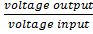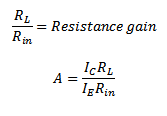RECTIFIER CIRCUITS:
HALF-WAVE RECTIFIER CIRCUIT
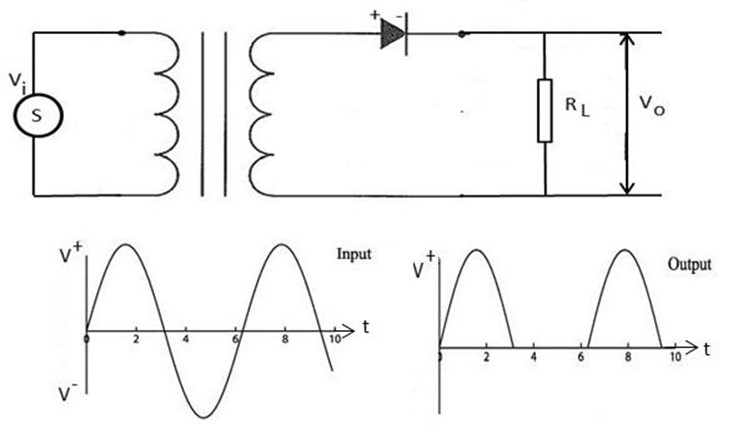
A rectifier is a circuit which allow the flow of current I P.d in one direction only:
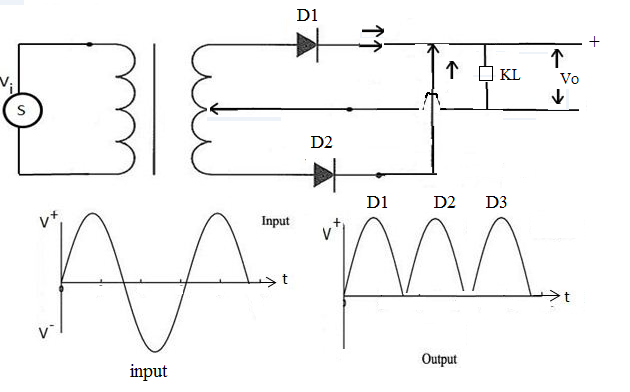
FULL –WAVE RECTIFIERS CIRCUITS:
a) Using centre –tapped transformer.
b) Using bridge circuits
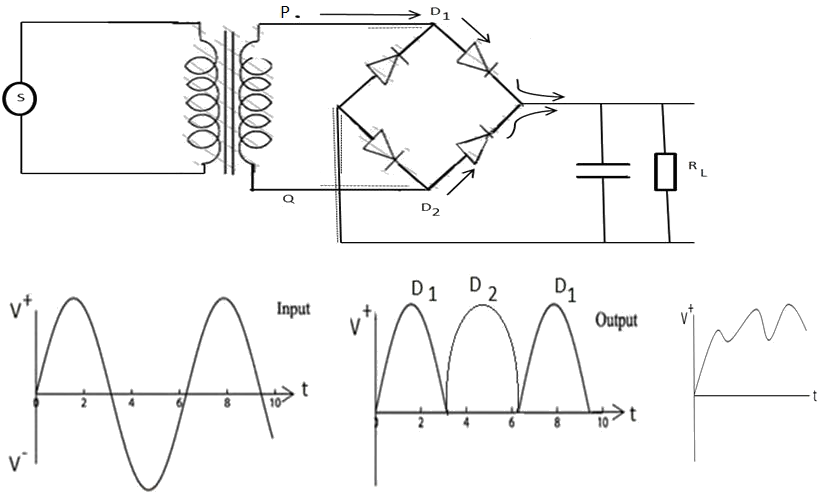
On one half of a cycle when P is +v relative to Q only diode D1 conducts
On one other half the same cycle only the diode D2 conducts.
In both cases the current gees through resistor RL in the same direction.
The large capacitor C is used for stabilizing the marying d.c voltage.
B) TRANSISTORS
Transistor is a component which amplifies current. It is made from three layers of P and n. Semiconductors. The layers are called the emitter (E) base (B) an collector (C)
There are two types of transistors.
