BARTER TRADE
-Is the exchange of goods for goods.
Advantages of Barter trade
edu.uptymez.com
-All forms of money can easily be stolen than commodities.
- The value of commodities tends to be stolen over a long time than the value of money which depreciates in value after a certain period of time.
- Barter trade is useful where money is too scarce to be used as medium of exchange
edu.uptymez.com
-Example in rural areas barter trade is widely used due to scarcity of money.
- The use of barter system makes the economy of a place not to be easily affected by economic problems like inflation.
edu.uptymez.com
Disadvantages of barter system
a.)Lacks of double coincidence of wants.
-Double coincidence of wants means that a person who has wheat and wants salt has to find a person who has salt and wants wheat. If he can’t find such a person who wants wheat and has salt then barter trade cannot take place.
b.)Lack of measure of value.
-It is very difficult to decide how much quantity of one commodity to be exchanged for another commodity.
-For example, it is very difficult to decide how much quantity of maize must be exchanged with units of cow
c.)Lack of store of value
-Under barter system it is very difficult to store perishable goods such as(tomatoes, vegetables) and exchange for another commodities in future.
d.)Indivisibility of some items
-It is not possible to divide some commodities into smaller units in order to exchange with units of other commodities.
-For example, if a person has certain units of cloth and wants to exchange with some units of cow the exchange is very difficult because a cow cannot be divided into smaller units if the value of the units of cloth is not equal to the value of the whole cow.
e.)Difficult of transporting some commodities
-Due to lack of modern means of transportation and immobility of some items it is difficult to transport some items from one place to another for exchange.
COMMERCE IN THE MODERN WORLD
-With the coming of industrial revolution and introduction of machinery the division of labour or specialization became more popular.
Different individuals and localities (countries) specialized in the production of different commodities.
-There was specialization in various aspects;-
.In industry example a manufacturer could choose to produce a specific commodity
.In commerce traders (retailers or wholesalers could specialize in only one line of commodity.
.Even individual’s example a doctor could be a dentist a pharmacist or surgeon
Teachers could specialize in subjects such as Book-keeping, Mathematics, and Economics and so on.
-Specialization leads to exchange. The products of one specialist need to be exchanged with those of another in the satisfaction of wants.
-Thus, modern commerce is a result of specialization
SPECIALIZATION AND DIVISION OF LABOUR
-Is the separation of jobs, activities and processes so that each person or group of persons concentrates on what he or they do best. Every person concentrates on what the performance of a particular activity.
SPECIALIZATION
– Is the Proccess of Concentrating on what he or she can do the best.
DIVISION OF LABOUR
-Is the process of divide or arrangement of labour in a particular activity.
Or
-Specialization is the arrangement of labour in such a way as to maximize the amount and quality of the output.
ADVANTAGES OF SPECIALIZATION AND DIVISION OF LABOUR
I.)Time and energy saving;
-No one worker does the whole process alone. This saves energy and the time that would be lost in switching from one job to another.
II.)Degree of choice;
-People have different natural abilities; Specialization enables individuals to choose those occupations for which they are most suited
III.) Developing skills;
-Specialization and division of labour develops skills to individuals through a process of learning by doing the same task repeatedly
IV.) Better standard of living
-Specialization leads to better standard of living because specialization leads to higher production, creating a wider choice.
V.)Physical toil is reduced through the use of machines.
VI.) It leads to efficiency because of the frequency of operation
VII.) Machinery is used more extensively and efficiently
DISADVANTAGES OF SPECIALIZATION AND DIVISION OF
LABOUR
I.)Boredom and monotony
-Have to do the same task over and over again becomes monotonous and can easily make a worker tired and bored.
II.) Greater risk of unemployment
-It may happen that too many people may opt to specialize in a certain field of work and that field may not be able to absorb all of them, hence unemployment.
III.) Limited form of production
-Specialization leads to a limitation in production. If the specialized community so on gets a better substitute the firm may decline
IV.) Depersonalization
-Specialization reduces human labour because of the application of complicated machinery.
COMMERCE AND ECONOMICS
-The main distinction between Economics and commerce is that;
-The subject matter of Economics is wider than the subject matter of commerce
-Economics deals with all activities involving production, nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution, exchange, consumption, scarce resources.
-Commerce is concerned with exchange and nglish-swahili/distribution” target=”_blank”>distribution
-Commerce is therefore a branch of Economics that deals with exchange and activities that facilitate exchange.
-This means that all the subject matter of commerce are studied in Economics but not all subject matters of Economics are studied in commerce
COMMERCE AND BUSINESS
-The relationship between commerce and business can be described as follows;
-Business is wider than commerce
-Business refers to any activity carried out with the intention of making profit.
-Business includes both commerce and non-commercial activities
-Commerce applies only to activities that involve trade and aids to trade

PRODUCTION
Definition of Production;
-Production is any activity which results in the creation of goods and services in order to satisfy human wants.
