BI CONDITIONAL STATEMENT
Consider the truth table for (P → Q) ∧ (Q → P)
The statement (P → Q) ∧ (Q → P) is known as bi-conditional statement and is abbreviated as P 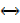 Q
Q
Truth table for P 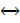 Q
Q
Note: P 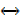 Q is read P if and only if Q
Q is read P if and only if Q
P 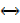 Q is true when both P and Q are true or when P and Q are false
Q is true when both P and Q are true or when P and Q are false
Example. The truth value of 43 > 3 if and only if 5< 3 (F)
43 < 3 if and only if 3 < 5 (F)
43< 3 if and only if 5 < 3 (T)
43> 3 if and only if 5 > 3 (T)
CONVERSE, CONTRA POSITIVE, INVERSE
Given a proposition: if a quadrilateral is a parallelogram then its opposite sides are parallel, P → Q
Converse: If the opposite sides are parallel, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram i.e. Q → P.
Contra positive: If the positive sides are not parallel, then the quadrilateral is not a parallelogram. i.e. ~ Q → ~ P
Inverse: if a quadrilateral is not a parallelogram, then the opposite sides are not parallel i.e. ~ P → ~ Q
Truth table for implication, converse, contra positive, inverse
| P | Q | P → Q | Q → P | ~ P | ~ Q | ~ Q → ~P | ~P → ~ Q |
| T | T | T | T | F | F | T | T |
| T | F | F | T | F | T | F | T |
| F | T | T | F | T | F | T | F |
| F | F | T | T | T | T | T | T |
edu.uptymez.com
Column 3 has exactly truth value as column 7
i. e P → Q 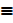 ~Q → ~ P
~Q → ~ P
Q → P 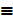 ~ P → ~Q
~ P → ~Q
EQUIVALENT STATEMENTS
Two propositions are logically equivalent if they have exactly the same truth values
E.g. P V Q and Q V P are logically equivalent
Solution: Draw truth for P V Q and Q V P
1 2 3 4
Since column 3 has exactly the same truth values as column 4 then
P V Q 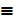 Q V P
Q V P
Questions
Show whether or not the following propositions are logically equivalent
i)P → Q, ~ P V Q
Since column 3 and 5 have exactly the same truth value therefore
P → Q 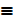 ~ P V Q
~ P V Q
ii) P → (P V Q); P → Q
Since column 4 does not have exactly same truth value as column 5 then p → (P V Q) 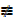 P → Q
P → Q
iii) P → Q: ~ P → Q
Since column 3 does not have exactly same truth values as column 5 therefore
P → Q 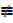 ~ P → Q
~ P → Q
iv) P → Q; Q → P
Since column 3 does not have exactly same truth values as column 4 therefore P → Q 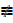 Q → P
Q → P
v) ~ (P → Q);PV ~ Q
(5) (6)
Since column 5 does not have exactly same truth value as column 6 therefore ~ (P → Q) 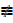 P V ~Q
P V ~Q
vi) ~ (P V Q); ~P ∧ ~Q
| P | Q | ~ P | ~ Q | P V Q | ~ (P V Q) | ~P ∧ ~Q |
| T | T | F | F | T | F | F |
| T | F | F | T | T | F | F |
| F | T | T | F | T | F | F |
| F | F | T | T | F | T | T |
edu.uptymez.com
Since column 6 has exact same truth values as column 7 therefore ~ (P V Q) →( ~P ∧ ~Q)
COMPOUND STATEMENTS
Compound statements with three components P, Q, R.
Consider the following compound statement,
Triangles have all three sides and either the area of a circular region of radius r is 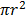 or it is false that the diagonals of a parallelogram do not meet.
or it is false that the diagonals of a parallelogram do not meet.