I. n.p.n transistor
II. p.n.p transistor
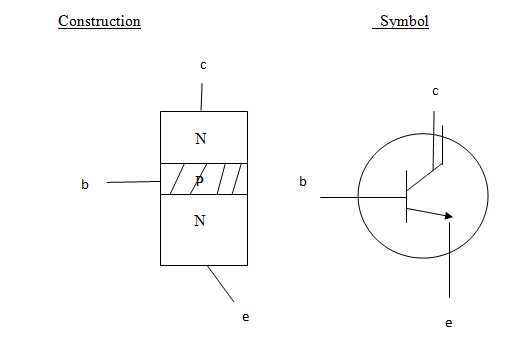
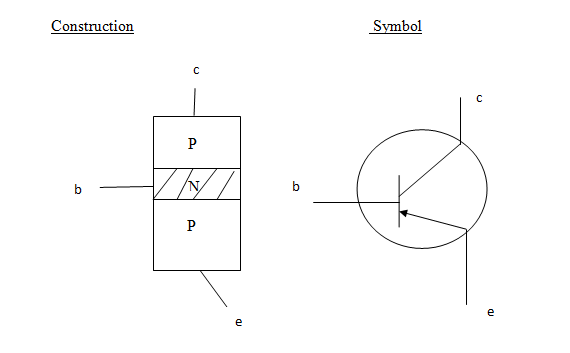
Formation of a transistor
A transistor is formed by putting the doped semiconductors together in such a way that two junction are formed.
The pnp transistor (bipolar transistor).
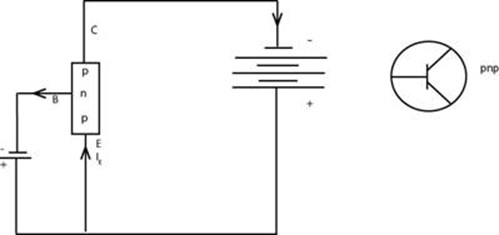
-Bipolar means n p n and p n p transistor as they have two opposite polarity of doped semiconductors and voltages across terminals
P n p
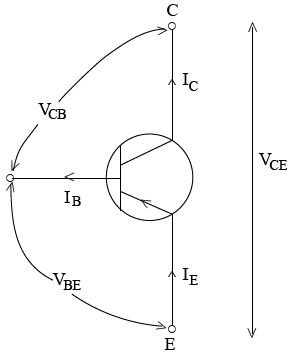
n p n
Transistor configuration
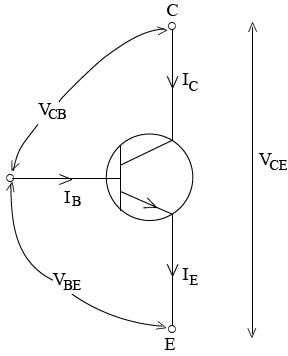
There are 3 basic configurations
1. Common emitter configuration
2. Common base configuration
3. Common collector configuration
1. Common emitter configuration (n p n)
Under thus configuration the transistor has both voltage gain and current gain.
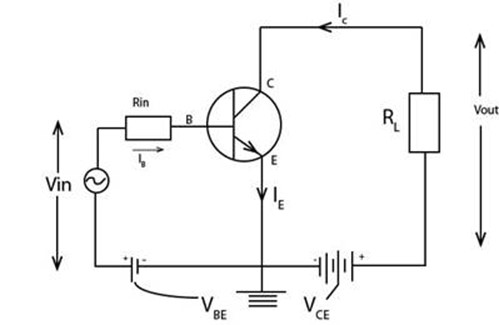
To get volt you need a resistance RL
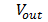 = I
= I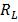
Ring is used for injecting only a small current for great amplification on E by C
Current gain
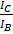 = very large
= very large 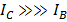
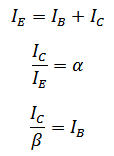
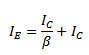
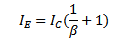
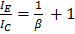
But
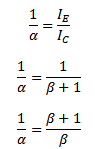
Also
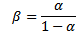
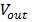 is the reflection of
is the reflection of 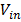
Common base configuration (PnP)
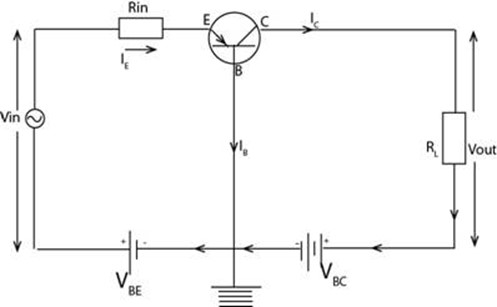
Under this configuration the transistor has voltage gain but no current gain
Earthing puts the common line at p.d=0
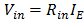
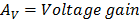 =
=