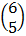SOLUTION
1. a) A = 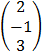 B =
B = 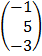
A + B
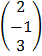 +
+ 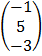
= 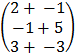 =
= 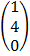
∴ A + B = 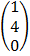
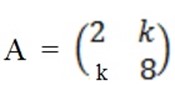
For singular matrix, 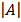 = 0
= 0
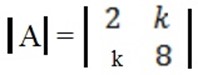
= 2 (8) – k (k) = 0
16 = k2 = 0
16 = k2
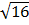 =
= 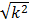
4 = k
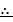 k = 4
k = 4
c) B = 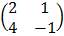
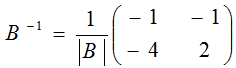
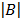 = 2 (-1) – 4 (1)
= 2 (-1) – 4 (1)
= -2 – 4
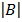 = -6
= -6
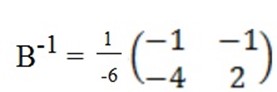
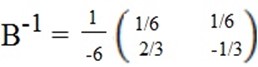
d) By using inverse method required to solve for x and y
x + 2y = 10
2x – y = 5
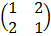
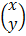 =
= 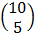
A = 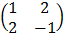
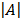 = 1 (-1) – 2 (2) = -1 – 4 – –5
= 1 (-1) – 2 (2) = -1 – 4 – –5
A-1 = 1/ 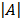
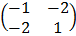
A-1 = 1/-5 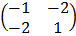
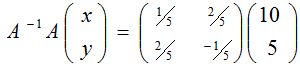
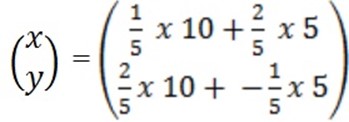
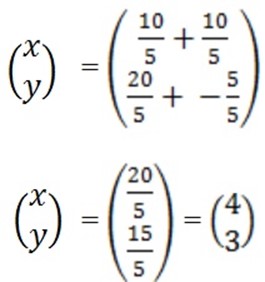
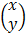 =
= 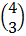
2. 3x – y + 2z = 2
x – 5y + 2z = 6
2x + 3y + z = 0
i) By determinant
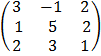
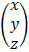 =
= 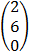
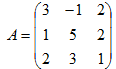
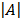 = 3
= 3 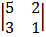 – –1
– –1 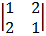 + 2
+ 2 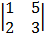
= 3 (5 – 6) – -1 (1 – 4) + 2 (3 – 10)
= 3 (–1) + 1 (-3) + 2 (–7)
= -3 + -3 + -4 = -20
B = 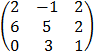
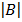 = 2
= 2 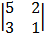 – 1
– 1 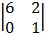 + 2
+ 2 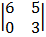
= 2 (5 – 6) + 1 (6 – 0) + 2 (18 – 0)
= 2 (–1) + 1 (6) + 2 (18)
= -2 + 6 + 36 = 40
C = 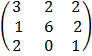
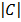 = 3
= 3 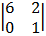 – 2
– 2 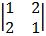 + 2
+ 2 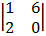
= 3 (6 – 0) – 2 (1 – 4) + 2 (0 – 12)
= 3 (6) – 2 (–3) + 2 (–12)
= 18 – 6 + -24 = -12
