- LABOUR
edu.uptymez.com
TYPES OF LABOUR
- Skilled Labour
edu.uptymez.com
- Semi Skilled Labour
edu.uptymez.com
- Unskilled Labour.
edu.uptymez.com
Skilled labour
-Are labours who are usually planners they use much brain (mental) in Planning rather than using Physical Effort example Doctors.
Semi skilled labour
Are those labours who use mental and physical effort to a lesser degree compared to skilled and unskilled labours example. Carpenters
Unskilled labour
Those are labours who use much physical effort than mental effort example Cargo Carrier
-Labor means any mental/physical effort of human beings in the process of production for any beneficial activity (productive activity)
NOTE; Any human effort which is not made for payment can’t be regarded as labour.
Features of labour
- Labour is the most mobile factor in both geographical and occupational senses
- Any labour must be aimed at production 3. Without labours other factors cannot produce.
- Labour differ in efficiency
- Labour is supplied only by living things especially human beings
- Labour isn’t transferable between people i.e the ability to do work cannot be transferable from one person to another
- Labour cannot be stored or reserved for later uses
edu.uptymez.com
3. CAPITAL
-Capital is any wealth (assets) used to produce other wealth (assets)
-Capital includes all types of producer goods e.g. machinery tools, buildings, raw materials etc.
Features of capital
- Capital increases efficiency of the other factors because it simplifies work
- Capital is made up by human beings
- Capital can depreciate or it can become obsolete
- Most of capital cannot work alone without combination with other factors like labour
-
It has an element of time
-Capital renders its services over a certain period of time
edu.uptymez.com
6.Capital results from the accumulation of assets over years
Types of capital
a.) Public and private capital
1. Public capital
-This is the type of capital owned by the whole society like public schools etc
.Private capital
-This is the type of capital owned by individual like car, clothes.
b.) i.)Fixed capital
-This is the type of capital which is durable in nature and is used in production for a long period of time.
For example; Furniture, buildings, some types of machines etc.
ii.)Circulating capital
-This is the type of capital used in the running of day to day activities
Or
-Is the type of capital used in running a business
-for example raw materials, fuel, money.
4. ENTREPRENEUR
-An entrepreneur is the owner of the business
-It’s a factor of production which organizes other factors of production in the production process and establishment of a business
Characteristics of Entrepreneur
-
An entrepreneur does not work alone he must employ other factors
-
The supply of entrepreneur is scarce and cannot be developed easily
-
The reward of entrepreneur depends on efficiency of other factors Functions of an Entrepreneur
- To start the business
- To employ and organize other factors of production in a production process
- He is responsible for economic decisions
edu.uptymez.com
-Economic decisions such as what to produce, how to produce, for whom to produce, and where to produce
- To forecast the demand for his products
edu.uptymez.com
-This is done by doing market research of a product
- Entrepreneur bears the risk of business
edu.uptymez.com
-He/she is responsible for all risks which cannot be insured
COSTS OF PRODUCTION
-This refers to the expenses incurred in running a business or producing a commodity
Or
-Refer to money used to buy other factors of production.
TYPES OF COSTS
Costs can be categorized into the following types;
- INDIRECT COST/ IMPLICIT COST/ OPPORTUNITY COST
edu.uptymez.com
-These are the benefits/ gains sacrificed by a firm by not engaging in the production of other commodities
-It means a firm by employing its resources in the production of a particular commodity it sacrifices other benefits which it could obtain by employing its resources in the production of other commodities.
Example;
If a peasant produces maize in his piece of land by doing so, he sacrifices other benefits that he could obtain by producing other crops in his plot of land for other economic activities.
