-
MIDI
The Musical Instrument Digital Interface was developed during the 1980’s as a mechanism of controlling electronic musical instruments such as keyboard synthesizers. MIDI files support a wide range of synthetic instruments, such as drum, clarinet, violin, piano and guitar. Musical sequences can both be recorded as the instrument is played, or composed on the PC and then downloaded to the instrument for later playing.To play MIDI on your computer, you must have a MIDI interface. Most modern sound cards support MIDI. MIDI files consist of information that relates to the instrument to be played, the note, and its duration. Files in MIDI format are significantly smaller in size than other formats such as WAV or AU. - WAVE:-
Waveform Audio is the most popular format available today for the personal computer. Waveform files consist of actual samples of the sound file. This tends to more accurately reflect the original sound, but file sizes are a lot larger. The more samples taken of the original sound, the better the quality is. Sound files consist of a header and a number of samples. The header defines the format of each sample and any compression technique that was applied to each sample. When the sound file is created, the sound is sampled at a regular rate and each sample converted into a digital number that represents the sound at the instant of sampling.
edu.uptymez.com
Sample Rates
Sound is digitized (converted to digital format) and stored as a sound file. Sample rate refers to the number of times a second that the original sound was sampled. Higher sampling rates mean better quality of sound. However, as the sample rate increases, the file size increases also. You must make a decision to sometimes trade quality at the expense of file size. The following table lists three common sound qualities and their sample rates.
|
Sound Quality |
Sample rate |
Description |
|
Telephone |
11,025 |
Suitable for speech |
|
Radio |
22,050 |
Suitable for music |
|
CD |
44,100 |
Suitable for high quality music |
edu.uptymez.com
Again, we are reminded of the fact that bandwidth is still scarce for most users of the Internet. This means designing for the lowest common denominator in mind. The highest percentages of users on the Internet are those with PC’s, so this means that WAV format will be more common. In addition, due to bandwidth restrictions, you should ensure that sound files are kept short and are small in size. For instance, a telephone quality sound file using ten seconds of speech is 110KB. This will take a minimum of 30.55 seconds to download at 28.8Kbps.
8 bit and 16bit
This refers to the size of each sample. It is thus obvious that a 16-bit sample is twice as large as an 8-bit sample. The advantage of using 16-bit sampling is that a wider range of values is possible, so the resultant sound appears to have better tonal characteristics (it sounds more realistic).
Again, sound files sampled at 16-bit will be twice the size in bytes as the same sound sampled at 8-bit. You will need to be able to justify the larger sample size, and must remember the negative effect this will have on download times.
Stereo and mono
We have two ears that we use to receive sound. The airwaves striking our eardrums are converted into electrical impulses and interpreted by our brain. Similarly, most computers use two speakers to generate sound, similar to the sound speakers of home sound systems. These are called left and right channels. They are designed to simulate the way we hear, by providing distance separation of sound.
Stereo uses two channels called left and right. The original sound is sampled as two separate channels and stored as two lots of information, one for the left channel, and one for the right channel. This means every sample contains both channels.
Mono refers to using a single sound sample. If you play this back on a stereo system, the single sound sample is sent to both channels. It is not possible to create the appearance of distance separation using mono. However, mono files are smaller in size (half the file size) compared to an equivalent stereo file.
Stereo files are twice the size in bytes as a mono file due to each sample containing left and right channel information. They have the advantage of appearing to give distance separation and are useful to create special effects. This must be traded against the available bandwidth and how long the file takes to download. Mono files are the most common format. The following table shows the comparative file sizes (approximate) for one second of recorded speech.
|
Sample Rate |
8 bit |
8 bit |
16 bit |
16 bit |
|
11KHz |
11KB |
22KB |
22KB |
44KB |
|
22KHz |
22KB |
44KB |
44KB |
88KB |
|
44KHz |
44KB |
88KB |
88KB |
166KB |
edu.uptymez.com
Compression(Codecs)
A codec is a “compression decompression” device. It is often implemented in software, though many new accelerated cards have codecs implemented in hardware for faster coding and decoding of signals. A codec is used to alter the signal in order to reduce the bandwidth requirements (i.e., the size of the file is compressed making it smaller and thus quicker to transfer or download). The codec converts the file format to a format suitable for playing on the destination hardware.
