Graphic Formats
There are a number of graphic formats available for the storage of images. The following table lists some of the more common graphic formats currently available.
|
Graphic Format |
File Extension |
Color Depth |
Description |
|
Bitmap |
.bmp |
All |
Microsoft Windows format. Supported by all Microsoft operating systems. Not used for web pages. |
|
GIF |
.gif |
8 bit |
Graphics Interchange Format. Used for web pages. |
|
JPEG |
.jpg |
24/16 bit |
Joint Pictures Entertainment Group. Used for web pages. |
|
TARGA |
.tga |
All |
Used primarily for image creation, composing and editing. |
edu.uptymez.com
Other image formats are available. It is worth saving an image in both JPEG and GIF format, then selecting the image based on your criteria (either the best quality or the smallest file size). JPEG offers varying levels of compression. The more compression applied, the smaller the file size, and the lower the image quality. This is illustrated in the images below.
|
|
|
|
|
Best Quality |
Medium Quality |
Low Quality |
edu.uptymez.com
Altering the image contrast and brightness
There are times that images should be manipulated for better results. Some images are better displayed as grayscale (shades of gray with no color). Examples of these are related to the medical profession, such as x-rays. Often, detail can be hidden in an image, and adjustment of the image characteristics will reveal this hidden information. Consider the following image on the left. It was taken with a digital camera. The image on the right has been enhanced by image processing software (Microsoft Image Composer), and shows more detail than the original image.
Special Effects
In general, most image editing software provide special effects that can be applied to an image. A web designer should consider these effects carefully. What is the desired message that the author wishes to convey to the receiver by using such effects? Every element, time and bandwidth is precious. Effects should be used sparingly so that the receiver does not become desensitized to their use. The following images illustrate some of the effects possible with Microsoft Image Composer.
Summary
Images are an important part of any multi-media project. Images are manipulated in color depth, size and other aspects before they are saved in a format suitable for inclusion on web pages. Consideration should be given to image size and file size when producing images for the web. The two most popular image formats for the web are JPEG and GIF. A good designer will manipulate the image to extract the best parts of the image in order to maximize its impact on the receiver. This can involve altering the image size, adding special effects, cropping the image (selecting only a part of the image) or combining the image with other image elements.
2. Animations
Animations are moving graphic images (normally without sound) that consist of a series of images played one after the other. These images are stored in a single file. The current format of these animations (for the web) is animated GIF. The following is an example of an animated GIF.

This animation comprises a series of 10 frames, each slightly different from each other. When played as a sequence, they simulate movement. The ten frames that make up this animation are shown below.
Each image is displayed for a specified time interval, and then replaced by the next image. The persistence of the images on the screen and perceived by the human eye give the impression of smooth movement. This is identical to the way that cinema movies are viewed.
Images must be the same size and should use the same color depth. There are a large number of sites on the Internet dedicated to animated GIF files. In addition, many CD-ROM can be purchased from computer stores that are full of animated GIF’s for use on web pages.
Construction of animated GIF images
In order to construct animated GIF images, special tools are required. Two such tools are Microsoft GIF animator and “GIF construction set for Windows XP. These tools allow you to
-
import a sequence of GIF files
-
specify the duration in time that each image will be displayed
-
specify the total time duration of the image or the number of repetitions
-
rearrange the order of the images
-
apply transparency rules (specify how the background will appear)
-
specify the output image size
-
save the image to an animated GIF file
edu.uptymez.com
|
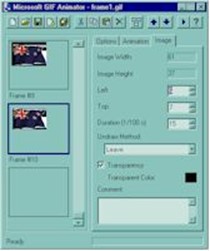
|
This is a screen capture of the Microsoft GIF animator program. The program is currently supplied with Microsoft Frontpage (as of December 1998). It is simple to use and creates effective animations. |
edu.uptymez.com
Other Issues
Animated GIF’s can be large in size. The more animations that are included on a web page, the longer the page will take to download. The larger the animation size, the larger the file size will be. It is important when creating animated GIF’s to keep the file size at a minimum.
Too many animated GIF’s on a web page can be distracting. In addition, the major use of animated GIF’s appears to be primarily a method of trying to improve the look of the page. Flashy graphics may not add to the recall or effectiveness of the message. However, a well thought out animation will aid recall and be very effective at communicating the idea or concept to the viewer.
3. Sounds
This section focuses on the technology of sound. An important aspect of multi-media applications, sound is very effective for creating mood and dramatization. In addition, certain types of music, namely from the Baroque period, have been shown to improve mental concentration and aid later recall.
We use sound every day in communication. Our early ancestors used sound to convey campfire stories, and aided by gestures and other dramatic effects, kept generations spellbound. The power of sound, used properly, should not be underestimated.
Types of sound files
This is a brief discussion of the two main sound formats for personal computers.