D = 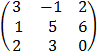
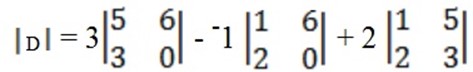
= 3 (0 – 18) + 1 (0 – 12) + 2 (3 – 10)
= 3 (–18) + -1 (–12) + 2 (–7)
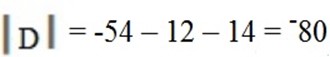
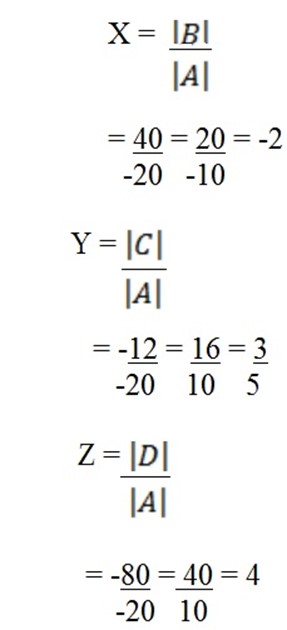
ii) By inverse
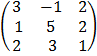
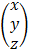 =
= 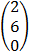
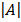 = 3
= 3 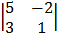 – 1 –1
– 1 –1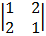 + 2
+ 2 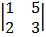
= 3 (5 – 6) + 1 (1 – 4) + 2 (3 – 10)
= 3 (-1) + 1 (-3) + 2 (-7)
= -3 + –3 + -14 = -20
A = 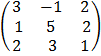
Cof 3: + 1 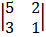 cof -1: 1
cof -1: 1 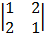
= + 1 (5 – 6) = – 1 (1 – 4)
= -1 = 3
Cof 2: + 1 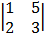 cof: – 1
cof: – 1 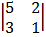
= + 1 (3 – 10) = -1 (5 – 6)
= -7 = 1
Cof 2: + 1 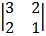 cof2: -1
cof2: -1 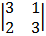
= + 1 (3 – 4) = -1 (9 – 2)
= -1 = -7
Cof 4 + 1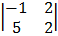 cof 3: -1
cof 3: -1 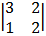
= + 1 (-2 – 10) = -1 (6 – 2)
= -12 = -4
Cof 1: + 1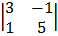
= + 1 (15 + 1)
= 16
Matrix of the Co factors
C = 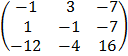
Adj A = 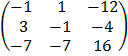
Inverse A
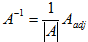
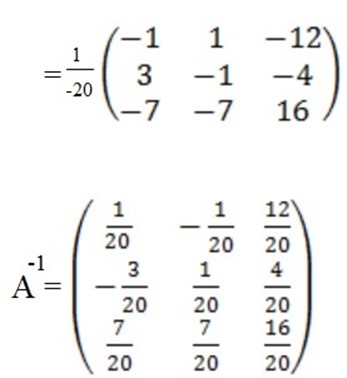
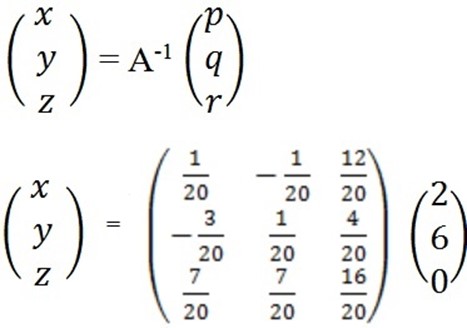
= 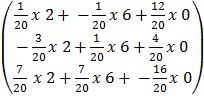
= 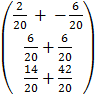
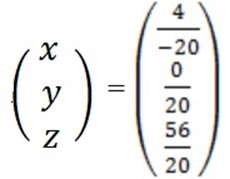
3. a) 2x + y = 8
4x – y = 10
i) Determinant
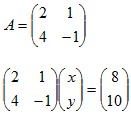
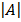 = 2 (-1) – 4 (1)
= 2 (-1) – 4 (1)
= -2 – 4 = -6
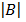 =
= 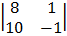
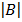 = 8 (-1) – 10 (1)
= 8 (-1) – 10 (1)
= -8 – 10 = -18
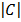 =
= 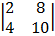
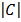 = 2 (10) – 4(8)
= 2 (10) – 4(8)
= 20 – 32 = -12
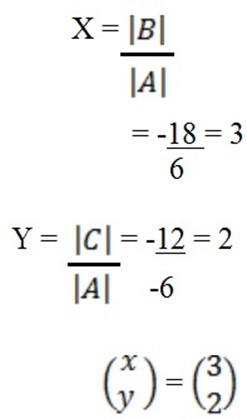
 X =
X = 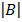
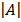
ii) By inverse
A = 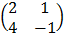
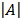 = 2 (–1) – 4 (1)
= 2 (–1) – 4 (1)
= -12 – 4 = -6
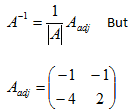
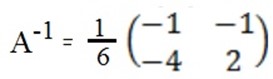
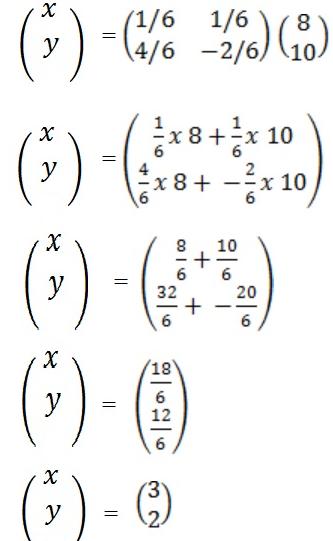
∴ 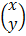 =
= 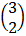
b) If A=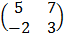 , B =
, B = 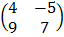 and C =
