When a battery is connected to a circuit the current flows steadily in one direction, this is called a Direct current (d.c).
The use of Direct currents is limited to a few applications e.g charging of batteries, electroplating etc.
Most of electrical energy is generated and used in the form of alternating current due to many reasons including,
i) Alternating voltages can be changed in value very easily by means of transformers.
ii) A.c motors are simpler in construction and cheaper than d.c motors.
ALTERNATING VOLTAGE AND CURRENT
i) Alternating voltage
An alternating voltage is one whose magnitude changes with time and direction reverses periodically. The instantaneous value (i.e value at any time t) of an alternating voltage is given by,
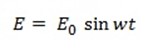
where,
E = Value of the Alternating voltage at time t
E0 = Maximum value of the Alternating voltage
ω = Angular frequency of supply
From 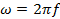 ,where f is the frequency of the alternating voltage, If T is the time period of alternating voltage then
,where f is the frequency of the alternating voltage, If T is the time period of alternating voltage then
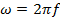
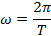
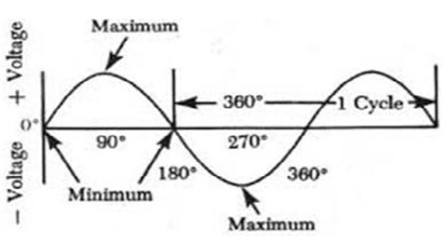
The voltage varies from zero to a positive peak (+E0) then back via zero to negative peak (-E0) and so on.
In time period T, the wave completely cycle.
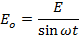
ii) (ii)Alternating current
This is one whose magnitude changes with time and direction reverses periodically.
The Instantaneous value (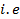 value at any time t) of sinusoidally varying alternating current is given by
value at any time t) of sinusoidally varying alternating current is given by
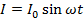
where
I = value of alternating current at time t
I0 = maximum value (Amplitude) of alternating current.
ω = Angular frequency of supply.
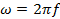
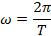
Figure below shows the waveform of alternating current.
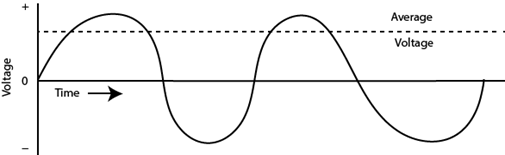
Current varies sinusoidally with time. The current increases gradually from zero to a positive peak (+Io), then back via zero to a negative peak (–Io) and so on.
In time period T, the wave completes a cycle.
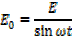
An Alternating voltage and current also be represented as a cosine function of time.
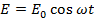
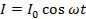
Both these representations give the same result as is given by the one containing sine functions.
MEASUREMENT OF ALTERNATING CURRENT
Since the average value of sinusoidal alternating current is zero, an ordinary (DC) ammeter or galvanometer will not show any deflection when connected in an AC circuit.
Due to inertia it will not be possible for the needle to oscillate with the frequency of the current.
Therefore to measure AC we use hot wire instruments because the heating effect of current is independent of the direction of current.
MEAN OR AVERAGE VALUE OF ALTERNATING CURRENT
The mean value or average value of alternating current over one complete circle is zero.
It is because the area of positive half cycle is exactly equal to the area of the negative half cycle.
However, we can find the average or mean value of alternating current over any half cycle.
Half Cycle Average Value of a.c
This is that value of steady current (d.c) which would send the same amount of charge through a circuit for half the time period of a.c 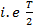 as it sent by the a.c through the same circuit in the same time.It is represented by Im or
as it sent by the a.c through the same circuit in the same time.It is represented by Im or 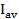
The instantaneous value of alternating current is given by, 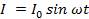
Suppose current I remains constant for a small time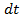 . Then small amount of charge sent by alternating current in a small time
. Then small amount of charge sent by alternating current in a small time 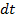 is given by
is given by
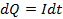
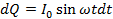
If Q is the total charge sent by the positive half cycle of a.c (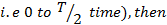
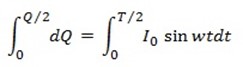
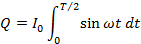
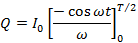
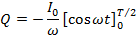
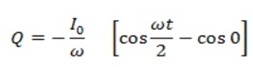
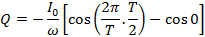
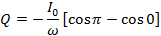
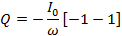
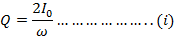
If the Im is the half cycle average means values of positive half cycle of a.c then by definition
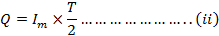
From equation (i) and (ii)
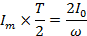
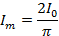
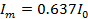
Hence half cycle average value of a.c is 0.637 times the peak value of a.c
For positive ½ cycle Im
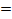 +0.637 I0
+0.637 I0
For negative half cycle Im
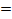 -0.637 I0
-0.637 I0
Obviously, average value of a.c over a complete cycle is zero.
