FORMULATION OF A LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEM.
Steps in formulating a linear programming problem.
1. * Read the problem several times and assess what is known and what is to be determined.
2. * Identify the unknown quantities and assign variables to them, be careful about the units.
3. * Determine the objective function; it involves the quantity to be maximized or minimized.
4. * Translate the constraints into linear inequalities,
* Constraints are limitation or restrictions to the problem for each constraints the units must be same.
5. * Graph the constraints and find the feasible solution
6. * Find the corner points of the feasible solution. These are points of intersection of the graph
7. * Evaluate the objective function. Highest value of the objective function has to be maximized or smallest value to be minimized.
Example
A student has 120 shillings to spend on exercise books. At a school shop an exercise book costs 8 shillings, at stationery store an exercise book costs 12 shillings. The school has only 6 exercise books and the student wants to obtain the greatest number of exercise books possible using the money. Find the greatest number of exercise books he can buy.
Solution
Let x be number of exercise books to be bought at school shop
Let y be number of exercise books to be bought at stationery shop
→Objective function
Let f (x, y) = objective function
Then f (x, y) = x + y
→Constrains or linear inequalities
8x + 12y ≤ 120
x ≤ 6
Non – Negative constraints
x ≥ 0
y ≥ 0
→Equations
8x + 12y = 120
4x + 6y = 60
2x + 3y = 30
When x = 0, y = 10
y = 0, x = 15
x = 6, y = 0
x = 6
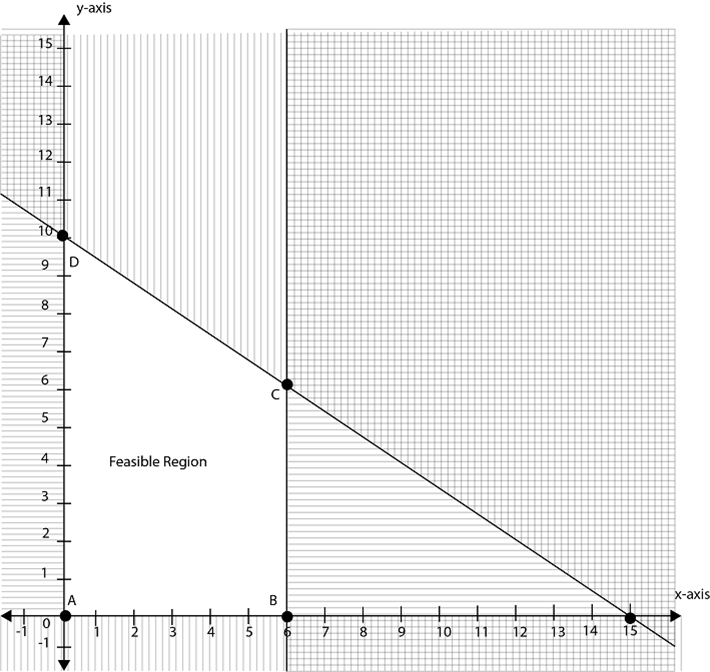
| Corner points | F (x, y) = x + y |
| A (0, 0) | 0 + 0 = 0 |
| B (6, 0) | 6 + 0 = 6 |
| C ( 6, 6) | 6 + 6 = 12 |
| D (0, 10) | 0+10 = 10 |
edu.uptymez.com
: . The greatest numbers of exercise books he can buy are 12 books 6 from the school shop and 6 from stationery.
Example
Student in a certain class are about to take a certain test of BAM which has two sections A and B; where in section A each question worth 10 marks while in section B; each worth 25 marks. The student must do at least 3 questions of section A; but not more than 12. A student must also do 4 questions from section B but not more than 15. In addition students cannot do more than 20 questions. How many questions of each type should the student do to obtain the maximum scores?
Solution
Let x be number of questions to be done in section A
Let y be number of questions to be done in section B
→Objective function
f (x, y) = 10x + 25y
→Constrains
3 ≤ x ≤ 12
4 ≤ y ≤ 15
x + y ≤ 20
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
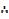 Maximize f (x, y) = 10x + 25y subject to;
Maximize f (x, y) = 10x + 25y subject to;
3 ≤ x ≤ 12
4 ≤ y ≤ 15
x + y ≤ 20
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Equations
3 = x = 12
4 = y = 15
x + y = 20
x = 20, y = 0
x = 0, y = 20
x = 0
y = 0
| Corner Points | f(x, y) = 10x + 25y |
| A (3, 4) | 10 (3) + 25 (4) = 130 |
| B (12, 4) | 10 (12) + 25 (4) = 220 |
| C (12, 8 ) | 10 (12) + 25 (8) = 320 |
| D (5, 15) | 10 (5) + 25 (15) = 425 |
| E (3, 15) | 10 (3) + 25 (15) = 405 |
edu.uptymez.com
 The student should do 5 questions from section A and 15 questions from section B to obtain maximum score of 425.