and C = 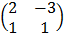 , Show that A + B – 2C is singular
, Show that A + B – 2C is singular
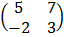 +
+ 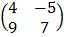 – 2
– 2 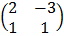
= 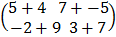 –
– 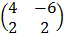
= 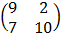 –
– 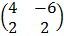
= 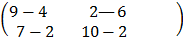
= 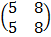
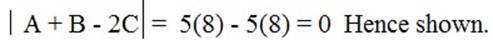
c) x + y + z = 6
3x – 2y – z = -1
2x + 4y + 3z = 19
i) Determinant
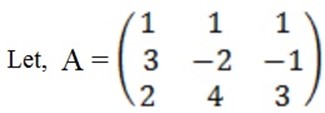
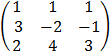
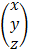 =
= 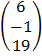
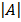 = 1
= 1 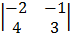 – 1
– 1 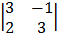 + 1
+ 1 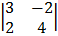
= 1 (-6 + 4) – 1 (9 + 2) + 1 (12 + 4)
= -2 – 11 + 16 = 3
B = 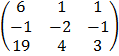
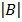 = 6
= 6 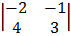 – 1
– 1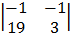 + 1
+ 1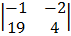
= 6 (-6 + 4) – 1 (-3 + 19) + 1 (-4 + 38)
= 6 (-2) – 1 (16) + 1 (34)
= -12 – 16 + 34 = 6
C =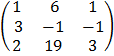
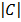 = 1
= 1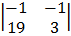 – 6
– 6 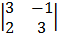 + 1
+ 1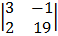
= 1 (-3 + 19) – 6 (9 + 2) + 1 (57 + 2)
= 16 – 6 (11) + 1 (59)
= 16 – 66 + 59 = 9
D = 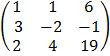
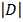 = 1
= 1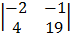 – 1
– 1 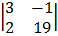 + 6
+ 6 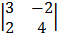
= 1 (-38 + 9) – 1 (57 + 2) + 6 (12 + 9)
= 1 (-34) – 1 (59) + 6 (16)
= -34 – 59 + 96 = 3
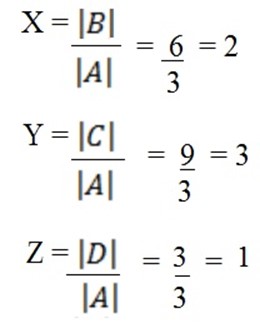
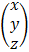 =
= 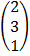
ii) By inverse
A = 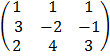
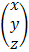 =
= 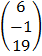
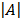 = 1
= 1 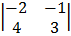 – 1
– 1 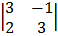 + 1
+ 1 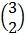
= 1 (-6 + 4) – 1 (9 + 2) + 1 (12 + 4)
= 1 (-2) – 1 (11) + 1 (16)
= -2 – 11 + 16 = 3
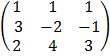
Cof 1: + 1 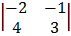 cof1: + 1
cof1: + 1 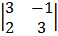
= + 1 (-6 + 4) = -1 (9 + 2)
= -2 = -11
Cof1: + 1 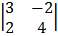 cof 3: -1
cof 3: -1 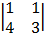
= + 1 (12 + 4) = -1 (3 – 4)
= 16 = -1
Cof2: + 1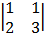 cof1: –
