series of complex change that alter form of colour, texture, and composition of rock particles. The rock first broken down to smaller fragment and eventually into individually constituent minerals
These fragments can combine with dead organic matter to form a soil layer
Agents of weathering
The agents of weathering are the factors that facilitate the weathering process. They include;
- oxygen
- water
- wind
- temperature
- plant roots and animal
- Ice.
- Human being
edu.uptymez.com
Types of weathering
There are;
- Chemical weathering.
- Physical weathering
- Biological weathering.
edu.uptymez.com
Biological weathering
This is the process in which the parent rocks break down into the fragments by the help of animals and plants.
Example; Plant roots, when penetrate through the depression in the rocks, on expanding causing the rock undergo disintegration; finally the rock gets a fault.

Also the group of animal when passing in the same area frequently and the burrowing animal they can cause weathering in the soil. 
Physical weathering
This is the disintegration of rock materials without any change in its chemical composition. It is common in area with little vegetation and area with wide temperature range, in this weathering process the parent rocks break to form the fragments due to the physical factor.
These factors are; temperature, wind, moving ice, water and earth quakes.
Earthquake
When the earthquake occurs, causes the vibration of the rocks within the soil, which finally collide with each other to form the fragments which combine with other substances then soil is formed
Moving ice
Moving cold ice on falling on warmed-up rock surface causes the rock to undergo suddenly contraction finally soil particles are formed due to the combination of the weathered materials.
Wind
The strong winds may cause the stones /rocks to collide with each other as the result of collision occur which leads to fragmentation.
Ways through which physical weathering takes place
- Pressure release
- Exfoliation
- Frost sheltering
- Crystallization
- Biological weathering.
edu.uptymez.com
Chemical weathering
This is the breaking down of rock by chemical alteration of a constitute minerals. The chemical weathering occurs due to the chemical reaction in the soil which destroys the internal structure of a rock. It commonly in warm and wet area, the main agents of chemical weathering is water and acid.
The ways through which chemical weathering takes place;
- hydrolysis
- dissolution
- oxidation
- Carbonation.This is the process whereby underground rock change its form by weak carbonic acid which is found in rain water. The rock such as limestone is changed into calcium bicarbonate which is weak to physical barrier.
edu.uptymez.com
- Hydrolysis.
edu.uptymez.com
This is the process in which the substance are broken down by the help of water. When the parent-rocks become into contact with water they disintegrate to form the soil particles.
- Dissolution.
edu.uptymez.com
This is the process which the substance dissolves of a solid substance solvent to make a solution. Hence the large rock they become small particles which combine with organic matter to form soil.
- Oxidation.
edu.uptymez.com
This is the gain of oxygen or loss of electrons. This occurs in the rock which is in iron state when they exposed to water and oxygen, oxidation takes place, they change into iron (iii) oxide (rust) form which are weak and easily to be destroyed by any physical barrier.
FACTORS WHICH AFFECT THE SOIL FORMATION
They include;
- Parent rock
- Temperature
- Rainfall
- Age of the rock
- Slope
- Nature of the parent rock.
edu.uptymez.com
The hardest parent rocks can not undergo disintegration quickly than the soft parent rocks which break down quickly and lead to the formation of fragments which finally combine with the dead organic matter to form the soil. So the soft parent rocks can lead to the formation of soil particles easily than the harder one which delay to form soil particles.
- Rainfall
edu.uptymez.com
The place which there are high rainfall, the rate of the soil formation becomes highest than the regions in which there are low rainfall. The reason is that rainfall, contributes more in the decomposition of the dead organic matter which finally combine with the other particles to form a soil layer.
- Temperature
edu.uptymez.com
The region with the highest temperature, rate of formation of the soil becomes very high because high temperature on heating the rock-surface causes it to expand but suddenly when the rock surface cools down- contract, these expansion and contraction they led to weathering of that rock. The formed fragment combines with other materials to form the soil.
- Age of the rocks Normally the oldest rocks can’t undergo disintegration as easy as soft rocks, which disintegrate fastest to form the soil particles
edu.uptymez.com
PLANT NUTRIENTS
These are the soil nutrients which are required by the plants for proper growth, productivity and protection against diseases. Some are needed for enzyme making and hormone including protein making. The one among characteristic of fertile soil is to give all plant nutrient in proper amount.
