Solutions
(a) for material A the susceptibility 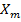 ( = slope of I – H graph) is small and positive therefore material A is paramagnetic and for material B, Susceptibility is small and Negative. Therefore , material B is Diamagnetic
( = slope of I – H graph) is small and positive therefore material A is paramagnetic and for material B, Susceptibility is small and Negative. Therefore , material B is Diamagnetic
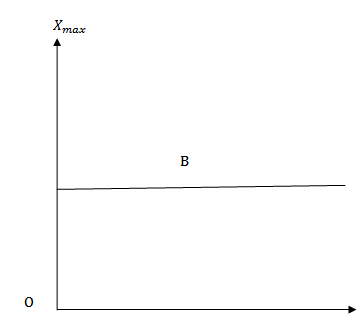
iii) The susceptibility of a diamagnetic material B is independent of temperature therefore 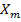 – T graph for material B will be shown in graph below.
– T graph for material B will be shown in graph below.
(b) (i) Permeability of material
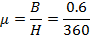
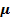 = 1.67 X 10-3 A -1Tm
= 1.67 X 10-3 A -1Tm
(ii) Susceptibility of the material
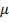 =
= 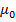 (1 +
(1 +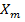 )
)
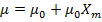
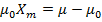
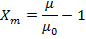
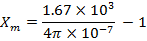
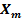 = 1328.62 Am -1
= 1328.62 Am -1
6. (a) What is Magnetic solution?
(b) Name two materials which have
(i) Position susceptibility
(ii) Negative susceptibility
(c) Obtain the earth’s magnetization , assuming that the earth’s field can be approximated by a giant bar magnet of magnetic moment 8.0 x 10 22 A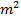 ? Radius of earth = 6400km
? Radius of earth = 6400km
(d) A bar magnet has Coercivity of 4×103 A/m it is desired to demagnetize it by inserting it inside a solenoid 12cm long and having 60turns. With current should be sent through the solenoid
Solution
(a) Magnetic saturation
Is the maximum magnetization that can be obtained in the material when all the domains of a ferromagnetic material are in the direction of the applied magnetic filed
(b) (i) paramagnetic material e.g. Aluminum and Antimony
(ii) Diamagnetic materials e.g. Copper and Zinc
(c) magnetic moment M = 8 x 1022Am2 radius of the earth Re = 6400km
Magnetization of the earth is given by
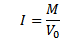
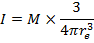
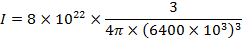
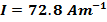
The bar magnetic has a Coercivity of 4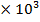
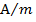 i.e. it needs a magnetic intensity H = 4
i.e. it needs a magnetic intensity H = 4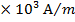 to get magnetized
to get magnetized
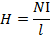
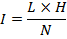
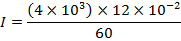
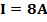
7. (a) Define hysteresis loop
(b)What does the area of hysteresis loop indicate?
(c) What is the use of hysteresis loop?
(d) Why is soft iron preferred in making the core of a transformer?
Solution
(a) hysteresis loop
Is the resulting B – H curve (Closed loop) obtained when a ferromagnetic material is subjected to one circle of the magnetization
(b) the area of hysteresis loop is a measure of energy wasted in a sample when it is taken through s complete of magnetization
(c) The hysteresis loop of a material tells us about hysteresis loss retentively and Coercivity. This knowledge helps us in selecting materials for making electromagnetic permanent magnets cores of transformer
(d) The area of hysteresis loop for soft iron is small. Therefore energy dissipated in the core for cycle magnetization is small. For this reason, the core of a transformer is made of soft iron
8. (a) state curie law
(b) Give the graph between I and B/T
(c) What happens if an Iron magnet is melted?
(d) Copper Sulphate is paramagnetic with a susceptibility of 1.68×10-4 at 293K. What is the susceptibility of copper at 77.4K if it fellows curie law?
Solution
(a) Curie law
States that intensity of magnetization (I) if a paramagnetic substance is directly proportional to the external magnetic field (B) and inversely proportional to the absolute temperature(T) of the substance.