cof1: – 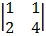
= + 1 (3 – 2) = – 1 (4 – 2)
= 1 = -2
Cof2: + 1 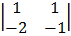 cof 4: – 1
cof 4: – 1 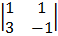
= + 1 (-1 + 2) = -1 (-1 – 3)
= + 1 = 4
Cof 3: + 1 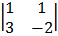
= + 1 (-2 – 3)
= -5
Matrix cofactors
A = 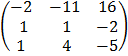
Adj A = 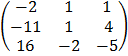
A-1 = 1/ 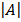 Adj A
Adj A
A-1 = 1/3 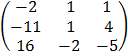
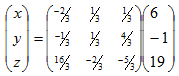
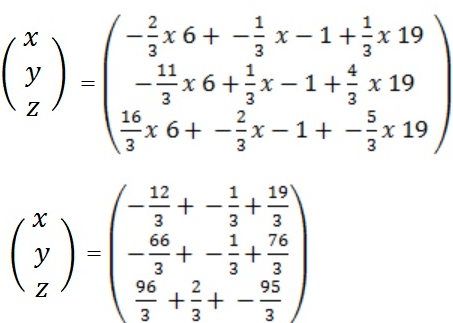
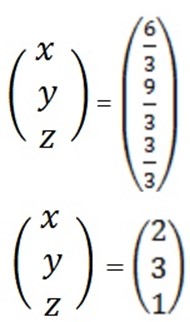
∴ 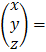
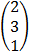
7. a) A = 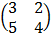 B =
B = 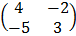
Calculate i) AB
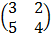 x
x 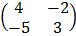
= 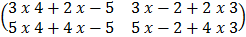
= 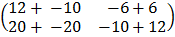
= 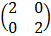
ii) BA
A = 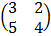 B =
B = 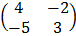
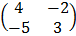
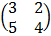
= 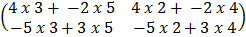
= 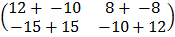
= 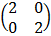
b) Find the value of x, y, w and z
3 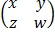 =
= 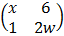 +
+ 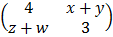
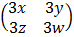 =
= 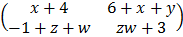
3x – x = 4
2x = 4
2 2
x = 2
3y – y = 6 + 2
2y = 6 + 2
2y =8
y = 4
3w = 2w + 3
3w – 2w = 3
w = 3
3z = -1 + z + w
3z – z = -1 + 3
2z = 2
2 2
z = 1
∴ x = 2, y = 4, z = 1, w = 3
5. A transformation is given by the matrix M where M = 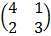
Find the (a) image of (-2, 5) under M (b) Inverse of M
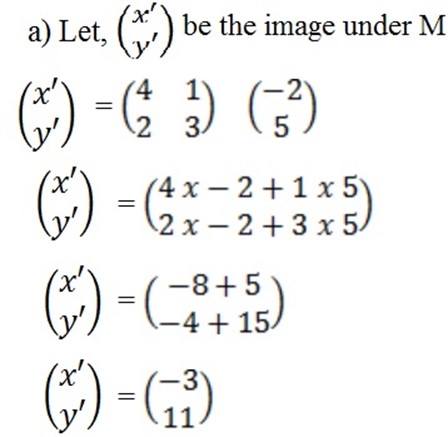
b) M = 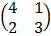
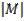 = 4 (3) – 2
= 4 (3) – 2
= 12 – 2 = 10
M-1 = 1/10 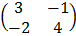
M-1 = 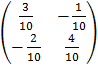
6. a) If T is linear transformation such that T = 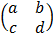 and T (x, y)
and T (x, y)
(3y, 5x)
Find T hence evaluate T (1, 2)
Solution
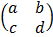
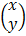 =
= 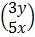
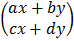 =
= 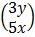
ax + by = 3y
a =0
b = 3
cx + dy = 5x
c = 5
d = 0
T = 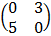
T (x, y) = (3y, 5x)
T (1, 2) = (6, 5)
OR
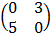
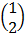
= 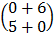 =
=