Plant nutrient they come from the parent rock during soil formation and other through manure and fertilizer.
Example of plant nutrient;nitrogen, iron, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, manganese, cobalt, phosphorous, boron, Chlorine, etc
Types of plant nutrients
There are two types of plat nutrient which are the following
- Micro nutrients or trace element
- Macro nutrients or bulk element
edu.uptymez.com
MACRO PLANT NUTRIENTS
These are nutrients required in by plant in large quantities for the proper growth of plant. They are categorized in two groups which are primary and secondary macronutrient.
Primary macronutrient they are required in relativity large quantity. They include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). Most used for the synthesis of hormones and proteins.
Secondary macronutrients are macronutrients that are required in a relatively small quantity if you compare with primary macronutrient. They include iron(Fe) , Hydrogen(H) , Oxygen(O) , carbon( C), Magnesium (Mg) , Calcium(ca), Zinc(Zn).
ROLE OF MACRO NUTRIENT
They are required in the following,
- Synthesis of the hormones which are required for the different metabolic activities. E.g. plant hormones- auxins, gibberillin hormone, ethylene hormone, absiscic acid hormone.
- Synthesis of the protein which help to promote the growth.
edu.uptymez.com
MICRO PLANT NUTRIENT
These are nutrients required by plant in small quantities. These nutrients are needed in small quantity, it doesn’t mean they are not needed, if they are absence in plant, this will affect their proper growth.
Examples of micronutrient are Cobalt (Co), Boron (B), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mb) Copper (Cu), etc.
ROLE OF MICRO NUTRIENTS
They are required to synthesize enzymes. Enzymes are required to control some of the metabolic activities such as digestion, respiration, required for energy production.
MANAGE AND LOSS OF PLANT NUTRIENT FROM THE SOIL
LOSS OF PLANT NUTRIENT
Plant nutrient are important in the soil for proper growth of plant. Plant nutrient they are found either natural or through applied. Sometimes soil can loss a nutrient naturally or through human activities, through the following the loss of soil nutrient occurs;
- Soil erosion
- Leaching
- Bad agriculture practice
edu.uptymez.com
SOIL EROSION
This is the removal and movement of the top soil layer from one place to another by the help of the soil erosion agent.
Agents are;
– Wind
– Water (removes top soil layer from one place to another)
– Animal.
Effects of soil erosion
- May cause loss of soil fertility since can remove top soil layer which is more fertile.
- May cause deposition of waste to the water bodies.
- May cause death to occur since soil organisms carried away then deposited into water.
- May cause galley.
edu.uptymez.com
Causes of soil erosion
They include;
- Overstocking.
- Cultivation along hills
- Deforestation
- Monoculture.
- burning of forest
edu.uptymez.com
• Overstocking
The excess stock farming in the small area cause the destruction of the soil structure hence soil erosion can occur easily because soil particles become loosely packed.
- Cultivation along the hill.
edu.uptymez.com
This allows moving water to collect and remove the soil particles away from the top hill downward hence soil erosion.
- Deforestation
edu.uptymez.com
This is the process of cutting down trees from the forest without planting other trees. Trees are cutting down for various uses such as for furniture, charcoal etc. this causes the land to remain bare. And this leads to the erosion agents carrying the soil away.
- Monoculture
edu.uptymez.com
This is the process of growing one type of crop each season. This causes the destruction of the soil structure and the soil particles become loosely packed, then the erosion agents can remove the soil easily.
• Burning of forest
This cause the land to remain bare, destruction of mineral salts, killing of organisms, (plant and animals in the soil) if this occurs, the land remains bare for the agents of erosion to remove soil particle which contain the plant nutrient from its area.
Prevention of soil erosion
They include
- Contour farming
- Afforestation
- Reforestation
- Destocking
-
Terracing.
METHOD TO PREVENT LOSS OF PLANT NUTRIENT
- Contour farming.
edu.uptymez.com
This prevents movement of water along the hills; hence provide the resistance of moving materials downward. These prevent loss of nutrient through soil erosion.
- Afforestation
edu.uptymez.com
This is the process of planting vegetation’s in the open space (desert). This prevents the soil erosion because branches of the trees become as wind barriers so the soil particles are not carried away.
