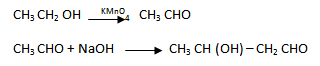H/W
3. Why is phenylamine more soluble in  than in H2O?
than in H2O?
4. Define the term “base.” Write down structural formula of the following compounds and arrange them in order of increasing basic strength;
Methylamine, ammonia, ethylamine, ethanamide, phenylamine. Give reasons.
5. Give structural formula of the organic products that are obtained when;
(a)Ethylamine
(b)Phenylamine
(c)Phenylmethylamin
(d)N – methylphenylamine are treated with;
(i) Chloromethane
(ii) A mixture of NaNO2 and HCl
(iii) Benzoylchloride
ANSWERS
Phenylamine is more soluble in HCl since they will form a stable hydrated ion but it is less soluble in water due to the large hydrophobic part i.e. the benzene ring.
4. A base is a substance which releases OH– as the only negative ion.
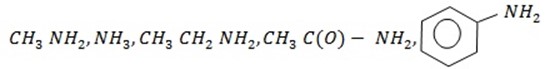
QUESTIONS
1.An aromatic compound contains 80% carbon, 9.6% hydrogen and nitrogen. Its relative molecular mass is 135g/mol. It is slightly basic and form salts but given no other reaction nitric (III) acid. Identify the structure of this compound.
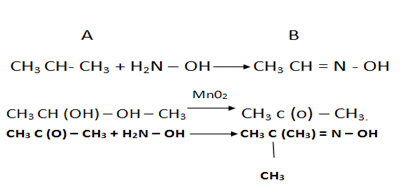
2. An organic base A contains 61% carbon, 15.3% hydrogen, 23.7% nitrogen. When treated with nitric (III) acid A yield an alcohol B and nitrogen gas is evolved. The alcohol B contains 60% carbon, 13.33% hydrogen and on careful oxidation yields compound C, which has a vapour density of 29. Compound C forms an oxime with hydroxylamine (H2 N – OH) but does not react with Fehling’s solution. Suggest structures for the compounds A, B and C and indicate the cause of the above reactions.
3. How does the introduction of nitro group – 2 – and – 4 – positions of phenylamine affect its basicity? Give reasons
(a) Give the conditions under which the following reactions proceed
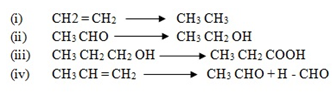
(b) Write the structural formula for each of the organic compound formed when compound M reacts with each of the following;
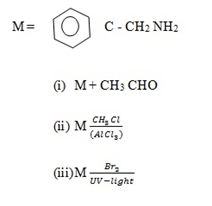
ANSWERS:
1.
| C | H | N | |
| Percentage | 80 | 9.6 | 10.4 |
| R.M.M | 12 | 1 | 14 |
 by R.M.M by R.M.M |
6.666 | 9.6 | 0.7428 |
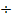 by smallest number by smallest number |
8.97 ≈ 9 |
12.924 ≈ 13 |
1 1 |
edu.uptymez.com
∴ Structure of the compound is C9 H13 N
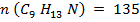
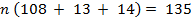
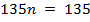
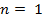
Molecular formula: 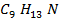
Probable structural formula:
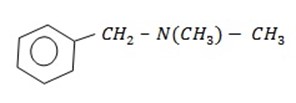
2.
| C | H | N | |
| Percentage | 61 | 15.3 | 23.7 |
| R.M.M : | 12 | 1 | 14 |
| Percentage divide by R.M.M |
5.083 | 15.3 | 1.69 |
| divide by the smallest no |
3 | 9.05 | 1 |
edu.uptymez.com
Empirical formula C3 H9 N
The organic base will be 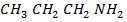
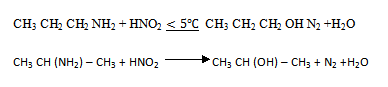
3. The nitro group attached to position – 4 – will make phenylamine to be more basic than the nitro group attached to position – 2
Reason:- This is because in – 2 – nitrophenylamine there might be hydrogen bonding between the hydrogen and oxygen hence basicity will decrease.