The student should do 5 questions from section A and 15 questions from section B to obtain maximum score of 425.
Diet problems on linear programming problem
Example 01
A doctor prescribes a special diet for patients containing the following number of units of Vitamin A and B per kg of two types of food F1 and F2
| Type of Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B |
| F1 | 20 units/kg | 7 units/kg |
| F2 | 15 units /kg | 14 units /kg |
edu.uptymez.com
If the minimum daily intake required is 120 units of A and 70 units of B, what is the least total mass of food a patient must have so as to have enough of these vitamins?
EXAMPLE 02
Rice and beans provide maximum levels of protein, calories and vitamin B2. If used as a staple diet. The food values per kg of uncooked rice and beans are as shown in the table below.
| Protein /kg | Calories/kg | Vitamin B2/kg | Price kg |
| Rice 60g | 3200 cal | 0.4 | 400 |
| Beans 90g | 1000 cal | 0.1 | 500 |
| Min daily req. 120 | 2000 cal | 0.2 |
edu.uptymez.com
What is the lowest cost of diet meeting, these specifications?
Solution.
Let x be number of kg of rice to be bought
Let y be number of kg of beans to be bought
→Objective function
400x + 500y
Constrains
60x + 90y ≤ 120
3200x + 1000y ≤ 2000
0.4x + 0.1y ≤ 0.2
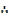 Minimize f (x, y) = 400x + 500y Subject to;
Minimize f (x, y) = 400x + 500y Subject to;
60x + 90y ≤ 120
3200x + 1000y ≤ 2000
0.4x + 0.1y ≤ 0.2
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
For 60x + 90y ≥ 120
60x + 90y = 120
2x + 3y = 4
When x = 0, y = 1.3
Y = 0, x = 2
For 3200x + 1000y ≥ 2000
32x + 10y = 20
16x + 5y = 10
When x = 0, y = 2
Y = 0, x = 0.63
For 0.4x + 0.1y ≤ 0.2
0.4x + 0.1y = 0.2
When x = 0, y = 2
When y = 0, x = 0.5
| Corner points | F (x, y) = x + y |
| A (0, 8) | 0 + 8 = 8 |
| B (3.6, 3.2) | 3.6 + 3.2 = 6.8 |
| C (10,0) | 10 + 0 = 10 |
edu.uptymez.com
: . The least total mass a patient should have is 6.8kg i.e. 3.6kg of food 1 and 3.2 kg of food 2.
Question
1. A doctor prescribes that in order to obtain adequate supply of vitamin A and C his patient should have portions of food 1 and food 2. The number of units of vitamin A and C are given in the following table
The doctor prescribes a minimum of 14 units of vitamin A and 21 units of vitamin C. What are the least portions of food 1 and food 2 that will fit the doctor’s prescriptions?
LINEAR PROGRAMMING PROBLEMS
1. Two printers N and T produce three types of books. N produces 80 types I books per day, 10 type II books per day and 20 types III books per day, while T produces 20 types I books per day 10 type II books per day and 70 types III books per day. The orders placed are 1600 type I, 500 type II and 2100 type III books. The daily operating costs for N shs. 10,000/=, for T shs, 20,000/= how many days should each printer operate to meet the orders at a minimum cost.
2. A small textile company manufactures three different size of shirts, Large (L), medium (M) and small (S) at two different plants A and B. The number of shirts of each size produced and the cost of production per day are as follows!
| A | B | Monthly demand | |
| Large size per day | 50 | 60 | 2500 |
| Medium size per day | 100 | 70 | 3500 |
| Small size per day | 100 | 200 | 7000 |
| Production Cost per day T. shs. | 2500 | 3500 | _ |
edu.uptymez.com
(i) How many days per month should each factory operate in order to minimize total cost.
(ii) What is the minimum cost of production
Solution 01
Let x be number of days printer N should operate
Let Y be number of days printer T should operate
→Objective function (f(x, y))
10000x + 20000y
→Constrains
80x + 20y ≥ 1600
10x + 10y ≥ 500
20x + 70y ≥ 2100
X ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
→Equations
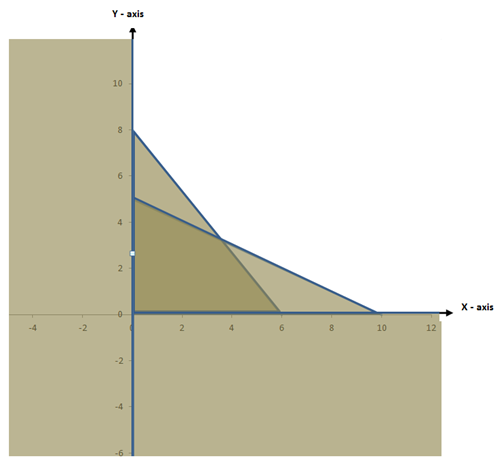
80x + 20y ≥ 1600
80x + 20y = 1600
8x + 2y = 160
When x = 0, y = 80
y = 0, x = 20
10x + 10y ≥ 500
10x + 10y = 500
x + y = 50
When x = 0, y = 50
y = 0, x = 50
20x + 70y ≥ 2100
20x + 70y = 2100
2x + 7y = 210
When x = 0, y = 30
y = 0, x = 105
| Corner points | F (x, y) = 10000x + 20000y |
| A (0, 80) | 10000 (0) + 20000 (80) = 1,600,000 |
| B (28, 22) | 10000 (28) + 20000 (22) = 720,000 |
| C (105, 0) | 10,000 (105) + 20000 (0) = 1,050,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
 Printer N should be operated for 28 days and printer T should work for 22 days to meet the orders at minimum cost.
