Home Work:
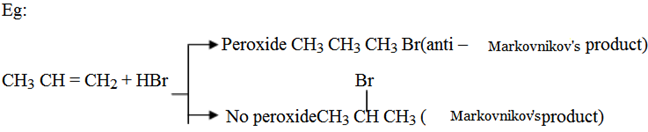
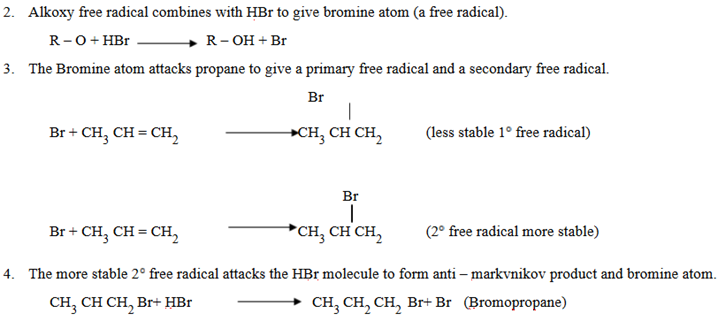
Anti – markovnikov’s rule (organic peroxide HBr). In 1933 the American chemist M. S. Kharasch discovered that the addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes in the presence of organic peroxide (R – O – O – R) takes a course opposite to that suggested by Markovnikovs rule.
NOTE:
It is strictly works using HBr with organic peroxide.
Mechanism:
1. Peroxide dissociates to give alkoxy free radicals.
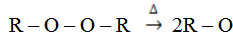
Weekly Test:
1. (b) N2(g) + 3H2(g) 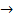 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
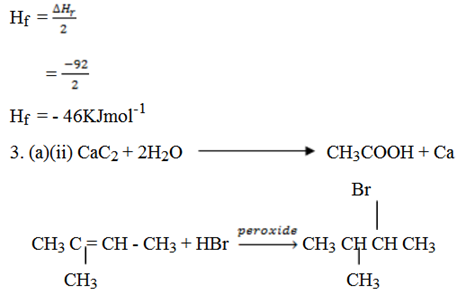
Given ∆Hr = – 92KJ
Since Hf you form 1mole
Hf =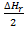
=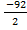
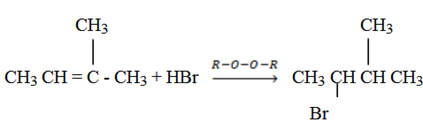
3. Halogenation
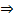 Addition of halogens to alkenes
Addition of halogens to alkenes
– This reaction is best carried out by simply mixing halogens in the inert solvents such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
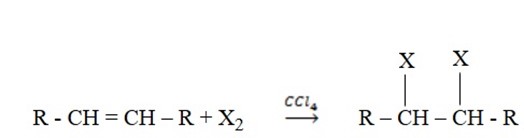
E.g.
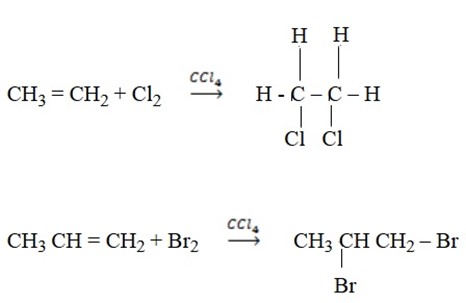
The reaction of Bromine with alkene can be used to test for the presence of double bonds.
Reason:
Addition of bromine (brown) to alkene since it makes the solution colourless. This is how we test for presence of double bonds.
Bromine tests unsaturation of hydrocarbons (alkenes and alkynes).
4. HYDROGENATION
Addition of hydrogen:
– Alkenes react with hydrogen in the presence of platinum or nickel catalyst to form alkanes.
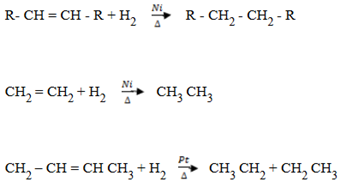
This cannot take place without catalyst.