- Reforestation
edu.uptymez.com
This is the process of replanting the trees in the forests; involve a campaign of cut tree and replant tree. This helps to keep the soil erosion agents away from the soil
- Destocking
edu.uptymez.com
It involves the reduction in the number of the stock in the certain place. This help to reduce the destruction of the soil structure, finally soil erosion.
• Terracing
This is the process of constructing the embankment. An embankment help to provide the resistance against moving materials, hence soil erosion is prevented.
GOOD AGROCHEMICAL METHODS.
These are good agricultural methods.
Example
- Crop rotation.
- Fallowing
- Liming
- Mulching
- Cover crops.
edu.uptymez.com
Crop rotation
This is the process planting the different types of the crops on the same piece of the land one season to the next.
Example
Three years crop rotation. Consider the rotation below showing three consecutive years.
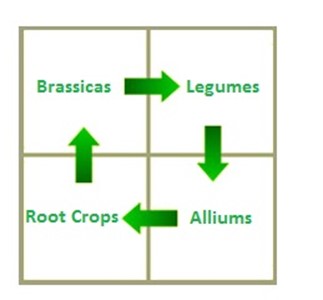
LEGUMINOUS PLANT
These are plants which have root nodules containing rhizobium bacteria. E.g. pea, beans groundnut
Consider the diagram below;
 
Principles used in the crop rotation:-
They include;
- Must involve different types of crops
edu.uptymez.com
e.g. beans , millet , rice(paddy), potatoes.
- Leguminous plants should be involved.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. ground nuts, beans, potatoes.
- Shallow and deep rooted plants should be involved.
edu.uptymez.com
Advantages of the leguminous plants to the farmer (gardener)
- Allow the nitrogen fixation.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. N2 to NO3–; the formed nitrate help to increase the soil nutrients; since the plant need nitrogen to make protein and hormones
- Help to maintain the soil structure since they help to make the soil soft and spongy.
- Help to prevent the soil erosion since some of the leguminous ground on the soil horizontally.
edu.uptymez.com
Advantages of crop rotation to the farmer
- Help to destroy the plant pests, the plant causing diseases. This occurs if the planted plants have no quality that can satisfy the pests. If no satisfaction, the pests can move away from the plant or death may occur.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. if the former insect loving to eat cotton leaves and nowadays they don’t like cotton leaf they should die to hunger.
- Favour or allow the recycling of the plant nutrients within the soil at different level. This becomes advantageous to the shallow rooted plant
edu.uptymez.com
Where
- Recycling of the nutrients from the down soil.
- Plant mineral soil absorbed by the plant root.
- Help to increase soil fertility since other have no nodules containing bacteria for nitrogen fixation.
edu.uptymez.com
 Advantages of deep rooted plant
E.g. bean, cotton
- Allow the circulation of the nutrients to the soil at different levels.
- Help to maintain the soil structure since some of the plants have extensive roots which can hold the soil firmly.
- They can allow nitrogen fixation
edu.uptymez.com
Fallowing
This is the cultivation of the soil and then leaving it without planting of any crops.
ADVANTAGES OF FALLOWING
- Help to increase soil fertility, since allow time for recycling of the nutrients
- Allow the time for the weathering and then deposition of the weathered materials to occur.
- Help to remove the occurrence of the plant pest, since some of them will escape during the time of fallowing.
edu.uptymez.com
MULCHING
This is the process of covering the top soil by using the mulching materials.
Mulching is commonly used by the gardeners who grow the vegetables.
Consider the diagram below for illustration;

MULCHING MATERIALS
These are the materials used for the mulching process. Example grasses, banana leaves, ground nut leaves.
Advantages of mulching to the farmer
- To help increase soil fertility.
- Help to reduce soil erosion. E.g. erosion caused by wind.
- Help to keep the moist in the soil since they prevent evaporation from the soil.
edu.uptymez.com
Disadvantages
of mulching
- Mulching materials can catch fire then causes the destruction of the crop in the field.
- Mulching materials can welcome (attract) ants that destroy crops.
edu.uptymez.com
Cover crops
Grow horizontally on the soil surface. The crops which can grow on the soil surface horizontally.
E.g. Ground nuts, beans, pumpkins.
Advantages of the cover crops
- Reduce or control the soil erosion.