- DIRECT COSTS/ EXPLICIT COSTS
edu.uptymez.com
These are money actually used in buying factors of production
TYPES OF DIRECT COSTS
There are two types;
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
edu.uptymez.com
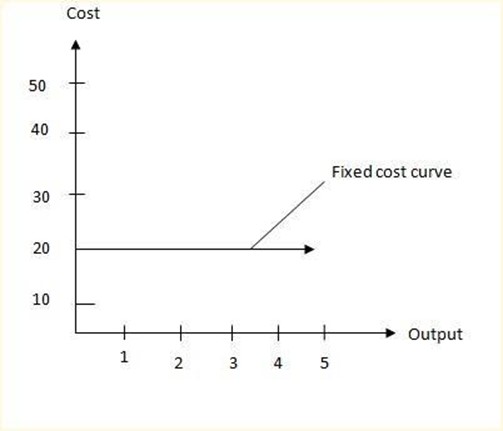
a.)Fixed costs/prime costs/overhead cost
-These are the types of costs which don’t change with the change in the level of output
-They must be insured even if production has not taken place.
Example;
Rent of hiring land and interest for the use of capital must be paid even when there is no production of any output.
Example of total fixed cost schedule
The schedule can be presented in a form of a curve as shown below;-
b.) Variable cost
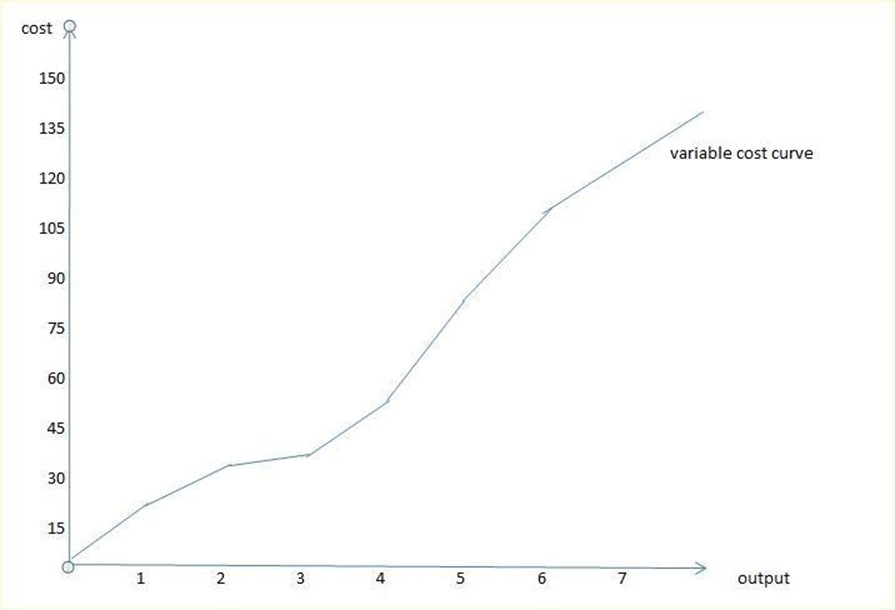
-Refers to the type of cost which changes with the change in the level of output
-It means when production increases, a firm occurs more costs such as of buying raw materials, transport charges, wages to skilled labours, electricity etc
Examples of variable cost schedule
The schedule above can be presented in a form of a curve as shown below.
Total cost
-It is a sum of all costs of production both implicit cost and explicit cost.