Printer N should be operated for 28 days and printer T should work for 22 days to meet the orders at minimum cost.
Solution 02
Let x be number of days per month factory A should operate
Let y be number of days per month factory B should operate
→Objective function
F (x, y) = 2500x + 3500y
→Constrains
50x + 60y ≥ 2500
100x + 70y ≥ 3500
100x + 200y ≥ 7000
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
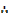 Minimize f (x, y) = 2500x + 3500y
Minimize f (x, y) = 2500x + 3500y
Subject to 50x + 60y ≥ 2500
100x + 70y ≥ 3500
100x + 200y ≥ 7000
X ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
→Equations
50x + 60y = 2500
When y = 0, x = 50
X = 0, y = 41.7
100x + 70y = 3500
When y = 0, x = 35
x = 0, y = 50
100x + 200y = 7000
When y = 0, x = 70
X = 0, y = 35
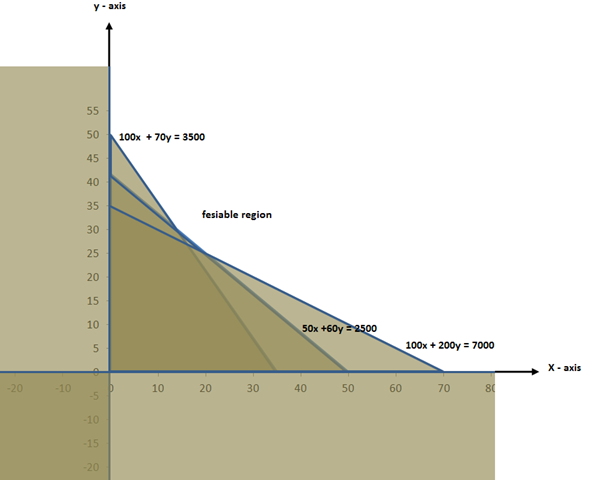
| Corner points | F (x, y) = 2500x + 3500y |
| A (0,50) | 2500 (0) + 3500 (50) = 175,000 |
| B (15, 30) | 2500 (15) + 3500 (30) = 142,500 |
| C (20,25) | 2500 (20) + 3500 (25) = 137,500 |
| D (70, 0) | 2500 (70) + 3500 (0) = 175,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
 Factory A should operate for 20 days and factory B should operate for 25 days in order to minimize total cost.
Factory A should operate for 20 days and factory B should operate for 25 days in order to minimize total cost.
→Minimum cost of production is 137,500
3. In a certain garage the manager had the following facts floor space required for a saloon is 2m2 and for a lorry is 3m2. Four technicians are required to service a saloon car and three technicians for a lorry per day. He has a maximum of 24m2 of a floor space and a maximum of 36 technicians available; in addition he is not allowed to service more Lorries than saloon cars. The profit for serving a saloon car is 40,000/= and a lorry is 60,000/=. How many motor vehicles of each type should be serviced daily in order to maximize the profit?
