Mendel’s 2nd law of Inheritance (Low of Independent assortment)
In the dihybrid inheritance, Mendel realized that during gametes formation in each sex either one or another pair of factors may enter the same gametes cell (random combination) with either one or another
cell. The law states that:-“Any one of a pair of characteristics may combine with either one of another pair”
Meiotic explanation of Mendel’s second low
Mendel’s second law is explained by Meiosis as follows:-
-
During gametes formation, the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of each allele from a homologous chromosome pair, is entirely independent of the nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution of alleles of another pair. It is the random alignment of the homologous chromosomes on the equator spindle in “Metaphase 1” and their subsequent separation in “Anaphase I” that leads to a variety of alleles in the gametes.
Examples
1. In the guinea pig (cavia), there are two alleles for hair colour, black and white, and two alleles for hair length short and long. In a breeding experiment the F1 phenotypes produced from a cross between pure – breeding short black haired and pure – breeding, long white – haired parents had short black hair. Explain;
(a) Which alleles are dominant, and
(b) The expected proportions of F2 phenotypes.
Answer
(a) If short black hair appeared in the F1 phenotypes, then short hair must be dominant to long hair and black hair must be dominant to white.
(b) Let B represent black hair
b represent white hair
S represent short hair
s represent long hair.
F1 phenotypes Short black hair x short black hair
F1 genotypes (2n) SbBb SsBb
gametes SB Sb sB sb.
edu.uptymez.com
| Gametes | SB | Sb | sB | sb |
| SB | SSBB | SSBb | SsBB | SsBb |
| Sb | SSBb | SSbb | SsBb | Ssbb |
| sB | SsBB | SsBb | ssBB | ssBb |
| sb | SsBb | Ssbb | ssBb | ssbb |
edu.uptymez.com
9 short black hair : 3 short white hair : 3 long black hair : 1 long white hair
2. Flower colour in sweet pea plants is determined by two allelomorphic pairs of gene (R,r and S,s). If at least one dominant gene from each allelomoorphic is present in the flowers are purple. All other
genotypes are white. If two purple plants, each having the genotype RrSs, are crossed, what will be the phenotypic ratio of the offspring?
Parental phenotype: Purple x Purple
Parental genotype: RrSs x RrSs
gametes RS Rs rS rs
| Gamete | RS | Rs | rS | rs |
| RS | RRSS | RRSs | RrSS | RrSs |
| Rs | RRSs | RRss | RrSs | Rrss |
| Rs | RrSS | RrSs | rrSs | rrSs |
| Rs | RrSs | Rrss | rrSs | rrss |
edu.uptymez.com
Offspring phenotype: 9 purple : 7 white
3. Consider a pea plant with round yellow seeds of the genotype Rr Yy. This means there are two pairs of homologous chromosomes. One pair carrying the allele for the colour and another pair carrying the allele for the seed form (texture). Thus chromosomes carrying the alleles for seed colour are homologous with another as those for seed form.
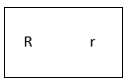
– At Meiosis, the homologous chromosomes come together (assort), but they carry themselves on the spindle independently of each other. They may arrange themselves in one of the following way
or
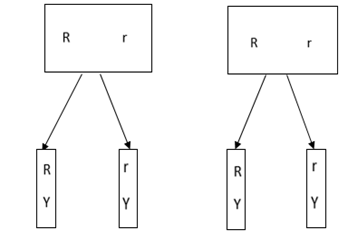
RrYy: Ry, RY, rY, ry
Question:-
(i) State Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
(ii) State the observations made by Mendel that led him to formulate his laws of inheritance.
(iii) Discuss in fully as you can how the behaviour and movement of chromosomes during meiosis, explain Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
NECTA 1973
In guinea pig, rough coat is dominant over smooth coat and black coat is dominant over white coat. When a rough black guinea pig was crossed with a rough white guinea pig the offspring obtained were.
328 rough black
311 rough black
111 smooth black
110 smooth white
What were the genotypes of the parents?
Soln
Let – R- rough coat
r- smooth coat
B- black coat
b- white coat
– In the dihybrid cross, each character behaves independently of the other. Thus considering coat texture we have:-
Rough Smooth
328 + 311 110 + 111
639 221
221 221
= 3 : 1
This is a basic monohybrid ratio obtained from a cross involving two heterozygous individuals. Thus, the genotype of the rough coat with respect to this gene was Rr.
Considering coat colour.
Black White
328 + 111 311 + 110
439 421
421 421
= 1 : 1
- This (1:1) is a monohybrid test cross ratio obtained from a cross of a heterozygous dominant and a homozygous recessive.
- Therefore the genotype of a black coat was Bb and that of a white coat
-
Therefore, the genotypes of the parents were:-
Rough black : RrBb
Rough white : Rrbb
5. A tall plant with red flowers, form a true breeding line was crossed with a short plant with white flowers. One of the resulting plants was crossed in short red flowered plant unknown parentage.