TC = I + E
TC = I + (TFC + TVC)
Total fixed cost, total variable cost and total cost
Output(kg) TFC(Tshs) TVC(Tshs) TC(Tshs) 0 50 0 50 1 50 15 65 2 50 25 75 3 50 34 84 4 50 42 92 5 50 52 102 6 50 64 114 7 50 78 128 edu.uptymez.com
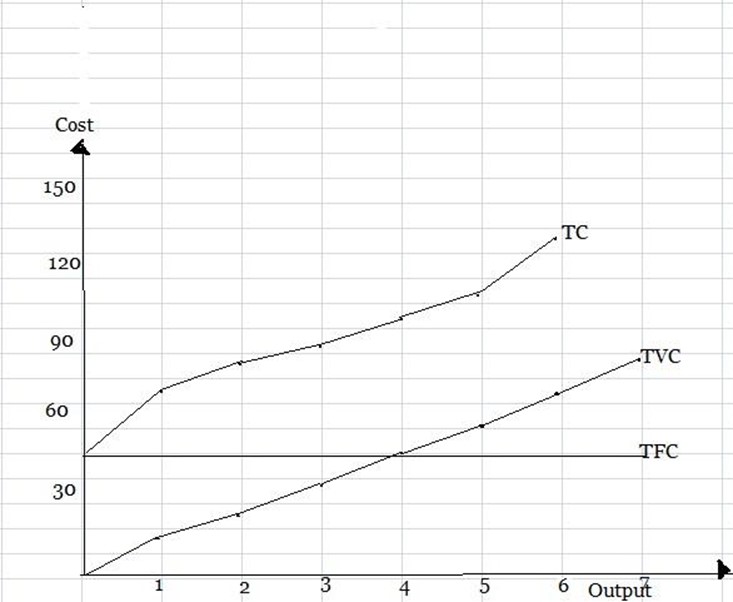
Total cost, Total variable cost and Total fixed cost curve
AVERAGE FIXED COST, AVERAGE TOTAL COST, AVERAGE
VARIABLE COST AND MARGINAL COST
AVERAGE FIXED COST (AFC)
-Is the fixed cost per unit of output
AFC = TFC
Q
Where;
AFC = Average fixed cost
TFC = Total fixed cost
Q = Quantity
