WORKED EXAMPLE
1. (a) How does a permanent magnet attract an unmagnetised iron object?
(b) Show that the unit of magnetizing force is Nm-2T-I or Jm-Iwb-I
(C) Why is electromagnets made of soft iron?
(d) An Iron ring has a cross – sectional area of 400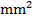 and a mean diameter of 25cm. It is wound with 500trns. If the relative permeability of iron is 5000 find;
and a mean diameter of 25cm. It is wound with 500trns. If the relative permeability of iron is 5000 find;
(i) The magnetizing force
(ii) The magnetic flux density set up in the ring.
The coil resistance is 474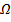 and the supply voltage is 240V
and the supply voltage is 240V
Solution
( a) The magnet’s field cause a slight alignment of the domains in the unmagnetised iron object so that the object becomes a temporary magnet with its north pole facing the south pole of the permanent magnet and viceversa. Therefore attraction results.
(b) The SI units of magnetizing (H) are Ampere/M(Am-I )
Now
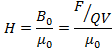
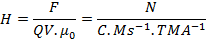
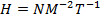
Also
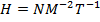
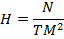
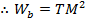
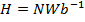
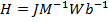
( c) The soft Iron has very small residual magnetism and coercive force. Therefore the material loses magnetism as soon as the magnetizing force is removed for this reason electromagnets are made of soft iron
(d) Current through the coil I
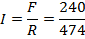
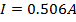
Mean length of the ring l
l = 2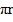
l = 2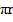 x (12.5 x 10-2)
x (12.5 x 10-2)
l = 0.785m
(i) Magnetizing force H
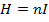
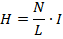
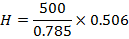
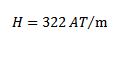
(ii) Magnetic flux density B
From
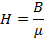
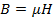
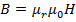
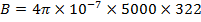
B = 2.02wb/m2
2. (a) Diamagnetic is a property of a material. Discuss
(b) What is the magnetic susceptibility and permeability of a perfectly diamagnetic Substance?
(c) Why is Diamagnetism independent of temperature?
(d) The core of a toroid having 3000 turns has inner and outer radii of 11cm and 12cm respectively. The magnetic flux density in the core per a current of 0.70A is 2.5T
What is the relative permeability of the core?
Solution
(a) Diamagnetism is a natural reaction to the applied magnetic field. Therefore it is present in all materials but is weaker even than paramagnetism. As the result, diamagnetism is overwhelmed by paramagnetic and ferromagnetic effects in materials that display these other forms of magnetism
Solution
B = 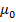 H +
H + 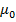 I
I
B = 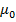 (H+I)
(H+I)
For perfectly diamagnetic substance
B = O
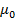 (H+I) = O
(H+I) = O
H +I = O
I = -H
Susceptibility
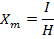
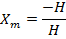
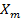 =
= 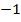
Also
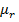 = 1 +
= 1 + 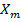
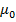 = 1 – 1
= 1 – 1
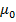 = O
= O
(c) The induced magnetic moment in atoms of a diamagnetic substance is not affected by the thermal motion of the atoms. For this reason, diamagnetic is independent of temperature.
(d) Solution
Mean radius of toroid
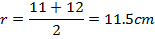
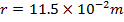
The magnetic flux density in the toroid is
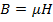
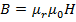
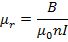
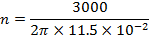
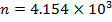
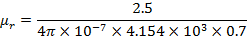
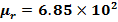
3 .(a) (i) What is a non Magnetic material?
(ii) Can there be a material which is non -magnetic?
(b) What do you mean by the greater susceptibility of a material?
(c) An iron rod of 0.1m2 area of x-section is subjected to magnetic field of 1000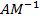
Calculate its magnetic permeability. Given susceptibility of iron are 599.
(d) Which material is used to make permanent magnets and why?
Solution
(a) (i) A non –magnetic material is that which is not affected even by strong magnetic fields.
(ii) No, every material is at least diamagnetic.
(b) From 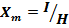
For a given H, 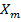 α
α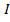 Thus the greater value of the susceptibility of the material the greater will be its intensity of magnetization i.e. more easily can be magnetized .Thus greater value of its susceptibility for iron means that it can be easily magnetized.
Thus the greater value of the susceptibility of the material the greater will be its intensity of magnetization i.e. more easily can be magnetized .Thus greater value of its susceptibility for iron means that it can be easily magnetized.