- Help to keep the moist in the soil.
- Promote nitrogen fixation.
- Allow the recycling of the nutrients since some of them have deep roots searching for nutrients downwards.
edu.uptymez.com
NOTE:
Do not plant excess cover crops in the field since some of them have extensive roots so can bring competition with other plants, finally led to the fall of productivity.
CONSUMPTION OF NITROGEN BY THE PLANTS
Although the plants use or consume nitrogen for making their protein plant, they do not use nitrogen as a molecule- N2. Why?
This is because nitrogen is insoluble therefore cannot be absorbed by the plant roots when occur in molecular form. So the plants convert the nitrogen into soluble nitrates, which becomes easily absorbed by the plant roots.
MANURE AND FERTILIZER
MANURE
This is the organic compound which contains and supply plant nutrients required by plant for proper growth, productivity and protection against diseases.
Common manure used in Tanzania;
- Kraal manure
- Farmyard manure
- Green manure
- Poultry manure
- Composite manure.
edu.uptymez.com
Advantages of manure to the farmer
- Supply all plant nutrients required for the growth and development but fertilizer do not since selective.
- It is cheap. Unlike fertilizers which are very expensive to the extent that farmers can not afford.
- Manure helps to maintain the soil structure but fertilizers do not.
- Less expertise is required for the use of manure unlike the use of fertilizers which requires more knowledge.
- Manure can support microbial activities.
- Manures help to maintain soil color
- Manure helps to keep the moisture in the soil
- Manures last long when kept on soils.
-
Manures do not cause soil acidity.
FERTILIZER
edu.uptymez.com
Fertilizer is chemical substances (inorganic compound) which contain the nutrients which required by plant for growth, productivity and protection against disease.
Example
- Urea
- Ammonium nitrate
- Ammonium sulphate.
- Calcium phosphate
- Calcium nitrate.
- NPK( nitrogen phosphorous and potassium)
edu.uptymez.com
Types of fertilizers
There are three types of fertilizer which are;
- Straight fertilizer
- Compound fertilizer
- Complete fertilizer
edu.uptymez.com
(i) STRAIGHT FERTILIZER
This is the fertilizer which contain one of the main plant nutrient e.g. It contains N, P and K. there are three types of straight fertilizer.
- Nitrogenous fertilizer
- Phosphorus fertilizer and
- Potassium fertilizer
edu.uptymez.com
NITROGENOUS FERTILIZER
These are the fertilizer which have or contain the nitrogen as only primary macronutrient.This fertilizer contains nitrogen than other fertilizers.
Examples of nitrogenous fertilizer
They are;
- Ammonium sulphate
- NPK
- Ammonium nitrate
- CAN
edu.uptymez.com
Properties of nitrogenous fertilizer
- They contain a lot of nitrogen
- They can scorch or burn the plant since some of them are acidic in nature e.g. S.A
- They can cause the accumulation of toxic substances in the soil. E.g. unwanted elements can settle within the soil
edu.uptymez.com
Effects of the repeatedly use of nitrogenous fertilizer in the field.
They include;
- They cause the soil acidity e.g. since some of them are acidic in nature
edu.uptymez.com
Examples ammonium sulphate
-
They cause the accumulation of poisonous and toxic elements to the plants.
CONSUMPTION OF NITROGEN BY THE PLANT
edu.uptymez.com
Although the plants use or consume nitrogen for making their protein plant, they do not use nitrogen as a molecule- N2. Why?
This is because nitrogen is insoluble therefore cannot be absorbed by the plant roots when occur in molecular form. So the plants convert the nitrogen into soluble nitrates, which becomes easily absorbed by the plant roots.
(ii) PHOSPHATE FERTILIZER.
This is the fertilizer which contains phosphate or phosphorus in large quantity than the other primary macronutrient.
Example; Calcium phosphate – Ca3 (PO4)3.This fertilizer supply phosphorous in high amount or percentage
(iii)COMPLETE FERTILIZER.
This is the types of fertilizer which contains all plant nutrients (main). The fertilizer contains all plant nutrients N, P, K.
Percentage composition of the element in the fertilizer
This helps the farmer to know how much fertilizer to buy for the fulfillment of the field requirements.