Solution
(To symbolize the above statement)
Let P  triangles have three sides
triangles have three sides
Let Q  circular region of radius r is
circular region of radius r is 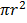
Let R 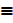 diagonals of parallelogram do not meet
diagonals of parallelogram do not meet
P ∧ (Q V ~R)
To find the truth values of the above statement
The statement has a truth value true
TAUTOLOGY
A tautology is a proposition which is always true under all possible truth conditions of its component parts
Example
Show that whether or not
~ (P ∧ Q) V (~P → ~Q) is a tautology
(6) (7)
| P | Q | ~ P | ~ Q | P ∧ Q | ~ (P ∧ Q) | ~ P → ~Q | 6 V 7 |
| T | T | F | F | T | F | T | T |
| T | F | F | T | F | T | T | T |
| F | T | T | F | F | T | F | T |
| F | F | T | T | F | T | T | T |
edu.uptymez.com
Since column 8 has all the truth values True (T) therefore it is TAUTOLOGY
Since column 8 has truth value true throughout then, ~ (P ∧ Q) V (~ P → ~Q) is a tautology
Questions
1. Show whether the given compound statements are tautology or not
i) (P ∧ Q) → P
Since column 4 has truth value true throughout then (P ∧ Q) → P is a tautology.
ii) P → (P ∧ Q)
Since column 4 does not have truth value true throughout then P → (P ∧ Q) is not a tautology.
iii) P → ~P
Since column 3 does not have the truth value true throughout then
P → ~ P is not a tautology.
iv) (P → Q) → (~ P → Q)
| P | Q | P → Q | ~ P | ~P → Q | (P → Q) → (~ P → Q) |
| T | T | T | F | T | T |
| T | F | F | F | T | T |
| F | T | T | T | T | T |
| F | F | T | T | F | F |
edu.uptymez.com
Since column 6 does not have the truth value true throughout then (P → Q) →(~ P → Q) is not a tautology
v) (P → Q) V (Q → P)
Since column 5 has all truth values true throughout then (P → Q) V (Q → P) is a tautology.
2. Express the following in symbolic form and then find its truth value
i) 2 is a prime, and either 4 is even or it’s not true that 5 is even
Solution
Let P 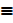 2 is a prime
2 is a prime
Let Q 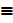 4 is even
4 is even
Let R 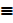 5 is even
5 is even
P ∧ (Q V ~R)
P ∧ (Q V ~R) has a truth value true.
ii) 7 is odd, or either London is in France and it is false that Paris is not in Denmark
Let P 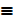 7 is odd
7 is odd
Q 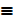 London is in France
London is in France
R 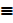 Paris is not in Denmark
Paris is not in Denmark
P V (Q ∧ ~R)
P V (Q ∧ ~R) has a truth value True
3. Find the truth values of P ∧ (Q V ~R) if
i) P, Q, R all has truth value T
ii) If P, Q, R all have truth value of F
iii) If P is true, Q is false and R is false
A complete truth table for general cases
1. Only one compound P
Two rows
2. Two components P and Q
Four rows
3. Three components P, Q, R
Eight Rows
4. Four components P, Q, R, S
Sixteen rows
| P | Q | R | S |
| T | T | T | T |
| T | T | T | F |
| T | T | F | T |
| T | T | F | F |
| T | F | T | T |
| T | F | T | F |
| T | F | F | T |
| T | F | F | F |
| F | T | T | T |
| F | T | T | F |
| F | T | F | T |
| F | T | F | F |
| F | F | T | T |
| F | F | T | F |
| F | F | F | T |
| F | F | F |
edu.uptymez.com
Example constructs a truth table for the compound statement
((P → Q) Λ R) 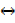 Q
Q
| P | Q | R | P → Q | (P → Q) Λ R | 5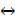 2 2 |
| T | T | T | T | T | T |
| T | T | F | T | F | F |
| T | F | T | F | F | T |
| T | F | F | F | F | T |
| F | T | T | T | T | T |
| F | T | F | T | F | F |
| F | F | T | T | T | F |
| F | F | F | T | F | T |
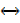 Q
Q