(c) Solution
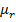 = 1 +
= 1 + 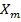
But
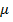 =
=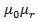
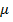 =
= 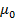 (1+
(1+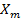 )
)
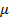 =4
=4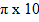 -7(1+599)
-7(1+599)
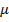 =7.54 x 10-4TA-4M
=7.54 x 10-4TA-4M
(d) Steel it is because has high coactivity. This ensures the stay of magnetism in steel for a longer period
4. (a) A toroid of mean circumference 50cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 0.15A
(i) Determine the magnetizing force and magnetic flux density if the toroid has an air core
(ii) Determine the magnetic flux density and intensity of magnetization if the core is filled with iron of relative permeability 5000
(b) Why do magnetic lines of force prefer to
(c) What is the SI unit of magnetic susceptibility?
Solution
(a) (i) given
L = 50cm = 50 x 10-2 m
N = 500 turns
I = 0.15A
Magnetizing force H
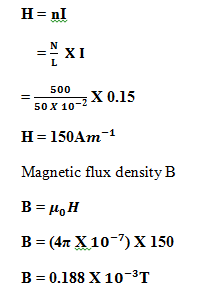
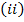 Magnetic flux density
Magnetic flux density
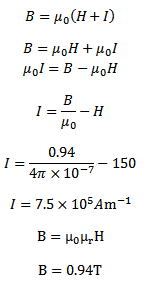
(b) It is because permeability of Iron (Ferromagnetic material ) is very high as compared to that of air .
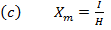
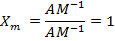
Therefore,  have no Units
have no Units
5. (i) Figure below shows the variation of intensity of magnetization (I) versus the applied magnetic field intensity (H) for two magnetic material A and B
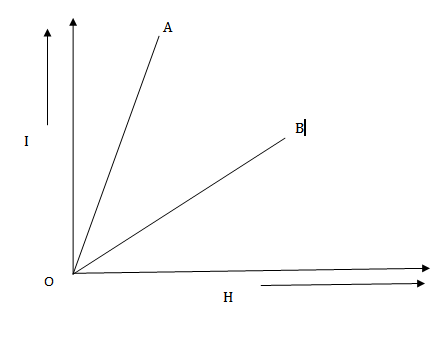
(a) Identify the materials A and B
(b) For the material A, plot the variation of I with temperature.
(ii) The relative permeability of a material is
(i) 0.999
(ii) 1.001
Solution
The slope I-H graph gives the magnetic susceptibility 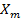 of the material
of the material
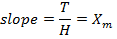
For material A the slope is positive and has a small value. Therefore, material A is paramagnetic.
For material B, the slope is position and has a large value. Therefore , material B is ferromagnetic
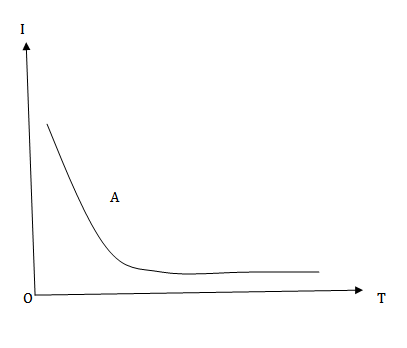
(a) The intensity of magnetization of a paramagnetic material A is inversely proportional to the absolute temperature 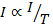 therefore I – T graph for material A will be as shown in figure below .
therefore I – T graph for material A will be as shown in figure below .
(ii) (i) Diamagnetic material
(ii) Paramagnetic material
6. (a) Graph below shows the variation of intensity of magnetization(I) versus the applied
Magnetic field intensity (H) for two magnetic material A and B
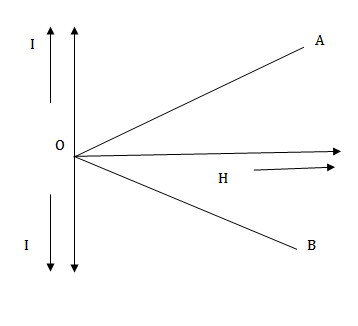
(i) identify the materials A and B
(ii) draw the variation of susceptibility with temperature for material B
(b)A magnetizing for of 360 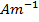 produce a magnetic flux density of 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. Calculate
produce a magnetic flux density of 0.6T in a ferromagnetic material. Calculate
(i) Permeability
(ii) susceptibility of the material
Solutions — do to next page.