Choice of fertilizer
This depends on
- Cheapness of the nutrient
- Soil requirement
- Nature of soil.
edu.uptymez.com
APPLICATION OF FERTILIZERS IN THE SOIL
Methods of adding fertilizer they are depend on the type of fertilizer applied, time for application and nature of the soil. The method of applying a fertilize include
- Placing
- Broadcasting
- Band strip
- Spraying.
edu.uptymez.com
Time of application of manure or fertilizer
They include
- Top dressing
- Basal dressing
edu.uptymez.com
(i)BASAL DRESSING
Is the application of the fertilizer/ manure in the field before seed planting and germination occurs.
This sometimes may occur depending on the nature of the soil and the soil plant requirements.
(ii)TOP DRESSING
This is the application of the fertilizer in the field after seed germination. This also depends on the nature of the soil.
(iii)PLACING
In these method which the fertilizer/ manure is placed about certain distance from the plant stem. Fertilizer applied in this method are nitrogenous fertilizer because they dissolve easily to avoid scorching effect in plant.
E.g. the soil is dug about 6-9cm from the plant stem.
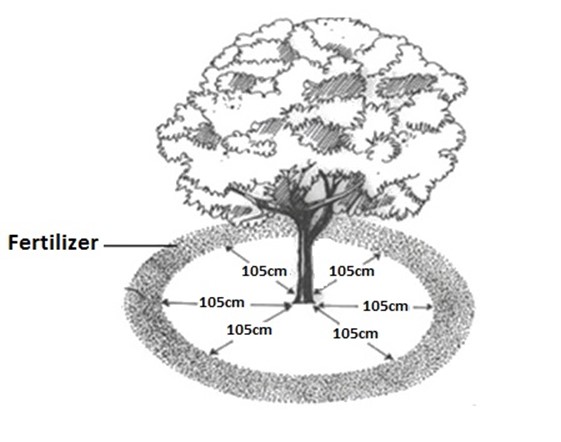
(iv)BROADCASTING
These method involve the spreading the fertilizer over the soil surface. Mainly applicable before planting and nitrogenous or potasic fertilizer applied in these method.

(v)BAND STRIP
These are the method of applying the fertilizer in rows. This occurs when the plants are planted in a straight line or in rows.
(vi)SPRAYING OR AERATION
This is the method of spraying the fertilizer over the soil which occurs in the solution from the powdered fertilizer.
SOIL PH
This is the degree measure of the acidic and basic nature of the soil. The knowledge of soil pH helps us to know the soil acidity or alkalinity.
E.g. Soil can become
- Acidic soil
- Neutral soil
-
Basic soil.
NB: acidic soils supply H+ and basic soils supply OH–
This means that a soil with a high concentration of hydrogen ions become acidic while OH– (hydroxyl) becomes basic.
ACIDIC SOILS
edu.uptymez.com
This is the soil which the concentration of hydrogen ions becomes dominant or excess. Acidic soils have pH less than 7.
BASIC SOILS
This is the soil which the concentration of hydroxyl ion- OH– is dominant or excess. Basic soil has pH greater than 7.
NEUTRAL SOILS
This is a soil with a pH of 7. It occurs when neutralization occurs.
SOIL ACIDITY
This is the condition which the concentration of hydrogen ion H+ in the soil becomes dominant.
TYPES OF SOIL ACIDITY
- Active acidity
edu.uptymez.com
This is the acidity which the pH of the soil becomes less than 1. This acidity is very dangerous to the soil because it can lead to death of the plant
- Potential acidity.
edu.uptymez.com
The acidity which the pH of the soil becomes greater than 1
pH = -log H+
pH is the negative logarithm to base ten of concentration of the hydrogen ion concentration.
E.g. H+ = 4
pH = – log 4
Causes of soil acidity
- Rainfall
edu.uptymez.com
This produce dilutes carbonic acid. H2CO3 or dilute nitric acid.
- Application of fertilizer.
edu.uptymez.com
Some of the fertilizer are acidic in nature, so when applied to the soil they cause the soil to become acidic e.g. ammonium sulphate.
- Soil living organisms.
edu.uptymez.com
These organisms produce carbon dioxide gas the combine with the soil water to form carbonic acid.
- Decomposition.
edu.uptymez.com
This cause production of carbon or nitrogen from dead bodies, which combine with oxygen to form acid
Causes or sources of hydrogen ion in the soil
-
Presence of metal in the soil.