Solution
Let x be number of saloon cars to be serviced daily
Let y be number of Lorries to be serviced daily
→Objective function
F (x, y) = 40000x + 60000y
→Constrains
2x + 3y ≤ 24
4x + 3y ≤ 36
x ≥ y
x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
 Maximize f (x, y) = 40000x + 60000y
Maximize f (x, y) = 40000x + 60000y
Subject to 2x + 3y ≤ 24
4x + 3y ≤ 36
x ≥ y
x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
→Equations
2x + 3y ≤ 24
When x = 0, y = 8
Y = 0, x = 12
4x + 3y ≤ 36
When x = 0, y = 12
y = 0, x = 9
x = y
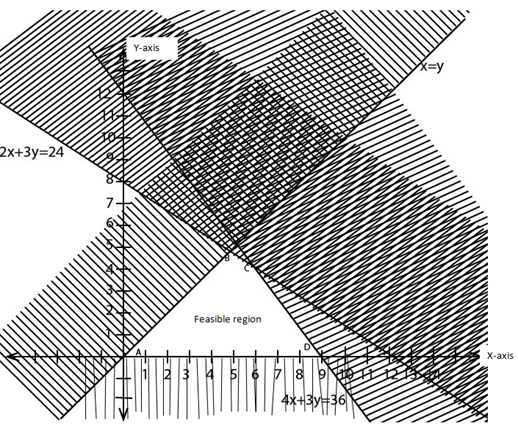
| Corner points | F (x, y) = 40000x + 60000y |
| A (0, 0) | 40000 (0) + 60000 (0) = 0 |
| B (4.8, 4.8) | 40000 (4.8) + 60000 (4.8) = 480,000 |
| C (6,4) | 40000 (6) + 60000 (4) = 480,000 |
| D (9, 0) | 40000 (9) + 60000 (0) = 360,000 |
edu.uptymez.com
 6 saloon cars and 4 Lorries should be serviced daily to maximize profit to 480,000/=
6 saloon cars and 4 Lorries should be serviced daily to maximize profit to 480,000/=
More example
A builder has two stores, one at S1 and the other at S2. He is building houses at P1, P2, and P3. He needs 5 tons of bricks at P1, 6 tons of bricks at P2 and 4 tons of bricks at P3. The stores contain 9 tons of bricks at S1 and 6 tons of bricks at S2. The transport cost per ton are shown in the diagram
How does the builder send his bricks at a minimum cost? What is the minimum overall cost?
Solution
Let the builder send x tons of bricks from S1 to P1 and y tons of bricks from S1 to P2
Then the transportation of bricks to P1, P2 and P3 will be as follow: –
The constrains are obtained as follows
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
9 – (x + y) ≥ 0 i.e. x + y ≤ 9
5 – x ≥ 0 i.e. x ≤ 5
6 – y ≥ 0 i.e. y ≤ 6
4 – [9 – (x + y)} ≥ 0 i.e. x + y ≥ 5
Objective function
F (x, y) = 6x + 3y + 4(9 – (x + y)) + 4 (5 – x) + 2(6 – y) +6 [4 – (9 – (x + y)]
= 6x + 3y +36 – 4x + 4y + 20 – 4x + 12 – 2y + 24 – 54 + 6x + 6y
F (x, y) = 4x – 3y + 38
 Minimize f (x, y) = 4x – 3y + 38
Minimize f (x, y) = 4x – 3y + 38
Subject to x + y ≤ 9
x + y ≥ 5
x ≤ 5, y ≥ 0
y ≤ 6, y ≥ 0
→Equation
x + y = 9
When x = 0, y = 9
y = 0, x = 9
x + y = 5
x = 0, y = 5
y = 0, x = 9
x = 5
y = 6
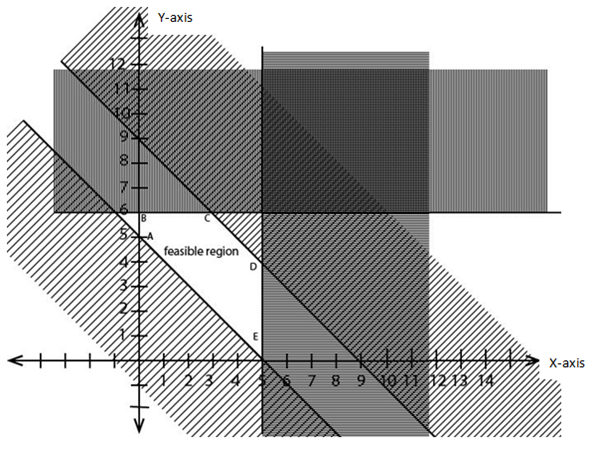
| Corner points | F (x, y) = 4x + 3y + 38 |
| A (0, 5) | 4 (0) + 3 (5) + 38 = 53 |
| B (0, 6) | 4 (0) + 3 (6) + 38 = 56 |
| C (3, 6) | 4 (3) + 3 (6) + 38 = 68 |
| D (5, 4) | 4 (5) + 3 (4) + 38 = 70 |
| E (5, 0) | 4 (5) + 3 (0) + 38 = 58 |
edu.uptymez.com
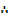 The builder should send the bricks of tons as follows
The builder should send the bricks of tons as follows
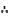 The overall minimum cost is 53/=
The overall minimum cost is 53/=
EXERCISE
There is a factory located at each of the places P and Q. From these location a certain commodity is delivered to each of the three deports situated at A, B and C. The weekly requirements of the deports are respectively 5,5 and 4 unit of the commodity while the production capacity of the factories P and Q are 8 and 6 units respectively, just sufficient for requirement of deports. The cost of transportation per unit is given.
Formulate this linear programming problem and how the commodities can be transported at minimum cost. What is the overall minimum cost?