This cross gave the following results:-
109 – short white
38 – tall red
29 – tall white
100 – short red
(i) Interprete the results.
(ii) What was the phenotype of the plants produced by cross I?.
Solution
According to Mendel’s 2nd law, in a dihybrid cross, each characteristic behaves independently of the other.
– Thus, treating each characteristic separately we have:
Short Tall
109 + 100 38 + 29
209 67
67 67
= 3 : 1
– This is a basic monohybrid ratio obtained from a cross between two heterozygous plants
– From this ratio, short is dominant over tall.
Colour
White Red
109 + 29 38 + 100
138 188
138 138
1 : 1
– This is a monohybrid test cross ratio obtained when a homozygous recessive is crossed with a heterozygous dominant.
Consider the two crosses for colour only
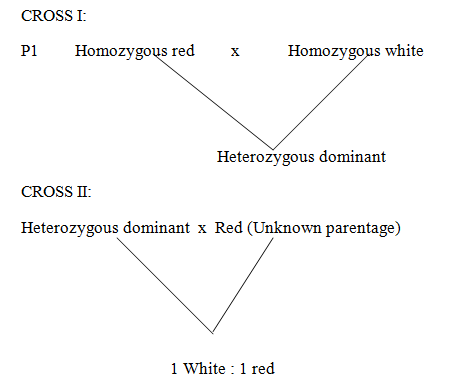
Heterozygous dominant x Red (Unknown parentage)
1 White : 1 red
From the above cross, the red colour was recessive to white.
Defn: of symbols
Let: W = White
w = red
S = short
s = tall
Punett square to show the fusion of gametes.
edu.uptymez.com
| Gametes | SW | Sw | sW | Sw |
| Sw | SSWw | SSww | SsWw | Ssww |
| sw | SsWw | SSww | ssWw | ssww |
edu.uptymez.com
The phenotypes are:-
3 short white
3 short red
1 Tall white
1 Tall red
(ii) From cross 1 above, the phenotypes of the product was short white.
6. Two form IV students Sophia and Issa were eager to put into practice their genetic knowledge. They carried out the following crosses:-
CROSS I
A pure breed plant for terminal purple flowers was crossed with a home plant for axial white flowers.
CROSS II
A plant with axial purple flowers of unknown percentage was crossed with one of the products of the first cross. This cross produced the following results.
338 axial white flowers.
109 terminal purple flowers.
84 terminal white flowers.
304 axial purple flowers.
– Due to their elementary knowledge in genetics, Sophia and Issa failed to interprete their results.
– Using your advanced biology knowledge, show how Issa and Sophia could;
(i) Interprete their results
(ii) Identify the genotypes and phenotypes of the plants produced in the first cross.
Solution;-
(i) According to Mendel’s second law, each characteristic in a dihybrid cross behaves independently of the other. Thus, treating each characteristic separately we have.
– Considering position of the flowers, we have:-
Axial Terminal
338 + 304 109 + 34
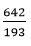
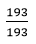 193
193
= 3 : 1
This is a basic monohybrid ratio obtained given a cross between two heterozygous individuals.
From this ratio, axial flowers are dominant over terminal flowers.
Considering colour of the flowers:-
Purple White
304 + 109 338 + 84
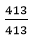
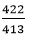
= 1 : 1
This is a monohybrid test cross ratio obtained from a cross between a heterozygous dominant and homozygous recessive.
Considering the two crosses for flower colours only.
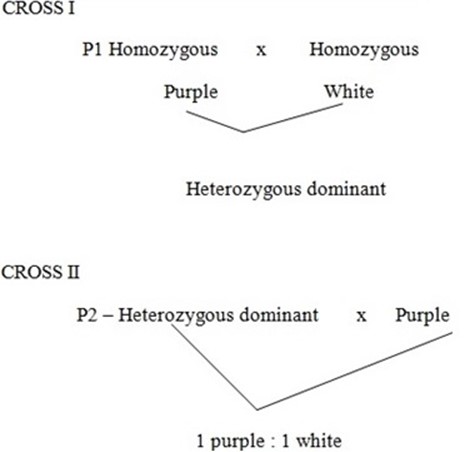
Since this ratio is obtained when a heterozygous dominant is crossed with homozygous recessive, then purple was recessive and white was dominant.
Definition of symbols:-
Let:- A – axial
a – terminal
W – white
w – purple
Punett square to show the fusion of gametes:-
| Gametes | AW | Aw | aW | aw |
| Aw | AAWw | AAww | AaWw | Aaww |
| Aw | AaWw | Aaww | aaWw | aaww |
edu.uptymez.com
The phenotypes are in the following proportions-
3 Axial white
3 Axial purple
1 Terminal white
1 Terminal purple
The results Issa and Sophia have been interpreted since the ratio obtained corresponds with the figures given.
From Gross 1 above, the genotype and phenotype of the products of the flowers cross are AaWw and axial white respectively.