E.g. Aluminium
Al + H2O Al(OH)3 + H+
Where H+ remains free
- Irrigation.
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. irrigation causes the deposition of water into the soil which dissociates to form H+ and OH– .
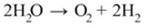
- Acidic compounds in the soil.
edu.uptymez.com
H3PO4 3H+ + PO43-
Sources of the hydroxyl ion in the soiL
They include;
- Alkaline metal
edu.uptymez.com
E.g. Na, K, Ca etc.
They react with water to form alkaline which supply hydroxyl ion- OH– to the soil.
E.g.
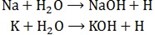
- Irrigation.
edu.uptymez.com
Excessively produce hydroxyl ion which causes the soil to become basic.
Presence of basic component
Liming and lime
Lime –This is the basic /alkaline compound in the nature added to the soil in order to correct soil acidity
Example
- limestone CaCO3
- quick lime CaO
- magnesium oxide MgO
- calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2
-
Magnesium Hydroxide Mg(OH)2
LIMING
– is the additional of the lime to the soil in order to correct (neutralize) the soil acidity.
NOTE – acid + base → salt + water…………. (Neutralization)
CLASSIFICATION OF THE LIMING MATERIALS
They have three natures;
- Carbonate e.g.CaCO3
- Hydroxide e.g. Ca(OH)2
- Oxide e.g. CaO
edu.uptymez.com
Advantages of liming to the farmer
- Help to neutralize the soil acidity
- Help to increase the soil fertility since make the soil in the pellet form consider the soil pH.
edu.uptymez.com
Components of fertile soil
They include;
- Soil living organisms.
- Soil dead organic matter.
- Soil mineral.
- Soil water.
- Soil air.
edu.uptymez.com
SOIL FERTILITY AND PRODUCTIVITY
Soil fertility
This is the ability of the soil to supply plant nutrients which are required for the productivity, growth and protection against diseases.
OR
Soil fertility is the ability of soil supply the essential plant nutrient that plant adequate in available and balance form.
The fertile soil can supply the nutrients which are very important to the plants growth, protection and productivity.
Fertile soil
This is the soil which can supply the nutrients required for the growth, productivity and protection against diseases
CHARACTERISTIC OF FERTILE SOIL
- Rich in basic plant nutrient such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium
- Contain sufficient minerals
- Soil pH range 6.0 to 6.8.
- Contain soil organic matters that improve structure and moisture retention.
- Large amount of top soil
-
Good soil structure
SOIL PRODUCTIVITY
edu.uptymez.com
- Soil productivity is largely determined by its ability to provide water and nutrient, to allow deep rooting of agriculture plant.
- To better understand potential productivity of soil, it important to examine key soil characteristic and indicator such as texture, depth, organic matter and fertility.
-
The measure of productivity is usually crop yield per millimeter of available water
Fertile soil is not necessary productive
edu.uptymez.com
This is due to the following;
- Leaching.
edu.uptymez.com
Is the downward movement of the mineral salt far away from near the plant roots, OR is the downward movement of the mineral salts in the soil far away from near the plant roots.
Leaching maybe caused by water logging so if leaching occur the plant lose its fertility hence it becomes not necessary productive.
- Water logging.
edu.uptymez.com
The soil become water logged if there is accumulation of water within the soil. If the soil become water logged, it causes mineral salts to go more downward finally top soil remain empty.
- climate
edu.uptymez.com
If the climatic conditions is very bad such that there is dryness, the plants in the fertile soil will be affected in case of their productivity, but if there is plentiful of enough rainfall, the plant will grow properly and productivity become high.
- Lack of certain minerals.
edu.uptymez.com
If the plant requires the certain mineral and planted in the fertile soil without the important mineral required, productivity will fall down.
- Type of the crop.
edu.uptymez.com
If the wrong choice made in the plantation of the certain place type of the crop in the fertile soil the productivity falls down.
- Soil structure.
edu.uptymez.com
If the soil structure is not good in the fertile soil, such that no good aeration, water movements than productivity will be affected
How to maintain the soil fertility
They include;
- Good agricultural method
- Application of manure
- Application fertilizer.
edu.uptymez.com