QUESTION
outline factors that enable elements to have diagonal similarities
A. similar electronegativity
B. similar atomic and ionic sizes.
C. have ions with similar polarization power.
ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOUR OF THE FIRST ELEMENT IN A GROUP OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
The first element in every group of the period show some properties which are not shown to other elements in the respective group .The element is said to show anomalous behavior when its properties differ with those of the rest group member. The anomalous behavior of the first element in a group is due to the following factors,
A. The first element in a group has the smallest atomic and ionic size when compared with the rest group members
B. The first element in a group has the highest ionization energy
C. The first element in a group has the highest electronegativity
D. The first element in a group has the higher electronic affinity
ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOUR OF LITHIUM
I. Lithium forms covalent compounds while other alkali metals form ionic compound example LiCl is a covalence compound while NaCl is ionic
II. Lithium reacts with nitrogen gas on heating to form ionic nitride while other alkali metals do not react
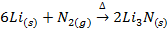
III. Lithium reacts slowly with cold water while other alkali metals react vigorously
IV. Lithium forms hydrated chloride while the rest group member form anhydrous chloride example LiCl.2H2O and NaCl (Li can polarize water due to high polarizing power)
V. When burnt in air ,lithium gives the monoxide while other alkali metals form peroxide and super oxide
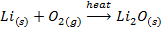
Lithium monoxide
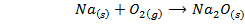
Sodium peroxide
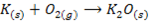
Potassium peroxide
VI. Lithium does not form acetylide with ethyne (acetylene ) while other alkali metals form acetylide with ethyne
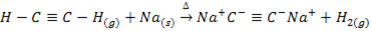
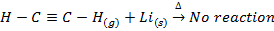
VII. Lithium is only alkali metal whose salts may undergo hydrolysis
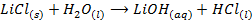
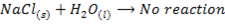
VIII. The hydroxides of lithium decomposes on heating to monoxide and water while hydroxide of other alkali metals sublime undecomposed
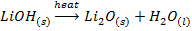
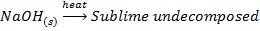
IX. Lithium nitrate decomposes on heating into Lithium monoxide, nitrogen dioxide and oxygen while the nitrates of other alkali metals decompose into nitrites and oxygen.
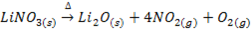
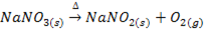
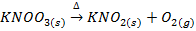
X. Lithium carbonate decomposes gently heating into monoxide and carbon dioxide while the carbonates of other alkali metals are stable .They decompose at higher temperature.
e.g. 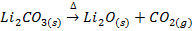
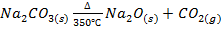
XI. Lithium hydroxide is less soluble in water and hence a much weak base than sodium hydroxide a and potassium hydroxide
XII. Lithium chloride is deliquescent while chloride at the rest group members aren’t deliquescent
XIII. Lithium sulphate do not form alums while the sulphate of the rest group form alums
ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOUR OF BERYLIUM
1. Beryllium react with concentrated solution of alkali to form hydroxo-complexes and hydrogen gas while other alkaline earth metal do not react
E.g. 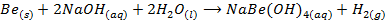
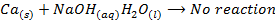
2. The oxides and hydroxides of beryllium are amphoteric while those of other alkaline earth metals are basic
3. Beryllium chlorides hydrolyze in water while the chlorides of the rest group members do not.
BeCl2 + H2O → Be(OH)2 + 2HCl (Hydrolysis)
4. Beryllium chloride dimerize in vapour state while the chloride of the rest group member do not dimerize.
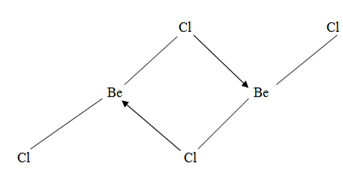
Beryllium chloride Dimer
5. Beryllium form fluoro-complexes while other alkali earth metals do not.
6. The chloride of beryllium readily dissolved in organic solvents while the chlorides of other alkali earth metals do not readily dissolved in organic solvents.
7. Beryllium do not react with water or steam while other group members can react with either cold or boiling water or steam.
8. Beryllium oxide do not react with water while the oxide of the rest group members react with water to form hydroxide.
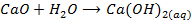
9. Beryllium do not react with either dilute or concentrated nitric acid 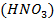 while the rest group member react with both dilute and concentrated
while the rest group member react with both dilute and concentrated 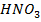
10. Beryllium carbide hydrolyses in water to form methane while the carbides of other group members give ethyne
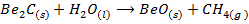 (
(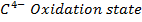 )
)
CaC2(s) + 2H2O(cold) → Ca(OH)2 + H – C ≡ C – H ((C– = C–)-2 Oxidation state)
11. Beryllium chloride fumes in moist air while chloride of the rest group members do not.
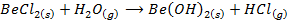
(From air)
The fumes are due to hydrolysis of  in water where
in water where  is given out.
is given out.