The following is a brief discussion on two popular speech codecs
- ADPCM (Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation)
This codec reduces the file size by over 50%. However, any compression causes loss of sound quality. There is no generally accepted standard for ADPCM, with codecs generally provided by manufacturers of sound cards that are installed using a software install program. - PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
Another common codec supported by all Windows operating systems.
edu.uptymez.com
Streaming Audio
The major problem associated with the previous format of waveform audio is the file size. When you use a waveform audio file on a web page, the browser must download the entire file before it can be played. For files of reasonable size, this leads to long delays for the receiver. Streaming audio addresses the issue of this delay by allowing the file to be played whilst it is still being downloaded. Special players are required for viewing and playing streaming audio clips.
Streaming audio is primarily associated with Real Networks. “Real Player” supports the playing of streaming audio over the Internet. The advantages of using streaming audio are
-
the use of a special codec that reduces the bandwidth requirements for audio down to about 5Kbps
-
instant playing of the audio clip
-
suits limited bandwidth connections (i.e., a dial-up user with a 28.8Kbps modem)
edu.uptymez.com
When a user selects a streaming audio clip, the streaming audio player contacts the server and establishes the bandwidth and delays between the user computer and the host server. A few seconds of the clip is then downloaded into temporary buffer storage before the clip begins to play. As the clip begins to play, more content is downloaded and placed into temporary storage. If there is a congestion delay in the Internet connection, the clip continues to play using the contents of the buffer storage. Hopefully, before the buffer storage is exhausted, the congestion delay will cease and thus the buffer storage will fill up again. In this manner, the streaming player tries to achieve smooth playback of the clip. Without using storage, gaps or breaks in the audio would be evident when a congestion delay occurred.
A special content provider program is necessary for producing streaming audio clips. A limited free version can be downloaded from the Real Networks web site. In addition, to provide streaming audio clips from a server requires the use of a streaming server.
|
Sample audio file |
|
|
|
Converted sound file from the WAV file above. |
edu.uptymez.com
Recording and editing of sound files
To record WAV sound files you need a microphone (or sound source such a tape recorder), sound card, and sound recorder program.
|
|
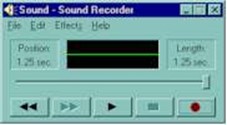
The Windows operating system provides the program “Sound Recorder”. This program is simple to use and can create short WAV files. The sample rate is adjustable and it can record in mono or stereo. Simplistic editing of the sound file (delete before cursor, delete after cursor) is provided. |
edu.uptymez.com
|
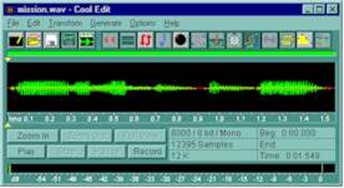
For more sophisticated sound recording and editing, a program such as “Cool Edit for Windows” is necessary. This program has many more features and is a good tool for producing quality sound WAV files. |
|
edu.uptymez.com
|
|
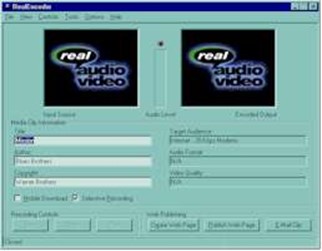
To create streaming audio files, you need a program such as “Real Encoder” from Real Networks. This takes an existing sound WAV file or a live sound source and converts it to a streaming audio file. It is possible to specify a number of parameters such as Internet bandwidth when creating the file. |
edu.uptymez.com
Other considerations
As always, bandwidth is a premium for the Internet. This means that you must tradeoff quality and size for quick download speed and fast display. New technology like streaming audio can deliver more content utilizing the same or less bandwidth.
However, streaming audio content is not currently supported (as at Dec 1998) within a web browser. This means using streaming audio poses the problem of requiring the receiver to have the streaming player installed on their computer. For this reason alone, you should ensure that an Internet link to where the player can be downloaded from is available on the web page.
In addition, using a separate player rather than the browser (which supports WAV format) means greater memory requirements. This is because the player needs to be started and loaded into memory, in addition to the web browser.
This also raises a contextual issue, as the user is now interfacing with two packages, the browser and the player. This can lead to confusion and reduce the effectiveness of the presentation or learning experience.
If producing for a CD-ROM, many of the issues related to sound file sizes and sampling rates do not apply to the same extent. A CD-ROM can provide information at a much faster rate than a dial-up modem. Typically, a 2X CD-ROM can transfer data at 300KB per second. This means higher quality sound can be used due to the larger available bandwidth.