5. Hydration of Alkenes:
– This follows Markrnkov’s rule.
Homework on hydration of alkenes
– Find the reagent which should be added to alkene to follow Anti markornikovs rule.
Oxidation reaction of alkenes
6. Addition of Bromine water (Br2/H2O)
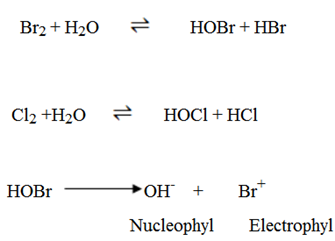
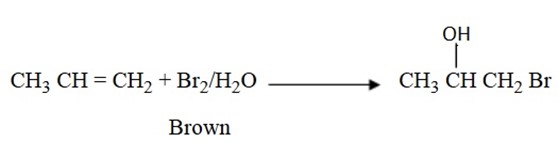
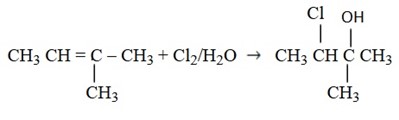
Alkenes decolourize Bromine water (Brown) apart from decolorizing Bromine solution.
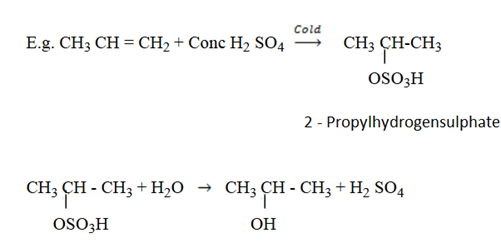
Reaction with conc H2 SO4
Structure of sulphuric acid
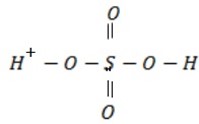
7. Oxidation reactions of Alkenes
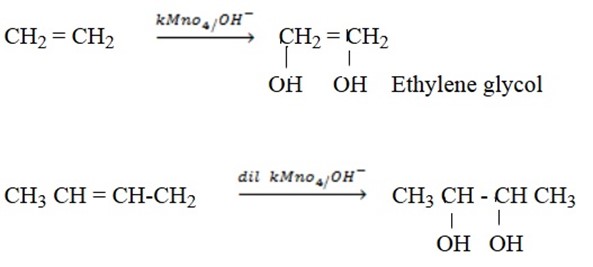
– Alkenes react with oxidizing agent to form diols. Oxidizing agent can be either KMnO4, K2CrO4.
– With cold dilute KMnO4 or cold alkalineKMnO4 you form diols.
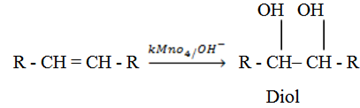
NOTE: Diol means two OH –
(b) When hot concentrated acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O4 is used. Alkenes are oxidized to carboxylic acid or oxidized to ketones or both.
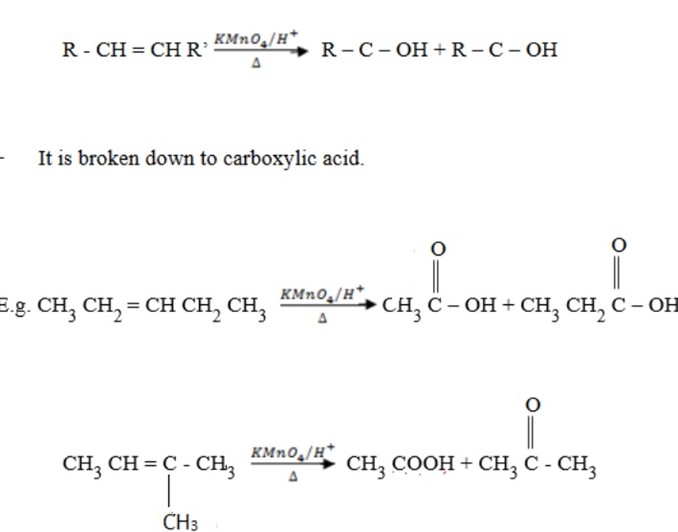
Note:
If double bond is branched, you can’t form carboxylic acid.
