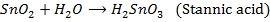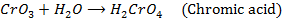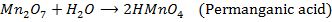ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOUR OF FLUORINE
Like other first elements in every group fluorine exhibit some properties which differ with the rest group members.
The anomalous behavior of fluorine is due to ;
i) Its smaller atomic and ionic size
ii) Absence of d-orbital
iii) Its highest electronegativity value
iv) Its higher electron affinity
The Anomalous behaviors of fluorine are as follows
1. Fluorine is a monovalent while other halogens show covalencies of 3 and 5. Chlorine and Iodine also show a valence of 7. Fluorine is a monovalent because it has no d-orbital while other members have d-orbital.
2. The elements in the periodic table show their highest oxidation states when combined with fluorine, example  and SF8. This is due to highest electronegativity value of fluorine.
and SF8. This is due to highest electronegativity value of fluorine.
3. Fluorine forms hydrogen fluoride molecules which are strongly hydrogen –bonded. The hydrides of the rest halogens do not form hydrogen bonds between their molecules
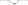
4. The solubility of fluorides often differ markedly from the solubilities of other halides of the same metal, example the alkaline earth metal halides are very soluble in water except the fluorides which are insoluble .On the other hand silver fluoride is the only soluble silver halide. The fluorides of alkaline earth metal have higher lattice energies than hydration energies.
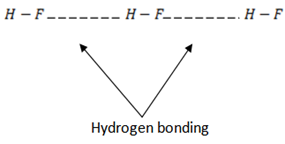
5. Metals show their highest degree of ionic character when combined with fluorine example 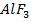 and
and 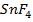 are ionic but Al
are ionic but Al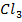 and
and 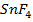 are covalent compound.
are covalent compound.
6. Hydrogen fluoride form acidic salts containing the biflouride ion (HF2–). The halide of rest halogens form normal salts only, example 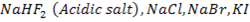 etc.
etc.
7. Fluorine is the only halogen more electronegativity than oxygen and it often behaves differently to other halogens in reaction with oxygen containing compounds example water (F displaces O from water unlike others). Fluorine liberates oxygen from water while other halogens do not
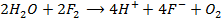
Or 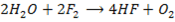
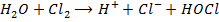
Or 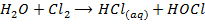
8. Fluorine evolve oxygen from hot concentrated alkalis while other halogens form chloride and chlorate (v)
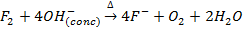
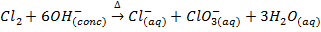
(Chlorate ion)
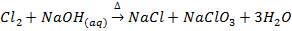
With cold dilute alkalis fluorine given a fluoride and difluorine monoxide while chlorine form chloride and hypochlorite.
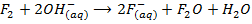
(Difluorine monoxide)
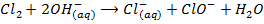
(Hypochlorite ion)
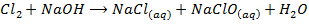
9. Fluorine combines directly with carbon while other halogens have no effect on it.
SELECTED COMPOUNDS OF METALS.
(i.e COMPOUNDS OF Na, Mg, Ca, Al, Fe, Zn, Cu AND Pb)
METAL OXIDES
Definition; An oxide is binary compound made up of oxygen and other elements, example MgO, PbO, Al2O3, H2O2, NO2, SO2 etc
Therefore metal oxides are binary compounds made up of oxygen and metal, example PbO, FeO, , etc
NOTE: The binary oxygen – fluorine compounds are not called oxides of fluorine, but are called fluorides of oxygen since fluorine is more electronegative than oxygen (example OF2- oxygen difluorine)
GENERAL METHODS IN PREPARATION OF METAL OXIDES.
There are two methods of preparing metal oxides
a) DIRECT METHOD
b) INDIRECT METHOD
A.
DIRECT METHOD OF PREPARATION OF METAL OXIDES
In this method a metal reacts with a reagent or oxygen or air to give metallic oxide
I) A metal oxide may be prepared by burning a metal in air or oxygen
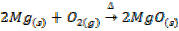
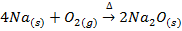
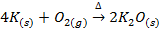
II) A metal oxide may be prepared by passing steam on red heat metal
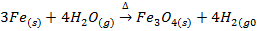
III) A metal oxide may be prepared by reacting a metal with an oxidizing agent like HNO3
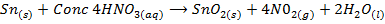
B. INDIRECT METHOD OF PREPARATION OF METAL OXIDES
In this method, the metal oxide is obtained by heating carbonates, hydroxides and nitrates etc
Example;
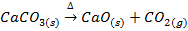
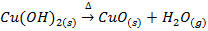
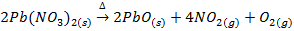
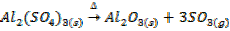
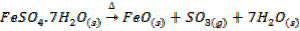
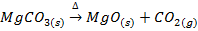
TYPES OF METALLIC OXIDE
The metal oxides may be classified as follows:
1) BASIC OXIDE
2) ACIDIC OXIDES
3) AMPHOTERIC OXIDES
4) PEROXIDES
5) SUPEROXIDE
6) MIXED OXIDES
1. BASIC OXIDES
These are oxides which react with acids to form salt and water only. They also combine with acidic oxides to form salts. Basic oxides may be ionic or covalent
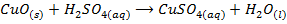
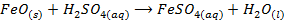
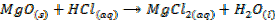
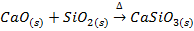
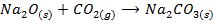
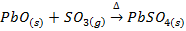
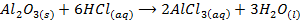
2. ACIDIC OXIDE
Acidic oxide are formed by metals in their higher oxidation states,
example 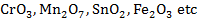
These oxides are generally covalent in nature. They dissolve in water to form oxy-acids and hence are called acid anhydrides.