OR
-Production is the process of creating utility.
What is utility?
-Utility is the ability of goods and services to satisfy human wants.
FORMS OF PRODUCTION/FORMS OF UTILITY
a.)Form utility
-This involves changing the forms of goods from raw materials into finished goods.
b.) Time utility
-This involves making the goods available at right time when needed
c.) Place utility
-This involves making the goods from the place of production to the place of consumption.
d.) Possession utility
-This involves transfer of ownership through the process of exchange.
TYPES OF PRODUCTION
There are two types of production
- Direct production.
-
Indirect production
DIRECT PRODUCTION
-This is a kind of production where by an individual produces goods and services for his own use or personal consumption.
─Example, when a farmer produces maize for his/her own use not for sale.
─Direct production is also known as subsistence production.
INDIRECT PRODUCTION
-Is a kind of production whereby individuals produce goods and services for sale.
-Example, when farmers produce maize for sale.
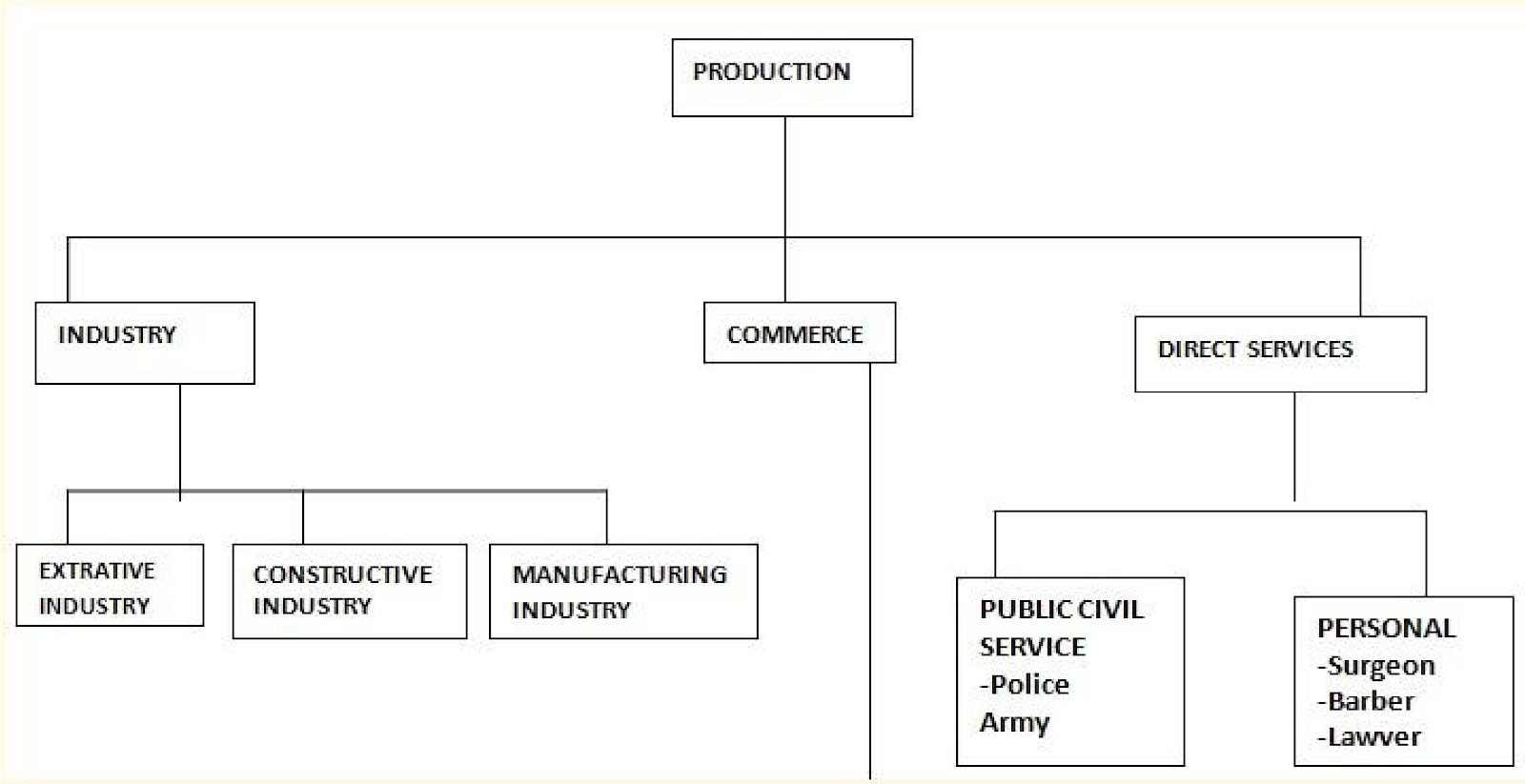
BRANCHES OF PRODUCTION
There are three branches of production namely;
- Industry
- Commerce
- Direct service
edu.uptymez.com
1. INDUSTRY
-Industries deal with changing the forms of raw materials into finished goods.