Terminal alkene
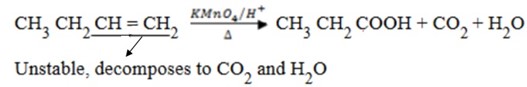
OZONOLYSIS (O3)Ozono 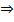 ozone
ozone
Lysis  Breaking
Breaking
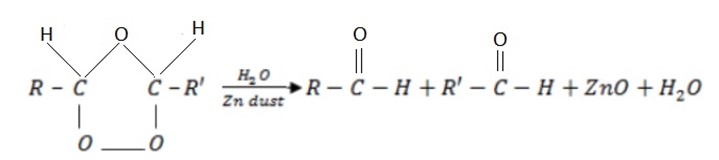
– This is a cleavage or breaking of carbon, carbon double bond by using ozone.
– In ozonolysis C = C is completely broken to produce aldehydes or ketones or both depending on the primary structure of alkene.
NOTE:
Ozonolysis is the best method of locating the position of double bond in unknown alkene.
The oxygenated carbon in carbonyl compound obtained by ozonolysis is the one that were joined by double bonds in the original alkenes.
Ozonolysis has 2 major steps:
i) 1st step:
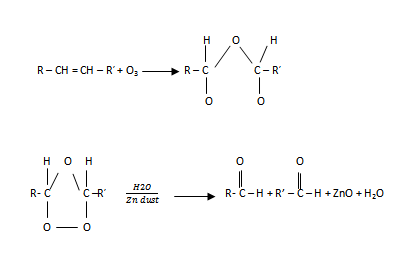
NOTE:
Zn dust is added to prevent oxidation of aldehyde to carboxylic acid.
E.g.
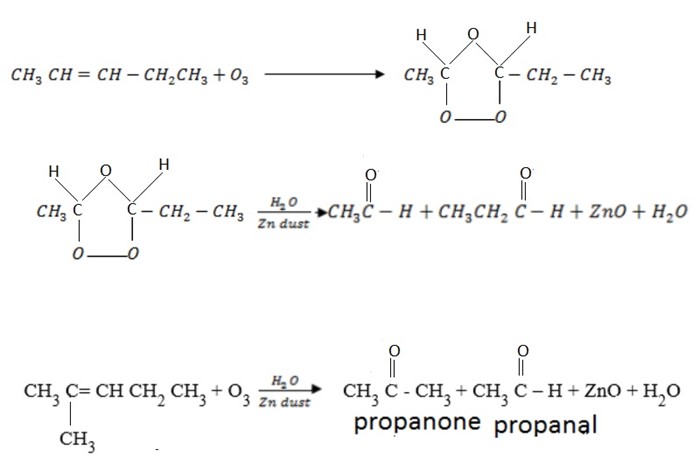
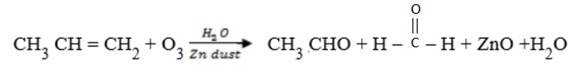
Questions
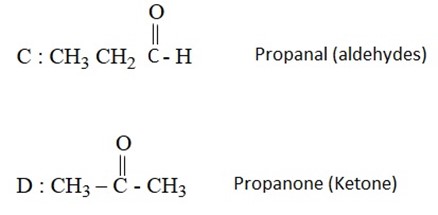
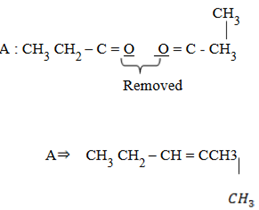
1. A certain compound A was unsaturated hydrocarbon with molecular formula C6 H12. During ozonolysis of A, two compounds C and D were formed with molecular formula C3H6O. Compound C and compound D was ketone. Identify A, C and D.
Solution: