What is Reproduction?
Reproduction Is the ability of an organism to produce an individual of its type in order to increase the number of individuals of that species.
MEANS OR TYPES OF REPRODUCTION
- Asexual reproduction.
- Sexual reproduction.
edu.uptymez.com
ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction which does not involve the fusion of gametes.
CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRODUCTION.
- Proceeds without fusion of gametes (asexual).
- A single parent is capable of asexual reproduction.
- It is a product of mitosis.
- It occurs fast enough to prevent the chances of occurring of sexual reproduction.
- It has few stages before the offspring are produced.
edu.uptymez.com
ADVANTAGES
- It is a quick process yielding a substantial number of offspring to increase the chances of survival of the species during unfavourable environmental conditions.
- It eliminates the possibilities of occurrence of sexual reproduction.
- No changes of genetic makeup as the process is a product of mitosis. This is a way of maintaining good qualities in a population.
- No mixing of materials from more than one parent therefore contamination and infections are minimized.
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGES
- Fast yielding of offspring leads to overcrowding and hence competition over necessities of life among organisms e.g. light, food, mineral salts, air etc.
-
The DNA replication does not mutate it produces daughter cell exactly the same as the mother cell no variation. This makes the individual less potential evolve into new species and cope with the
environmental challenges.
- It may be a way to propagate defective gene into species/progeny the defective gene may affect the entire population.
-
The process involves no mixing of gene from the two different parents this eliminates the diversity or divergence among the individuals of the same species hence limits the advancement of the entire
species.
edu.uptymez.com
The lower species lies only on mutations as the main form of diversification and adaptation e.g. viruses and bacteria that reproduce asexually survive in harsh environment e.g. antibiotic resistant bacteria
and HIV viruses that mutate when patients do not take a combination of drugs. Mutations may be occurring slowly and hence the organism may fail to cope with the environmental conditions.
Sexually reproducing organisms on the other hand combination of some of variation (mutation, gene recombination, random alignment of chromosomes at metaphase I and the subsequent movement,
crossing over) which ensure diversity in their species and hence survival value.
TYPES OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION
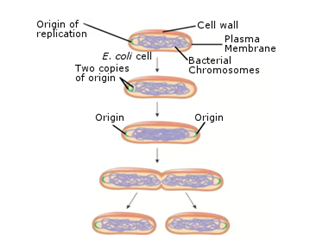
- Binary fission
edu.uptymez.com

-
Multiple fission
Is the repeated division of cells to form more than two daughter cells e.g. Plasmodium which has infected liver cells.
-
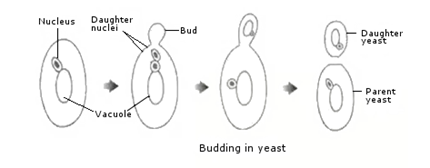
Budding
E.g. Yeast, Hydra.
Definition:
Budding is the form of asexual reproduction in which new individual is produced as an outgrowth (bud) of the parent and later is released as independent identical copy of the parent.
-
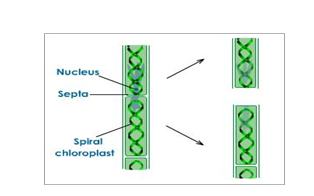
Fragmentation E.g. spirogyra, ribbon, worms.
Is a form of asexual reproduction by which organism breaks into two or more parts each of which grows into a new individual.
-
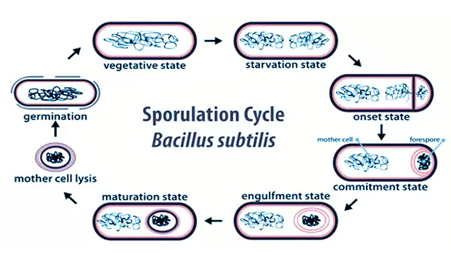
Sporulation
Is the form of asexual reproduction which involve production of spores which are then dispersed for germination to grow into a new individual e.g. fungi, plants.
-
Vegetative propagation
Is the form of asexual reproduction in which a bud grows and develop into a new plant.
Eg. A stem of cassava develops into a cassava plant.
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION.
Sexual reproduction is the production of new organism by combining the genetic material of two sex cells (gametes) from either a single parent or two different parents.
The two main processes of sexual reproduction are:-
- Meiosis which involves halving the number of chromosomes.
- Fertilization involving the fusion of two gametes and the restoration of the original number of chromosomes.
edu.uptymez.com
- During meiosis the chromosomes of each pair usually cross over to achieve homologous recombination during sexual fertilization.
edu.uptymez.com
PROPERTIES OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
-
It involves the application of gametes (sex cells) hence termed sexual reproduction. The two sex cells may come from two different parents (i.e. dioecious) or from single parent (i.e. monoeciousness).
The sex cells can be isogametes (i.e. gametes of same morphology from lower animals to higher animals respectively.
- The organisms carrying out sexual reproduction may be monoecious or dioecious.
-
The process involves lots of stages which may delay the product.

- The process is associated with lots of risks e.g. risk to miss a mate, to miss fertilization etc.
- Provides variation among the offsprings by its;
edu.uptymez.com
- Meiosis involving crossing over which produce, recombinant chromosomes and normal chromosomes.
- Random fertilization where genes are randomly mixed (i.e. random combination of genes occurs due to any sperm fertilize the given egg).
edu.uptymez.com
6. The process is affected by age where the young and old cannot reproduce while adults can.
ADVANTAGES OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
- It involves more space for genetic shuffling which leads to the evolution of the organism.
-
It produces variation in the offspring when crossing over during prophase I and random assortment during metaphaseI occurs. Variation will increase the survival of the species and prevent from
extinction.
- The process delays the production of offspring due to age factor. The delayed product is a natural way to reduce over population hence less competition among organisms.
edu.uptymez.com
DISADVANTAGES OF SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
-
Very uncertain especially for external fertilization where the sperm has to meet the ovum outside, this might not occur; the process of fertilization might fail on the way to produce the zygote.
Even in internal fertilization so many risk of missing a mate, killing of sperms by acidic fluids in female reproductive organs etc reduces the probability of occurance of sexual reproduction.
-
Maturity of offspring is slowly achieved.
This delays their production of offspring and may lead to extinction of the species in case of disaster.
Despite the setback sexual reproduction is the primary method of reproduction for the vast majority of microscopic organisms including almost all animals and plants. This is the most preferred type of reproduction because it allows the population to change (evolve) rapidly in response to a changing environment through recombination of alleles which makes organism vary.
edu.uptymez.com