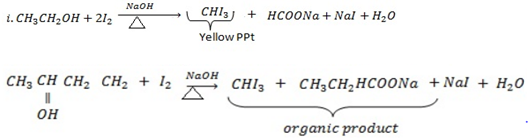
IODOFORM TEST
Ø This is the chemical test for presence of terminal methyl group which is directly bonded to carbon with OH– group or (to carbonyl group in the case of carbonyl compounds) by giving yellow ppt of trichloromethane ( Iodoform) CHI3.
Ø When compounds with terminal methyl group bonded to carbon with OH group is heated with 12 in presence of NaOH they give yellow ppt of Iodoform.
Example
CHEMICAL TEST TO DISTINGUISH BETWEEN PRIMARY, SECONDARY AND TERTIARY ALCOHOLS.
– Three classes of alcohol can be distinguished by using Lucas reagent.
– Lucas reagent is the mixture of concentrated HCl and ZnCl mixed at equal proportion.
– With Lucas reagent at room temperature, primary alcohol do not form cloudness or turbidity ( insoluble substance) at all.

– Secondary alcohol tends to form turbidity ( insoluble substance which is chloroalkane within 5 minutes).

– Tertiary alcohol, tend to form turbidity immediately.

Example
Qn. Gave chemical test to distinguish between
i. Ethanol and propanol ( I test)
ii. Butan – 1-ol and butan – 2- ol (2 test)
iii. Butan -2- ol and 2- methyl propan – 2-ol ( 2 test apart from using Lucas reagent)
ANS
i. Ethanol gives positive Iodoform test while propanol give negative Iodoform test.

ii. 1st TEST
With Lucas reagent at room temperature butan -2-ol give turbidity ( cloudness) within 5 minutes while butan -1-ol do not give turbidity at all.

2nd TEST ( Iodoform Test)
Butan -2- ol give positive iodoform test while but-1-ol give negative iodoform test.
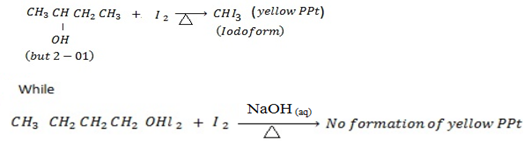
iii.1st TEST
When butan -2- ol is mixed with  solution the orange colour of
solution the orange colour of  is changed to green while 2- methylpropan- 2 – ol do not show any change.
is changed to green while 2- methylpropan- 2 – ol do not show any change.
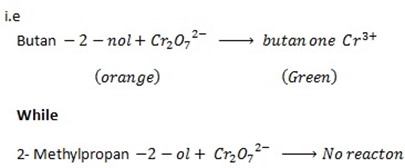
2nd TEST
Butan  decolourise KMnO4 with black ppt appearing at the bottom of the beaker which is deep purple while 2-methylpropan
decolourise KMnO4 with black ppt appearing at the bottom of the beaker which is deep purple while 2-methylpropan  do not.
do not.
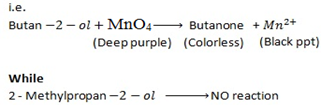
NECTA 2006 PP2 QN. 8(a)
Organic compound C4H10O reacts with PCl5 to form an organic compound “Q” In organic compound “N” and gas ‘R’ which produce denser white fumes with a aqueous ammonia “P” also react with a mixture of Iodine and NaOH forming a sodium salt “W” and triodomethane.
i. Identify and write the structural formula Q, R and W.
ii. Write an equation of each of the above reaction.
ANS:
The molecular formula 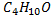 confirm general molecular formula of CnH2n+2O
confirm general molecular formula of CnH2n+2O
– Thus P is either alcohol or ether.
– A gas which produce dense white fumes with aquous ammonia is HCl
– So since the reaction “P” and PCl5 produce HCl then there is OH group in P.
– Hence compound “P” reacts with mixture of iodine and NaOH to give triodemethane then compound “P” give positive Iodoform.
– Hence in “P” there is terminal methyl groups bonded to carbon with 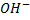 group. This “P” is butan -2-ol.
group. This “P” is butan -2-ol.
Its structure is
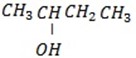
– Q is 2 – chlorobutane
– Its structure is
– N is PoCl3
– R is HCl
– W – is sodium propanoate
– Its structure is
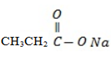
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF PHENOL
Generally chemical reactions of phenol can be divided into two types;
i. Electrophilic substitution reactions inside OH– group.
ii. Electrophilic substitution reactions in benzene ring.
1. ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTION INSIDE OH– GROUP
a) REACTION WITH ALKALINE SOLUTION
Unlike Alcohol, phenol react with alkaline soluble NaOH
i.e. Alcohol + Alkaline solution. e.g, 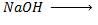 No reaction
No reaction
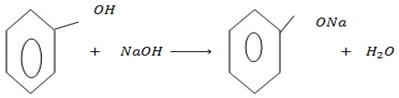
The reactions give one of the differences between alcohol and phenol
b) REACTION WITH ALKALING METALS
Phenol reacts, with alkaline metals like 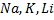 etc to form phenoxide and hydrogen gas is involved.
etc to form phenoxide and hydrogen gas is involved.
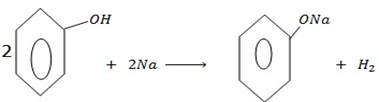
The reaction show one of the similarities between alcohol and phenol.
i.e
Alcohol + alkaline metal  Allcoxide + Hydrogen gas.
Allcoxide + Hydrogen gas.
c) FORMATION OF ETHER
Phenol react with haloalkane in presence of acqueous sodium hydroxide to form ether.
Generally
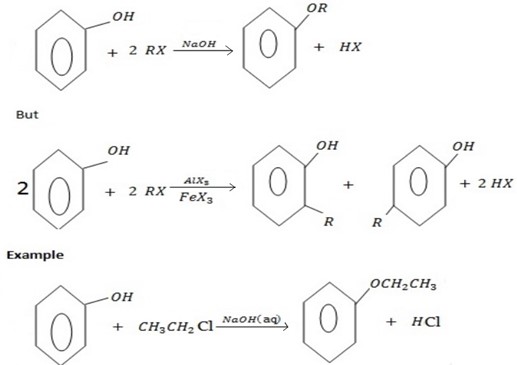
The reaction show another similarity between alcohol and phenol although in alcohol there is no need of  .
.
i.e
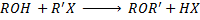
Example