MEAN OR AVERAGE VALUE OF ALTERNATIVE VOLTAGE
Half Cycle Average value of alternating 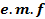
This is that value of steady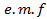 , (
, (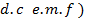 which would send the same amount charge through a circuit for half the time period of alternating
which would send the same amount charge through a circuit for half the time period of alternating 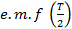 as is sent by the alternating
as is sent by the alternating 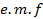 through the same circuit in the same time.It is denoted by
through the same circuit in the same time.It is denoted by 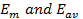 The instantaneous value of alternating e. m. f is given by
The instantaneous value of alternating e. m. f is given by 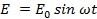
Suppose this alternating 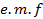 is applied to a circuit of resistance R. Then by ohm’s law the instantaneous value of alternating current is
is applied to a circuit of resistance R. Then by ohm’s law the instantaneous value of alternating current is
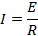
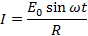
If this current remains constant a small time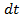 , then small amount of charge send by alternating
, then small amount of charge send by alternating 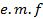 in small time
in small time 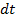 is given by
is given by
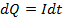
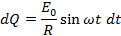
If Q is the total charge sent by positive half cycle of a alternating 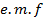 then
then
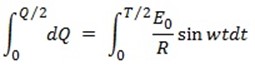
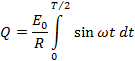
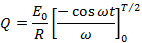
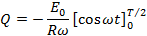
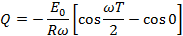
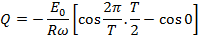
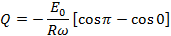
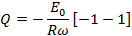
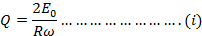
If 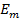 is the half cycle average or mean value of the positive half cycle of alternating
is the half cycle average or mean value of the positive half cycle of alternating 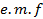 then by definition
then by definition
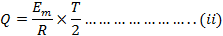
From equation (i) and equation (ii)
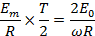
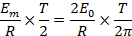
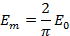
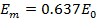
Therefore, half cycle average value of alternating 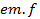 is 0.637 times the peak value of alternating
is 0.637 times the peak value of alternating 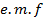 .
.
For positive half cycle
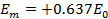
For negative half cycle
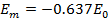
A d.c voltmeter or ammeter reads average (or d.c) value. Therefore, they can be used to measure alternating voltage on current.
It is because the average value of alternating voltage or current over a complete cycle is zero.
We use a.c meters to measure alternating voltage/current.
ROOT MEAN SQUARE VALUE OF ALTERNATING CURRENT
The average value cannot be used to specify an alternating current (or voltage).
It is because its value is zero over one cycle and cannot be used for power calculations.
Therefore we must search for more suitable criterion to measure the effectiveness of an alternating current or voltage.
The obvious choice would be to measure it in terms of direct current that would do work (or produce heat) at the same average rate as a.c under similar conditions.
This equivalent direct current is called the root mean square (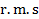 ) or effective value of alternating current.
) or effective value of alternating current.
Effective or value of Alternating Current
The root mean square (r.m.s) of alternating current is that steady current (d.c) which when flowing through a given resistance for given time produces the same amount of heat as produced by the alternating current when flowing through the same resistance for the same time.
– It is also called virtual value of a.c
– It is denoted by called 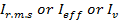
For example, when we say that 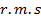 or effective value of an alternating current is 5A, it means that the alternating current will do the work (or produce heat) at the same rate as 5A direct current under similar conditions.
or effective value of an alternating current is 5A, it means that the alternating current will do the work (or produce heat) at the same rate as 5A direct current under similar conditions.