QUESTIONS
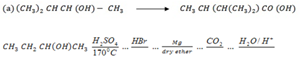
Give the equations for preparation of propanoic acid stating with;
(a) Haloalkane
(b) Ethene
Give equations (including reagents and conditions) for the following conversions;
3. Arrange the following compoounds in order of their increasing acidity. Explain the differences in their acidity.
a) ethanol
b) Ethanoic acid
c) Pentanoic acid
d) Ethanedioic acid
e) 1, 2 – benzenedicarboxylic acid
f) Trichloroethanoic acid
g) Butenedioic acid
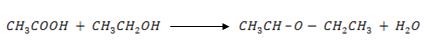
4. Convert the ethanoic acid into;
a) Ethylethanoate
b) Ethanoylchoride
c) Ethanol
d)Trichloromethanoic acid
e) Ethanamide
For each each conversion give a chemical equation
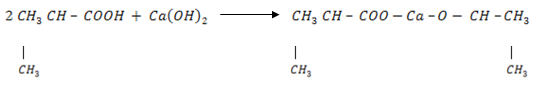
5. A compound A of molecular formula C4H8O2 gives propane when fused with alkali. When A reacts with Na2CO3(aq), CO2 is evolved. When A reacts with molecular formula C8H14O4 which on strong heating yield 2, 4 – dimethylpentanone. Establish the structural formula of A & B and give reason.
6. (a) An unknown compound W undergoes ozonolysis and hydrolysis. This produces an acid and a compound of formula C4H80 and Y which gives a positive Iodoform test. When X is reacted with LiAl3 the product Z, is mixed with an equal amount of ethanol, a litter conc. H2SO4 is added and the mixture is heated to 1400C major products are formula of R.M.M 74, 88 and 107 called P, Q and R.
(b) Why has an acid been produced on ozonolysis?
7. Descried, giving necessary experimental conditions, the reactions which occur between sulphuric (VI) acid and;
(a a)Ethene
(b b)Ethanol
(c c)Benzene
(d d)Methanoic acid
ANSWERS
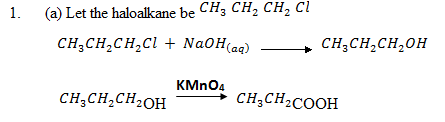
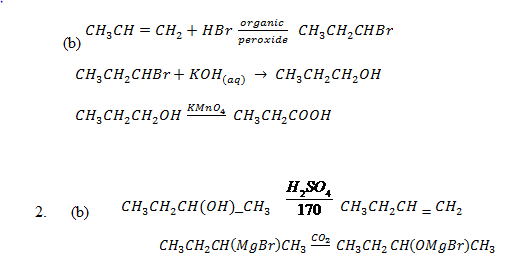
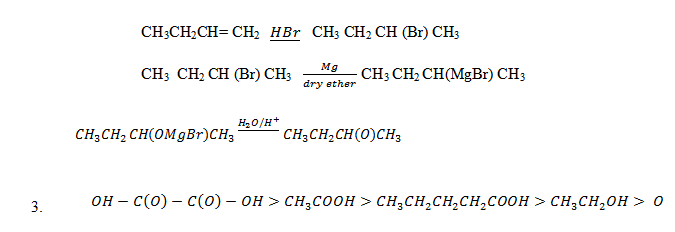
4. (a)
(b)

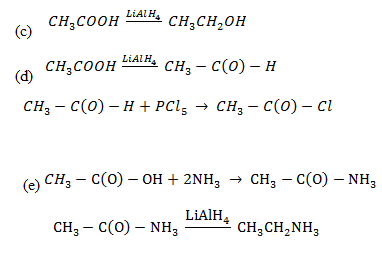
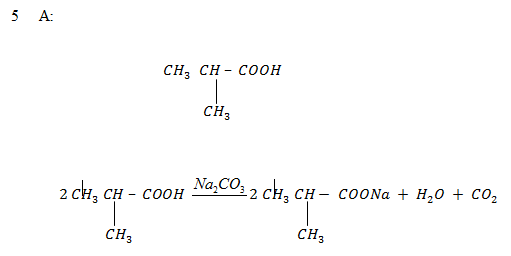
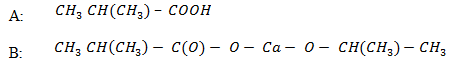
When you oxidize 2, 4 – dimethylpentanone you will get carboxylic acid A.
7.
(a) 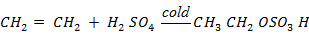
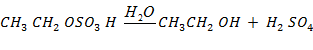
(b ) 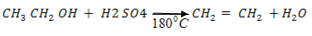
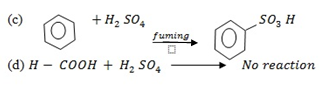
Reason:- They are both acids.
EXERCISE
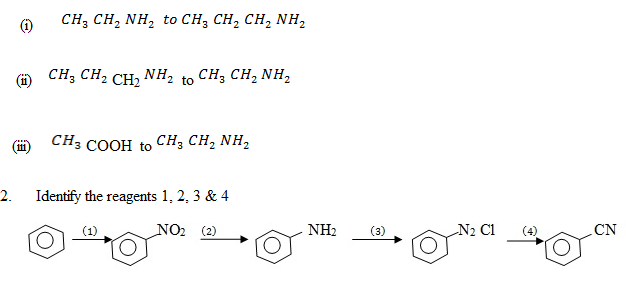
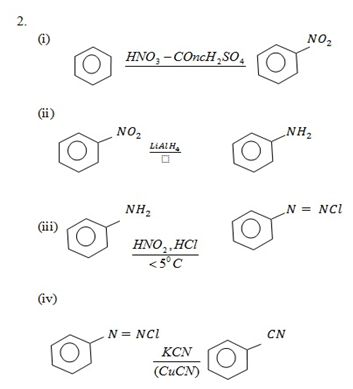
1. Suggest the reagents that bring about the following conversions;-
i. Pent – 2 – yne to pentan – 3 – one
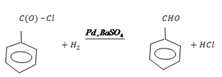
ii. Benzoylchloride to Benzaldehyde
iii Ethanenitrile to ethanol
iv.1 – hexyne to hexan – 2 – one
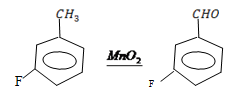
v. 4 – florotoluene to 4 – florobenzaldehyde
2.How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds:-

3. How will you bring about the following in not more than 2 steps:-
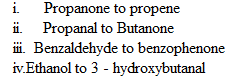
ANSWERS
1.
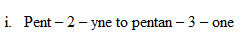
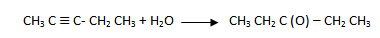
ii. Benzoylchloride to Benzaldehyde
iii Ethanenitrile to Ethanal
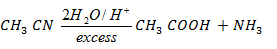
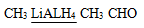
iv1 – hexyne to hexan – 2 – one
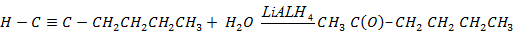
4 – Florotoluene to 4 – florobenzaldehyde
1. (i) By aldo – keto condensation
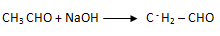
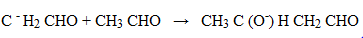
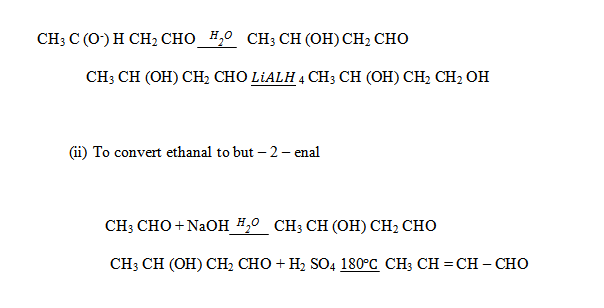
(iii) Ethanal to butan – 1 – ol
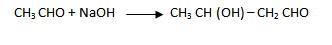
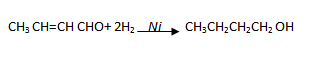
(iv) Ethanal to butanoic acid
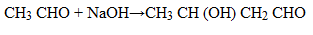
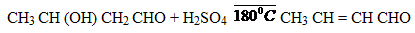
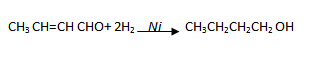

(v) Ethanal to butan – 2 – ol
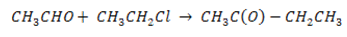
(vi) Ethanal to but – 2- enoic acid
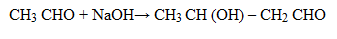
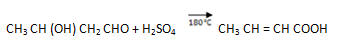
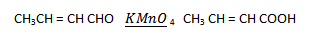
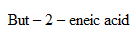
2. (i) Propanone to propene
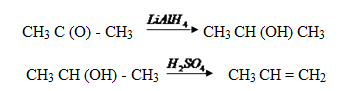
(ii) Propanal to butanone
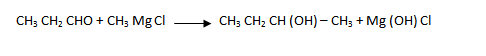
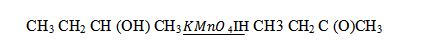
(iv) Ethanol to 3 – hydroxybutanal
Solution