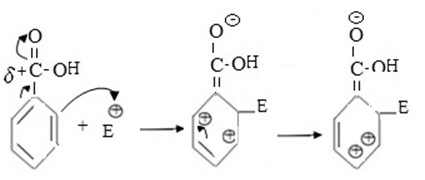
II. STABILITY OF INTERMEDIATE CARBONIUM ION
- Consider the electrophilic substitution reactions in benzoic acid.
edu.uptymez.com
1st CASE
If incoming electrophile substitute of ortho position.
i.e.
- Intermediate carbonium is not stable as result of very large repulsion force between closer positively charged ions in adjacent carbons.
edu.uptymez.com
2nd CASE
If incoming eletrophile substitute of meta position.
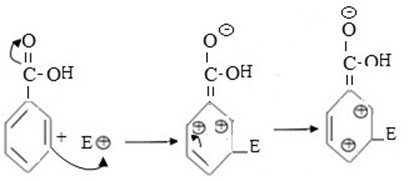
- Carbonium ion formed in this case is somehow more stable as a result of comparable small repulsion force between position charged carbons which are not adjacent.
edu.uptymez.com
3rd CASE
If incoming electrophilic substitutes at para position. Also Intermediate carbonium ion formed is not stable as a result of very large repulsion force between closer positively charged ions in adjacent carbons.
i.e.
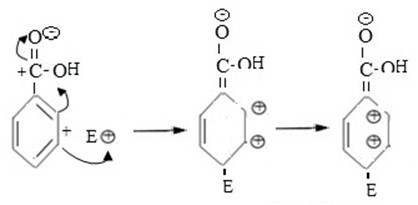
CONCLUSION
Intermediate carbonium ion formed in second case is more stable than in 1st case and 3rd case and hence meta position is better site for incoming electrophile.
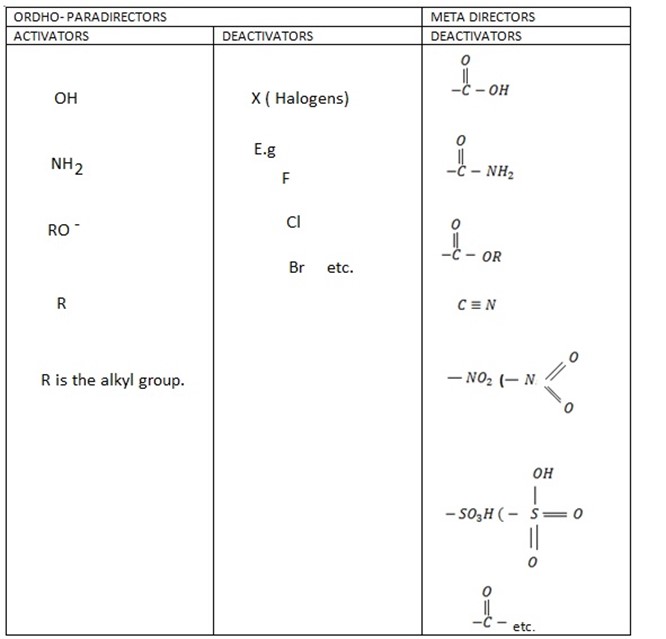
SUMMARY ON DIRECTING EFFECT
SOLVED PROBLEMS
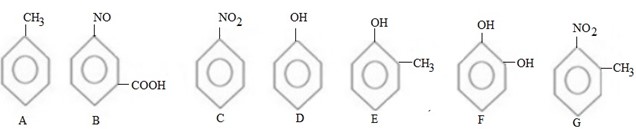
QN 1. Arrange the following compounds in order of reactivity towards.
i. Nucleophile.
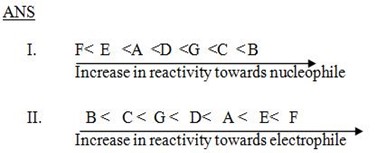
Qn. 2. Explain why alkylation of nitrobenzene is much slaver that of methy l benzene?
ANS
Alykylation in given compounds is electrophile substitution reaction so presence of nitro group which is an electron withdrawing (deactivator) in nitrobenzene deactivate. Its reaction towards electrophile while presence of methyl group which is electron receptor group (activator) in methyl benzene activate its reaction towards electrophile and hence alkylation of nitrobenzene become less than that of methyl benzene.
Qn. 03. Complete the following organic reactions.
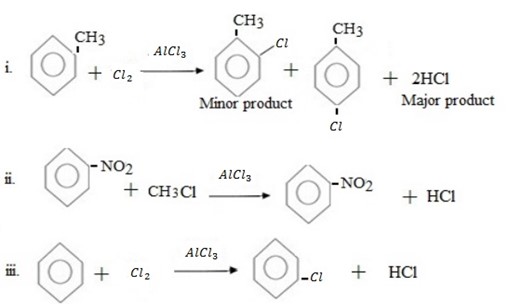
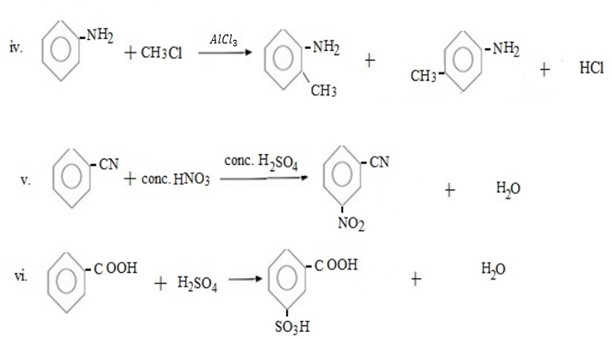
Qn. 04. NECTA 1994
Write structural formula of main substitutional product in the following organic reactions.
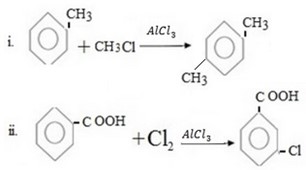
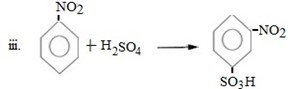
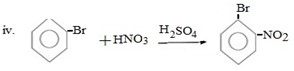
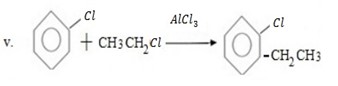
Qn 05. NECTA 1993
Which substituent entered first in the following organic compounds giving reasons.
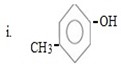
ANS
i. Either of the two substituents entered first.
Reason
In given compound OH and CH3 are para related and OH– and CH3 are ortho –para directors forming para product as a major product and hence either of the two entered first so as to direct incoming substituent at para position.
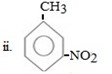
ii. NO2 entered first
Reason
In given compound CH3 and NO2 are meta related so being meta director it must be entered first so as to direct the incoming CH3 group at meta position.
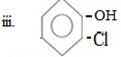
iii.Cl entered first
Reason
In given compound OH and Cl are ortho related and OH and Cl are orth-para directors, OH– forming product a major product (as result of its large steric hinderance while Cl form ortho product as major product (as result low steric hinderance ) and Cl– must be entered first so direct at ortho position.
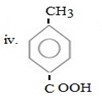
Reason
In given compound CH3 and COOH are para related, CH3 being ortho –para product forming para product as major product must be entered first so as to direct incoming – COOH at para position.
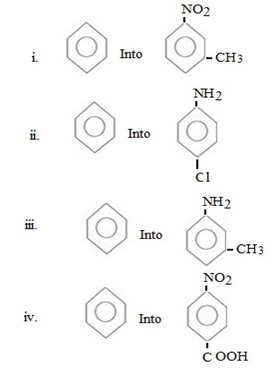
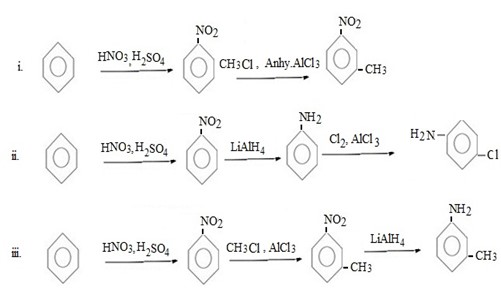
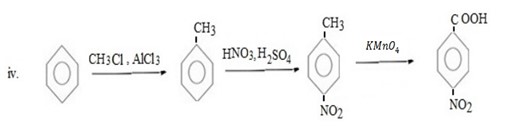
Qn 6.
Show how the following conversions can be achieved.
ANS
FURTHER CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF BENZENE
Apart from electrophilic substitution reactions benzene can undergo the following reactions.
i. ADDITION REACTIONS
- Under vigorous condition benzene can undergo addition reaction.
edu.uptymez.com
eg.
(a) HYDROGENATION
Benzene can react with hydrogen under presence of nickel or platinum catalyst yielding cyclohexane.
i.e.
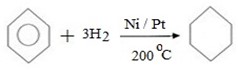
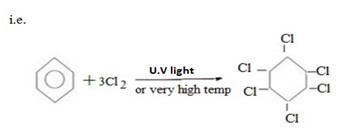
(b) CHLORINATION
- Under presence of U.V a very high temperature benzene react with chlorine to give 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane.
edu.uptymez.com
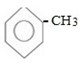
TOLUENE (METHYL BENZENE)
- Toluene is the aromatic compound which is formed when one halogen atom of benzene is replaced by methyl group.
edu.uptymez.com
i.e. Structure of toluene is ;-
PREPARATION OF TOLUENE
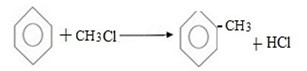
(a) METHYLATION OF BENZENE
Generally;
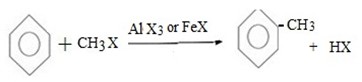
Example:
( b) Reaction between halobenzene and halomethane under;
Presence of sodium and dry ether.
Generally.
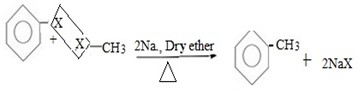
Example;
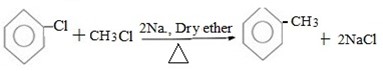
PHYSICAL PROPERTICES OF TOLUENE
- It is more denser than water.
- It is solube in non-polar solvents like organic solvent (Toluene itself is good organic solvent)
- It melts at temperature of -950C and boils at 1110C
- Its vapour density is large than that of the air
- It is colourless liquid at room temperature.
edu.uptymez.com
In most cases toluene is used as organic solvent instead of benzene because it is less toxic.
CHEMICAL REACTION OF TOLUENE
Commonly toluene undergo the following chemical reactions
i. Side chain chemical reactions
ii.Electrophilic substitutions in benzene ring
I. SIDE CHAIN CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Under this heading toluene undergo the following
a)Oxidation
b)Free radical substitution reactions.
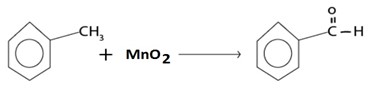
A) OXIDATION
With milder oxidizing like MnO2 agent benzaldehyde is med.
i.e
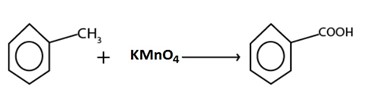
But with strong oxidizing agent like kmno4 and K2Cr2O7 ie acid is formed
eg.
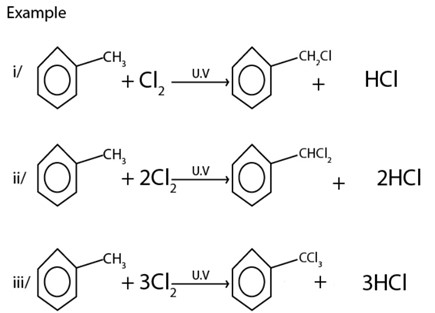
B) FREE RADICAL SUBSTITUTION REACTION
· With halogens under presence of U.V or very high temperature tends to undergo side chain radical substitution reactions.
II. ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTIONS IN BENZENE RING
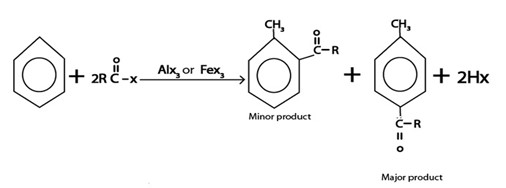
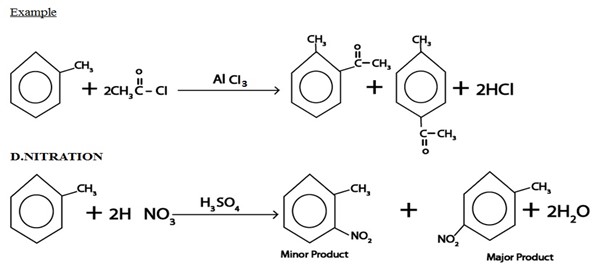
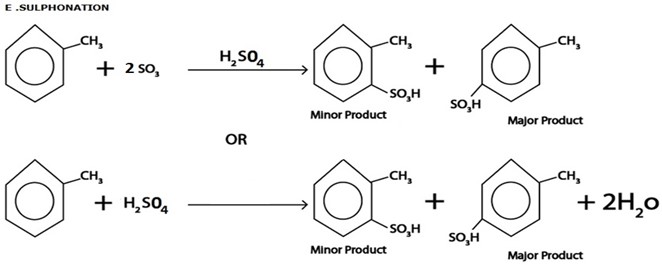
Consider this heading toluene undergo similar chemical reaction as those of benzene. The only difference is that methyl group in toluene act as ortho director forming para product as major product
Example of electrophilic substitution reactions of Toluene
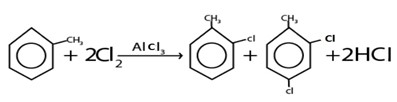
i. HALOGENATION
Generally
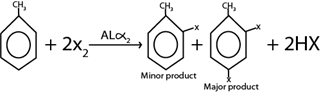
Example
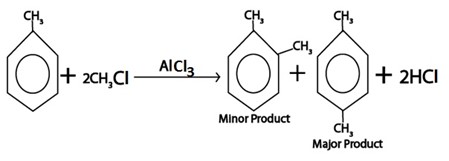
ii. ALKYLATION
Generally
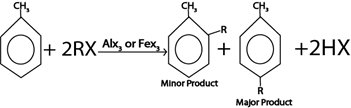
Example
iii. ACYLATION
Generally