BRANCHES OF ECONOMICS.
There are two main branches of Economics.
- Micro-economics
-
Macro-economics.
MICRO ECONOMICS.
Micro means small. Micro economics refers to a branch of economics which studies the behavior of individual economic units such as; price determination of a commodity (goods), behavior of consumers or producers (firms) etc.
edu.uptymez.com
Micro economics is also termed as the price theory. Micro economics also deals with;
- Price determination in the market.
- How a product is made by the firm (individual) producer.
- How income is distributed.
- How wages, interest, rent and profits are determined.
edu.uptymez.com
IMPORTANCE OF MICRO ECONOMICS
- Helps in explaining the functioning of the free enterprises economy. The working of capital economy is based on micro economics.
- It tells us how consumers and producers make decisions on how to allocate their limited (scarce) resources. They use the marginal approach to determine the part they will gain more.
- It helps in determination of prices of various commodities in the market.
- It explains the conditions for efficiency for both production and consumption.
edu.uptymez.com
MACRO ECONOMICS.
Macro means large. Macro economics analyzes economic problems on national or aggregate basis. Macro economics is also known as the income theory. Therefore Macro economics is a branch of economics which deals with the studies of aggregation and overall performance of the economy such as;
- Total consumption.
- Total employment.
- National income.
- General Price level.
- Consumer price index (CPI).
- Total savings etc.
edu.uptymez.com
It addresses issues like the relationship between inflation and unemployment, effects of deficit in the balance of payment, relationship between money supply and general price level.
Thus for comprehensive economic analyze both micro and macro approaches must be adapted.
IMPORTANCE OF MACRO ECONOMICS.
- Useful in understanding the functions of complicated economic systems such as the Command economy system.
- Useful in the formulation of various economics polices in the country such as the taxation policy.
- It helps to provide solutions to urgent economic problems facing the economy such inflation, unemployment.
edu.uptymez.com
DEVELOPMENT OF ECONOMICS
It studies the principles and problems concerning economic development of the country.
ECONOMIC LAWS.
There are economic statements which show the relationship between economic variables. It shows that a certain thing happens under given economic conditions. It regulates relationship in main economic activities of production, exchange, consumption and nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution.
Lionel Robbins defined economic laws as a statement of uniformity which govern human behavior concerning utilization of resources for achieving of unlimited ends. Example of economic laws is laws of demand and supply.
Therefore economic laws shows tendencies of what happens under given economic conditions thus they express people‘s reaction to economic forces Eg In the example about the laws of demand show that consumer tend to buy more as the price of commodity decreases and suppliers tend to supply more when the price of commodity increase.
Sometimes people believe contrary to the laws e.g under given conditions of exceptional demand people with low income demand more inferior goods at higher price that at lower price.
CHARACTERISTICS OF ECONOMIC LAWS.
- They are not static i.e. they change with time and economic conditions.
- They are hypothetical i.e. they are based on assumptions.
edu.uptymez.com
CLASSIFICATION OF ECONOMIC LAWS.
-
Pure and Natural laws.
These emerged purely from interaction of economic variables such as price and quantity demanded as supply scarcity and choice etc.
These laws can operate in all economic systems. E.g. the laws of demand and supply and the law of diminishing marginal utility.
-
Law of super structure (Government or state law).
These are laws provided by the government or state to regulate or control economic activities. E.g. law of taxation, law of controlling consumption of certain commodities. Law of stabilizing the economy etc.
-
Law of specific economic system.
These are the laws specific to a certain economic system and they control relationship among the people in the process of production, consumption nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution, exchange once a system is replaced by the new system. E.g of specific laws is;
edu.uptymez.com
- Laws of private ownership of means of production.
-
Laws of public ownership of major means of production.
General laws.
These are laws which operate in all economic systems whether socialist or capitalist E.g. Demand and supply.
IMPORTANCE OF ECONOMIC LAWS.
edu.uptymez.com
- Guide economic events and serve as a basis for the formulation and evaluation of economic policies Eg the law of demand and supply. Help the tax authority to fix a rate that will not cause a big increase on price.
-
They are useful in planning process ie planner can forecast implication of various plans by using economic laws of what will happen in production if domestic industries are given subsidizing.
FUNDAMENTAL ECONOMIC PROBLEMS.
edu.uptymez.com
The main central economic problem is the scarcity of resources in relation to unlimited wants.
There are sources of basic economic problems which exist in societies needed to confident three inter-related questions. These are;
-
What to produce.
It is related with the types (ranges) and quantity of goods to produce. Since resources are scarce, we must choose between different alternative collection of goods and services that may be produced.
It also involves the allocation of resources between different types of goods. For example, consumer goods and producer goods .
The decision to this question is unanswered. Differently under capitalist economy it is answered by price mechanism while in planned socialist t is determined by central planning authority and also by mixed economy.
-
How to produce.