I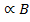
I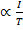
Combining these two factors, we have
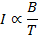
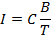
where
C is a constant of proportionality and is called curie constant
This law is physically reasonable As B increase the alignment of magnetic moments increases and therefore I increases
If the temperature is increased the thermal motions will make alignment difficult thus decreasing I
The curve law is found to hold good so long as 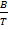 does not become too large
does not become too large
Since
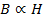
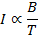
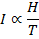
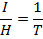
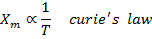
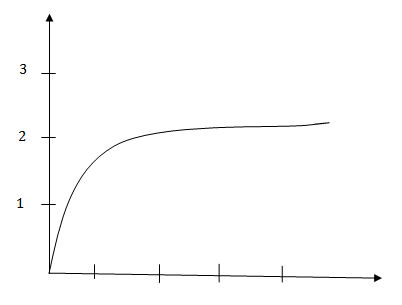
(b) The temperature of molten iron 7700C is above the Curie temperature i.e. On malting the iron becomes paramagnetic. Therefore it loses its magnetism
Solution
According to curie law the susceptibility depends inversely on the temperature
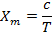
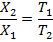
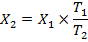
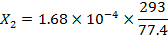
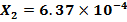
10. (a) A solenoid 0.6m long is wound with 1800 turns of copper wire. An iron rod having a relative permeability of 500 is placed along the axis of the solenoid. What are the magnetic intensity H and field B when a current of 0.9A flows through the wire? What is the intensity of magnetization I in the iron? Find the average magnetic moment per iron atom. Density of iron is 7850 Kg/m3.
(b) An Iron sample having mass 8.4Kg is repeadly taken over cycle of magnetization at a frequency of 50cyles per second it is found that energy equal to 3.2 x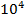 J is dissipated as heat in the sample in 30Minutes if the density of the iron is 7200kg/m3 find the energy dissipated per unit volume per cycle in the iron sample.
J is dissipated as heat in the sample in 30Minutes if the density of the iron is 7200kg/m3 find the energy dissipated per unit volume per cycle in the iron sample.
(c) A domain in ferromagnetic iron is in the form of a cube of side length 1μM. Estimate the number of Iron atom in the domain and the maximum possibility dipole moment and magnetization of the domain and the maximum possible dipole moment and magnetization of the domain. The molecular mass of Iron is 55g/mole and its density is 7.9g/cm2 assume that each Iron atom has a dipole moment of 9.27 x 10-24 Am2
Solution
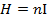
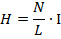
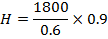
H = 2700A/m
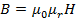
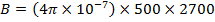
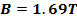
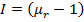 H
H
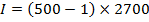
I = 1.35 X 106A/m
One Kilo mole (55.85Kg) of Iron has 6.2 x1026 atoms. Therefore, number of atoms in 1 m3 of Iron
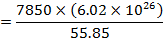
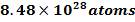
Average magnetic moments per iron atoms
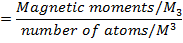
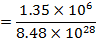
=1.59 x 10-23 Am2
Solution
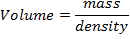
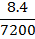
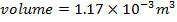
f =50 HZ
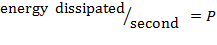
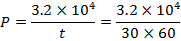
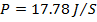
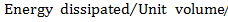 cycle
cycle
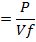
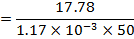
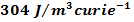
Length of cubic domain l
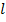 =1
=1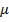 M = 10-6M
M = 10-6M
Volume of Domain
V = 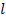 3
3
V = (10-6)3
V = 10-18M3
Mass of domain
=Volume X Density
=10-12cm x7.9g
= 7.9 x10 -12g/cm
It is given that 55g of Iron contain 6.023 x1023 Iron atoms (Avogadro’s no)
Number of atoms in the domain is
N = 6.023 X 1023 X 7.9 X10-12
55
N = 8.65 X 1010atoms
The maximum possible dipole moment 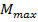 is achieved per the case when all the atomic domains are perfect aligned (This condition is unrealistic)
is achieved per the case when all the atomic domains are perfect aligned (This condition is unrealistic)
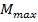 = (8.65 x1010) x (9.27 x10-24)
= (8.65 x1010) x (9.27 x10-24)
= 8 x 10-13 AM2
Maximum intensity of magnetization of the Domain is
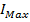 =
= 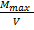 =
= 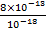
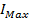 = 8 x105 Am-1
= 8 x105 Am-1