Is an element which has half filled ‘d’ orbital.Transition Element are element which have at least one unpaired electron in the outer most sub energy level ‘d’. The transition element is an elements which have incompletely field d – orbital. The transition element is known as transition because have intermediate properties which differ from. ‘S’ block element and ‘P’ block element. Transition elements are d – block element, but not all d-block elements are transition elements. Most of transition element are metal element which called transition metal.
There are three series of transition metal:-
(i) Transition Metal of the first series.
(ii) Transition metal of the second series or LANTHANIDE METALS.
(iii) Transition Metal of third series or are sometime known as ACTINAMIDE METAL. (The strongest metal)
II. TRANSITION METALS OF THE FIRST SERIES
Are these which have half filled 3d – orbital are those which have at least ONE UNPAIRED ELECTRON IN SUB ENERGY LEVEL 3D.
Transition metals of the first series are given below
| ATOMIC NUMBER |
ELEMENT |
SYMBOL |
ELECTRONIC |
STRUCTURE |
| 21 | SCANDIUM | Sc | [Ar]4S2 3d1 | |
| 22 | TITANIUM | Ti | [Ar]4S23d2 | |
| 23 | VANADIUM | V | [Ar] 4S23d3 | |
| 24 | CHROMIUM | Cr | [Ar] 4S13d5 | |
| 25 | MANGANESE | Mn | [Ar] 4S23d5 | |
| 26 | IRON | Fe | [Ar] 4S23d6 | |
| 27 | COBALT | CO | [Ar] 4S23d7 | |
| 28 | NICKEL | Ni | [Ar] 4S23d8 | |
| 29 | COPPER | Cu | [Ar] 4S13d10 | |
| 30 | ZINC | Zn | [Ar] 4S23d10 | |
| To remember use | ||||
| Science | Teacher | Are very | Craver mostly | From |
| Congo | Nigeria | and | Coastal | Zanzibar |
edu.uptymez.com
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF TRANSITION METALS
Transition metals have the following general properties.
(i) Form colour (colour formation)
(ii) Are paramagnetic substance
(iii) Have variable oxidation states
(iv) Form complex compound
(v) Have catalytic action.
A. COLOUR FORMATION BY TRANSITION METALS
Transition metal appear coloured at room temperature of form colour when occur in ionic or combined state. But non – transition metal does not form colour at room temperature. The non – transition metal appear coloured when heated during flame test. The energy of flame excite electron which jump from low energy level. This cause atom to be unstable. In order to maintain the stability the effective nuclear force returns back the electron to the ground state. When the electron drop back emit the radiant energy which have a wavelength detected by a human eye. This radiant have definite colour.
But Magnesium does not produce colour during flame test instead remain colourless because energy of the flame is not enough to excite electron of Magnesium.
Transition metals colour formation can be explained by two theories.
(i)4s – 3d electron transition theory
(ii)d- Electron transition theory (crystal field theory)
(i) 4s – 3d ELECTRON TRANSITION THEORY
According to this theory colour formation is a result of movement of electron between sub energy level 4s and 3d. The energy difference between sub energy level 3d and 4s(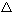 E) is so small that normal radiant energy absorbed cause electron to move from 4s level to 3d level. Radiant energy absorbed from the sun makes 4s electrons to jump to 3d orbitals and the atoms becomes UNSTABLE. To maintain stability of the atoms excited electrons fall back to 4s orbital. During this process when electrons (excited) fall to their ground state heat energy is emitted and came out in form of radiation those wave have wavelength which are within the range that can be detected by human eyes with specified definite colour.
E) is so small that normal radiant energy absorbed cause electron to move from 4s level to 3d level. Radiant energy absorbed from the sun makes 4s electrons to jump to 3d orbitals and the atoms becomes UNSTABLE. To maintain stability of the atoms excited electrons fall back to 4s orbital. During this process when electrons (excited) fall to their ground state heat energy is emitted and came out in form of radiation those wave have wavelength which are within the range that can be detected by human eyes with specified definite colour.
(ii) d – d ELECTRON TRANSITION THEORY OR CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY
Colour formation by transition metal can be explained by crystal field theory. This theory suggested that for transition metals to express colour there are two conditions which are necessary and must be fulfilled.
a.There must be at least one unpaired electrons in 3d – orbital
b.Presence of ligands.