This question arise from the basic economic problem that since resources are scarce in relation to unlimited wants, we need to consider how resources are used that the best outcome may arise.
The question requires the determination of the method or techniques, the choice of the techniques of production will depend on the Efficiency and the price of factors of production i.e. the cost of production.
-
For whom to produce.
Since we cannot satisfy all the wants of all the population, decisions have to be taken concerning how many of each person’s want are to be satisfied i.e. it involves who should get how much. However the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution will depend on the economic system of socialist, capitalist economic system.
edu.uptymez.com
In some economies the deliberate attempt to create policies that re-distributes wealth and income from rich to poor. This could be through the adaption of progressive taxation system.
In other economies there are no such policies and qualities of wealth and income usually based up on inheritance remain extreme.
Answering this question moral aspect of decision making become important.
-
Where to produce.
The producer has to make decision regarding the place where the firm has to be located. The location of the firm depends on the;-
edu.uptymez.com
- Availability of the means of transport and communication, power and water supply.
- Supply of labor.
- Availability of banks, hotels, schools, and hospitals etc.
edu.uptymez.com
-
When to produce.
A producer must also decide the right time to produce a given commodity.
-
How much to produce.
It relates to mankind decision regarding the quantity or amount of the commodity to be produced.
The answer to the above problem is determined by different economic systems.
- In socialist economy, the use of central planning authority.
- In capitalist economy, the use of price mechanism.
-
In mixed economy, the use of both methods.
SCARCITY AND CHOICE
edu.uptymez.com
Other decisions on economic problems centers round the two basic concepts, scarcity is useful to understand them more clearly.
Scarcity: – The scarcity implies limitlessness in supply therefore; when we say the resources of a country are scarce it means that the resources are limited in supply.
A resource is said to be scarce when there isn’t enough of it to satisfy all the people‘s wants, but if;
- Economic goods and services are scarce in the sense that is not available in sufficient of zero prices. If something is so abundant that we can have all we want without paying for it is not a scarce commodity e.g. Air under ordinary circumstance is not scarce.
- Economic goods and services are scarce relatively to the people‘s desires for them.e.g. There are more good bananas than bad banana, but it is good bananas which are scarce because it is the good one which people desire to consume.
-
The scarcity of economic goods and services arises from scarcity of resources such as land, labor, capital and entrepreneur used to produce them.
edu.uptymez.com
NOTE
Regarding the problem of scarcity we must be very clear in our minds that it is found in all countries whether it may be poor or rich country. However the form scarcity here is used in relative sense of resources is limited in relation to man’s wants. In this sense if it is true for a rich and developed country thus scarcity is a fundamental problem and universal in nature.
Because of scarcity in resources, we must choose from among the many wants and whenever we choose we must force go satisfying. Some economists defined economics as a study of how people choose to use their scarce resources in attempt to satisfy their unlimited wants. Since there are insufficient productive resources in the world, therefore man is left to find the solution to that problem and the first option is to economize, that is to make the best and efficient use of the resources available without any wastage.
A SCALE OF PREFERENCE
Is a sort of list of all unsatisfied wants arranged in the order of importance. In the scale of preference the most pressing wants are placed on top while the less pressing wants are placed at the bottom.
OPPORTUNITY COST
If has been observed that in reality, scarcity leads to the problem of choice and once we choose we must go without others.
Satisfaction of one’s must involve foregoing something else. Therefore the opportunity cost of real cost of satisfying any wants is the alternative that has to be foregone in order to do so.
That is the real cost of satisfying anything in the alternative that has to be forgone. In simple language opportunity cost is the sacrificed alternative in deciding to do one thing and not the other.
-
Human wants are unlimited while the means to satisfy them are limited. Therefore one has to choose what want to satisfy because one cannot satisfy all wants due to scarcity of resources.
Usually one satisfies the most pressing wants before satisfying the less pressing wants.
The sacrificed goods are thus the real cost or opportunity cost of satisfying the wants that are sacrificed.
E.g. If you had to choose between leisure and work, sacrificing leisure then the real cost or opportunity cost is very useful in the process of planning especially in the question of resources allocation. When we choose to allocate more resources to production of consumer goods we are necessarily forced to the reduce the allocation of resources to the production of producer/ investment goods.
PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY FRONTIER OR CURVE (PPF OR PPC)
edu.uptymez.com
A production possibility
curve is a curve representing all possible combinations of total output that could be produced by the economy when its resources were fully and efficiently utilized under a given state of technology.
The production possibility curve is also known to other economist as production possibility frontier or Boundary.
The concept of production possibility curve helps to explain the concept of scarcity and opportunity cost.
The following are the assumptions of the production possibility curve;
- The resources are fully and efficiently utilized.
- There is a constant state of technology.
- Only two commodities are being produced.
- The amount of resources is fixed.
edu.uptymez.com
Given that the resources and technology are fixed, we can produce more of every commodity from the resources which can be used to produce more of another commodity.