-Industries are classified into three categories according to the different stages of production.
a.) EXTRACTIVE INDUSTRIES (Primary production)
-These are industries which are concerned with extraction of raw materials (natural resources) from the earth crust.
-Examples are –farming, hunting, mining, and lumbering. Etc
b.) MANUFACTURING INDUSTRIES (Secondary production)
-These are industries concerned with changing the form of raw materials into finished goods by machines or hands.
c.) CONSTRUCTIVE INDUSTRIES
-These are industries that assemble already manufactured goods into finished products.
-Examples;-House building(builders) use cement, timber, bricks, iron, glass and paint which have been extracted and manufactured
-Other examples are; Car assembly, furniture making, radio assembly.
- COMMERCE
edu.uptymez.com
-The goods and services produced must reach the ultimate consumers
-The role of commerce in the production process is to make goods and services available to the consumers.
- DIRECT SERVICE
edu.uptymez.com
-This involves activities which render services directly to consumers
-A person who wants to give a service must have direct contact with the person receiving the service.
Examples of direct services are; – Teaching, medical care (doctor), lawyers, policeman, hair dressers.
A CHART SHOWING CLASSIFICATION OF OCCUPATIONS
NOTE; Production process ends when goods and services reach to the final (ultimate) consumers 
GOODS
-Are things which we can see and touch.
-Are things which satisfy human wants. E.g. clothes, cars, radio, T.V.
Classification of Goods;-
Goods are classified under the following categories;-
1. Consumer goods and producer goods
-
.Consumer goods
-These are goods produced for final consumption.
Examples; foodstuffs, radio, T.v, furniture.
-
.Producer goods/capital goods
-These are goods which are produced to assist production of other goods.
Examples; machinery, buildings, roads and railways.
2. Perishable goods and Durable goods
-
.Perishable goods
-These are goods which can easily be destroyed or decayed.
Examples; foodstuffs, (e.g. milk, meat, flour, fruits, vegetables, etc.)
-
.Durable goods
-These are the goods which can stay for a very long period of time without being destroyed.
Examples; buildings, machinery, furniture etc.
3. Private goods and Public goods
-
.Private goods
-These are goods owned by individuals or family
-
.Public goods
-These are goods owned enjoyed collectively Example; defense, roads.
4. Intermediate goods and Final goods.
-
.Intermediate goods
-These are goods in progress.
-
. Final goods
-These are goods ready for consumption.
5. Free goods and Economic goods
-
.Free goods
-These are goods which are provided freely by nature.
Examples; air, sunshine, rainfall, ocean water, forest. Etc
Features of free goods
Free goods have the following features;
edu.uptymez.com
- They are not made by human effort
- They are not scarce( i.e.) they are abundant
- They possess utility (i.e.) ability to satisfy wants
- They lack exchange value (i.e.) they cannot be bought or sold
- They are not transferable in terms of ownership
edu.uptymez.com
-
Economic goods
-These are the goods produced by human efforts.
Features of economic goods
edu.uptymez.com
- They are made by human efforts
- They are scarce
- They possess utility
- They have exchange value(i.e. they can be bought and sold)
- They can be transferable in terms of ownership from one person to another person.
edu.uptymez.com
NOTE;
Economics is concerned with economic goods not free goods because production in economics is for exchange and economic goods have exchange value
IMPORTANCE OF PRODUCTION
- Satisfaction of human wants. Goods and services are used to satisfy human wants.
- Increases the size of wealth of both personal and national income.
- Increases the level of welfare of the people goods and services which are produced are aimed to improve welfare of the people.
-
Creation of employment. Production creates employment to various factors of production.
edu.uptymez.com
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION OR AGENTS OF PRODUCTION
-These are the economic resources which assist the process of production
-Factors of production are also known as;
- . Inputs
- . Tools of production
-
.Agents of production
CATEGORIES OF FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
There are four major categories of factors of production
edu.uptymez.com
| Factor of production | Reward of factor of production/ payment |
| 1.Land | rent |
| 2.Labour | Wages or salaries |
| 3.Capital | interest |
| 4. Entrepreneurship | Profit |
edu.uptymez.com
- LAND
edu.uptymez.com
-Land includes all kind of natural resources i.e. things which are not made by man like soil, farm land, forests, ocean, rivers etc.
Features of land
- It is a gift of nature; It has been provided freely by God. It is non-man made.
- Land is limited in quantity or fixed in supply
- Location of land is fixed
- Each part of land has a unique natural characteristics
-
Land provides site or place where production can take place.
For example place for construction of buildings, school, industries etc.
edu.uptymez.com
6.Land lacks geographical mobility. It means that it can’t be moved or transported from one place to another.
IMPORTANCE OF LAND
- It provides site/place for production to take place
- It’s a source of raw materials
- It’s a source of power example; Hydro electric power