d) FORMATION OF ESTER
Phenol reacts with acyl compounds in presence of NaO to form ester.
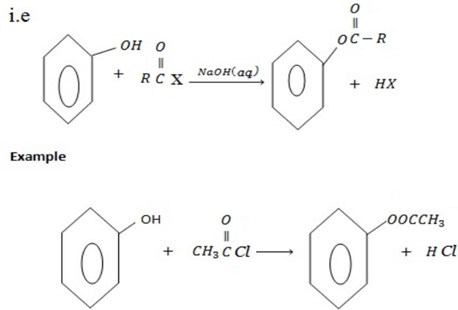
and phenol i.e alcohol also reacts with acyl compounds to form ester although in alcohol there is no need of NaOH(aq).
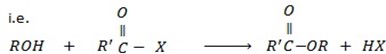
e) REACTION WITH SODIUM CARBONATE.
Phenol reacts with sodium carbonate to form phenoxide and the gas which turn lime water milky i.e. CO2 gas is evolved.
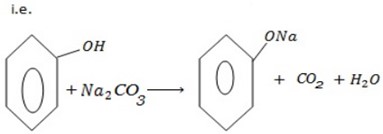
– The reaction show another difference between alcohol and phenol i.e. Alcohol reacts with 
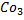 .
.
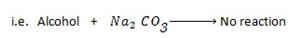
II. ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTION IN BENZENE RING
– Under this heading phenol reacts like benzene the only difference is that OH– group in phenol directs incoming electrophile at ortho and Para position.
TESTS OF PHENOL
Phenol turns blue litmus paper into red
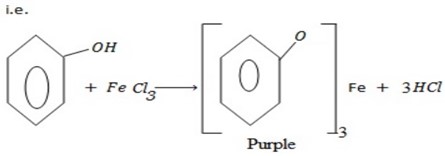
– With ion (III) Chloride phenol tends to form purple violet color of ion(III) phenoxide.
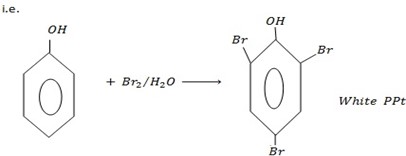
– With bromine water phenols tend to form white ppt of 2-tribomophenol.
SOME DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ALCOHOL AND PHENOL
Do not undergo oxidation easily
2
Do not react with bromine water
Form white ppt of 2, 4, 6 – tribomophenol with bromine water.
3
Do not react with FeCl3
Form purple colouration with ion(III) chloride.
4
Form ester ( has fruity smell)
Do not react with carboxylic acid
5
Do not react with sodium hydroxide solution
Form white ppt of sodium phenoxide with NaOH(aq).
6
Do not react with sodium carbonate
Form white ppt of sodium phenoxide and gas which turns lime water milky (i.e CO2 is evolved).
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN ALCOHOL AND PHENOL
– Evolve hydrogen gas with alkaline metals.
– They form ether with haloalkane.
– They form ester with acyl compound.
– They reacts with hydrogen halide.