Example of Total fixed cost and Average fixed cost
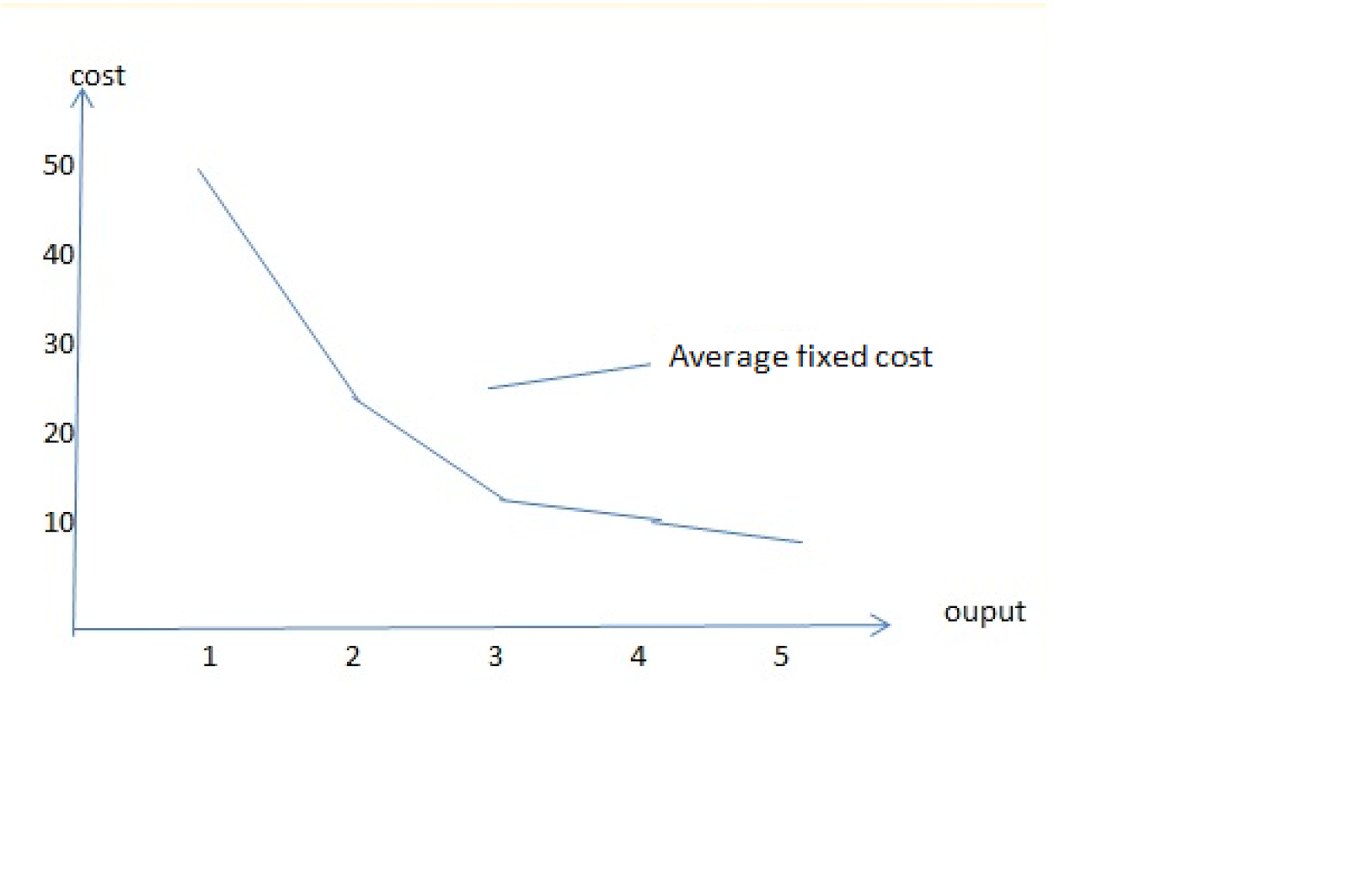
-It is a curve which represents graphically average cost and the respective output levels.
AVERAGE VARIABLE COST (AVC)
-This is the ratio between total variable cost and the level of output produced.
Or
-Is the variable cost per unit of output.
AVC = TFC
Q
Example of average variable cost.
Output(kg) TVC(Tshs) Average cost(Tshs) 0 0 0 1 18 18 2 30 15 3 40 13.3 4 52 13 5 65 13 6 82 13.7 7 106 15.15 edu.uptymez.com
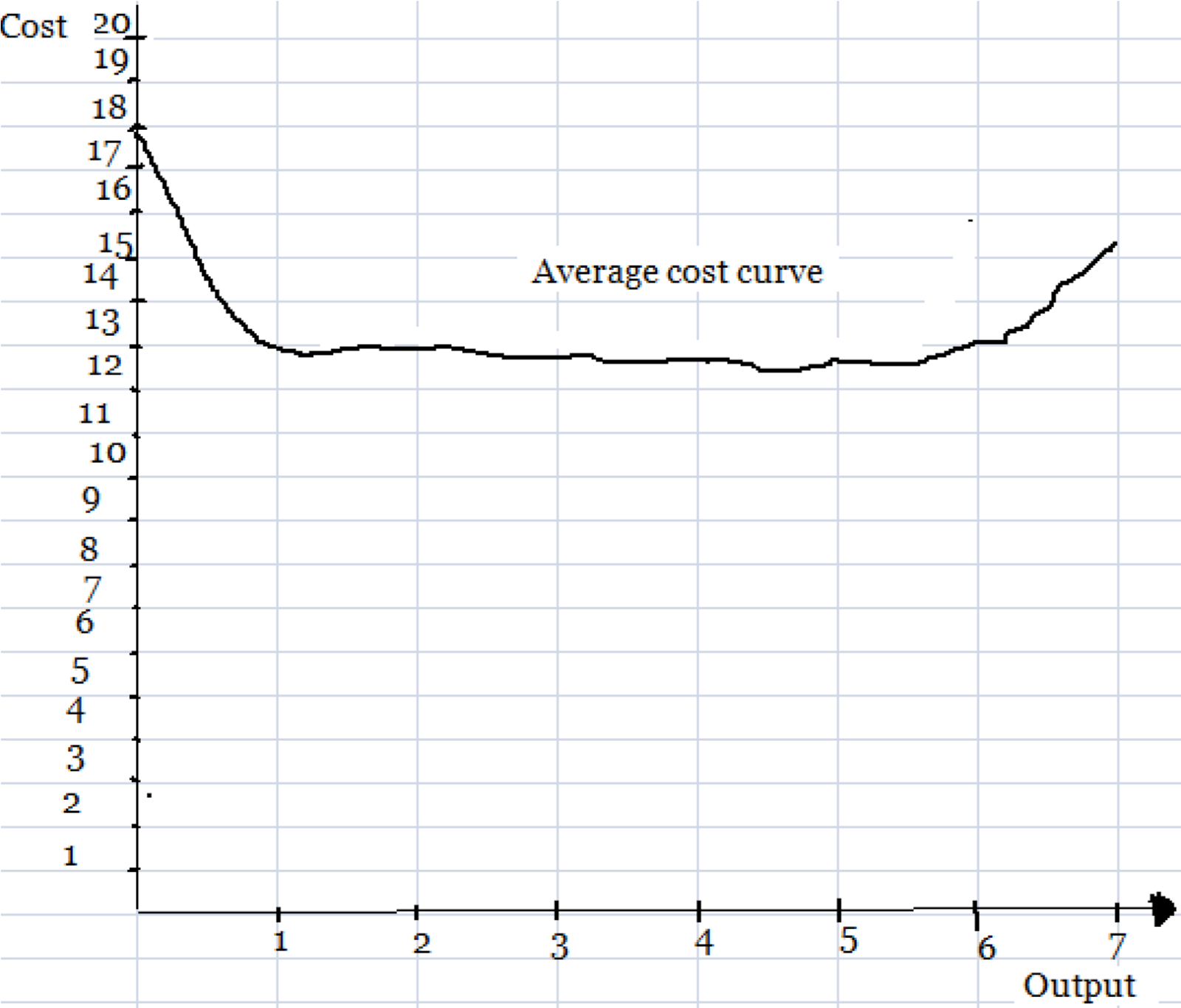
AVERAGE TOTAL COST(ATC)