In the production possibility curve, since the resources are scarce, we are forced to choose between production of capital goods and consumer goods. Sacrificing the production of consumer goods. Thus the opportunity cost of more capital goods is the consumer goods that we have to sacrifice.
GRAPH OF PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE
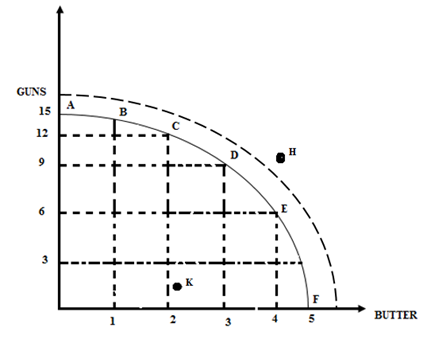
From the graph, we learn that the shape of the production possibility curve is concave to the origin. Because there must be the decrease in output of guns in order to add more unit of butter e.g. To produce one unit of butter we have to foregot one unit of gun i.e from A to B.
This is called the marginal rate of technique substitution of butter for gun and it goes on increasing.
If the economy devoted all its resources to the production of gun it can produce 15 thousand guns but the production of butter will be zero.
Therefore if we decide to produce 1unit of butter we have to produce 14 units of guns.
From the graph therefore we learn that if butter we want to produce more butter we have to reduce the output of guns and vice verse i.e. we can transform guns into butter or butter into guns.
The point on the boundary of PPC i.e. A, B, C, D, E and F represents the combination of goods that can be produced using the country’s available resources and technology.
Any point inside the boundary say K is one from the diagram it shows inefficiency of which may be under utilization or unemployment of the countries resources.
From point A to point F, it indicates the increase in the production capacity of the economy. The new graph tells us that economy can now produce large quantity of output.
Point H on the graph indicates unattained point of which it is outside the PPC .point K will be attained when the economy increases its production leading to the shift of the PPC from its original position to point K.
- How choice, opportunity cost and scarcity are shown on the PPC.
edu.uptymez.com
Choice is indicated by selecting any point on the PPF. When resources are fully utilized i.e. a,b, c,d,e and f.
Opportunity cost is indicated by movement along the PPF i.e. a, b, c, d, e and f. e.g. The opportunity cost of producing 15 units of guns is the 0 unit of butter that you forego at full employment of the resources.
Scarcity is indicated by point H which has not been attained. It will depend on the expansion of the production in the economy.
In order to move the economy from the current production possibility curve to the outer production possibility curve, the economy has to;-
- Increase in the stock of its resources.i.e. To increase the quality of labor, land, capital and entrepreneurship.
-
Improve the state of the technology to more advanced methods in order to find move output of maximum cost of production of capital.
DIAGRAM FOR INNOVATION OF NEW RESOURCES
edu.uptymez.com
In some other cases the PPC curve tends to shift inwards, this signifies the decline of the economy which may be due to;-
- Exhaustion of the economy’s natural resources such as land.
- Working population is falling.
- Technology available was changed.
- Underemployment of the resources of a country of which some of the resources are left idle.
edu.uptymez.com
SHAPES OF PRODUCTION POSSIBILITY CURVE
The graph is concave to the origin due to the law of diminishing return, as resources are transformed from goods A to goods B the extra out of B becomes successively smaller while the amount being sacrificed in A becomes large and large.
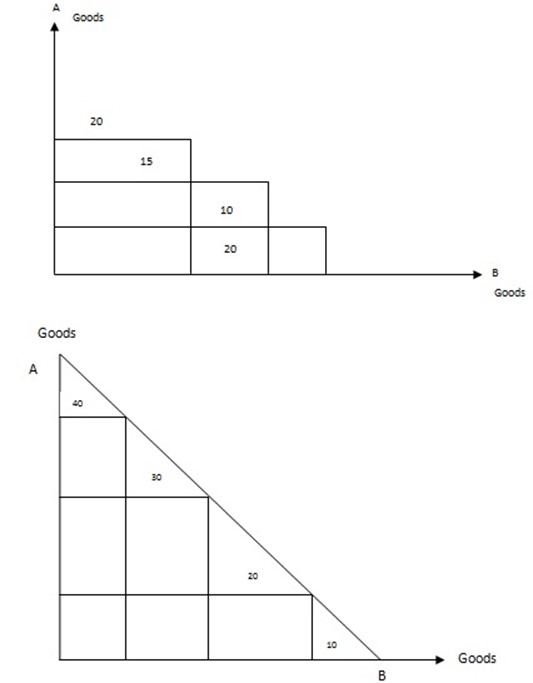
Amount sacrificed for one good and gained by the other is constant represented by a straight line.
Features of production possibility curve
- Two commodities involve.
- There is fixed technology.
- Full employment and productive efficiency.
- Fixed resources.
- Perfect factor substitution.