-Is the total cost per unit of output.
ATC = TC
Q
Total cost average total cost
Output(kg) TC(Tshs) ATC(Tshs) 0 50 0 1 65 65 2 75 37.5 3 84 28 4 92 23 5 102 2.40 6 114 19 7 128 18.28 edu.uptymez.com
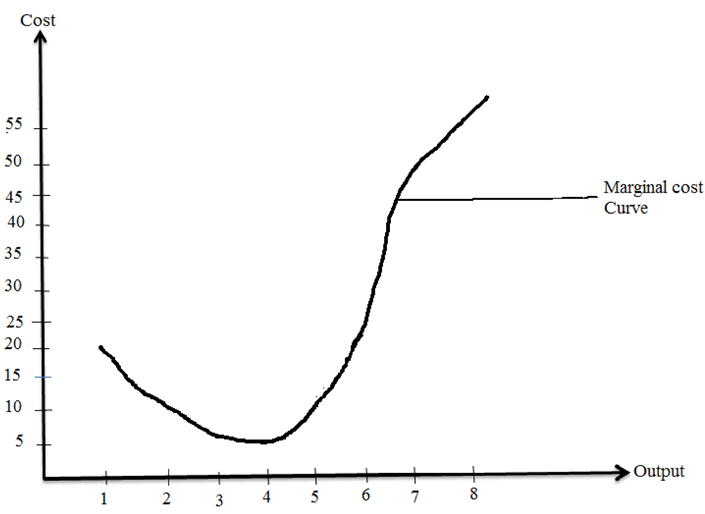
MARGINAL COST (MC)
-Refers to additional cost due to one more unit of output produced.
MC = Change in Total cost
Change in output (Q)
= TC2 – TC1
__________
Q2 – Q1
Total cost and Marginal cost
OUTPUT(Kg) TC (Shs) MC(Shs)
0 60 – 1 80 20 2 90 10 3 95 5 4 100 5 5 110 10 6 130 20 7 175 45 8 230 55 edu.uptymez.com
- To start the business