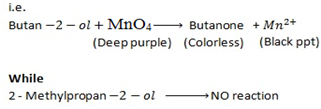EXPLANATION ON COMPARISON OF ACIDIC STRENGTH IN ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
Phenol is stronger acid than alcohol due to following reason
1. Easier of releasing hydrogen proton
2. Stability of phenoxide ion formed after releasing hydrogen proton
1. EASIER OF RELEASING HYDROGEN ATOM
Lone pair electrons in oxygen of  groups in phenol are localized they are involved in mesomerism (+M) i.e they are delocalized.
groups in phenol are localized they are involved in mesomerism (+M) i.e they are delocalized.
The delocalization of lone pair electron tends to form +ve charge in oxygen atom of 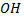 group thus making easier to releasing oxygen proton.
group thus making easier to releasing oxygen proton.
There is no such occasion in alcohol
2. STABILITY OF PHENOXIDE ION FORMED AFTER RELEASING HYDROGEN PROTON
Consider
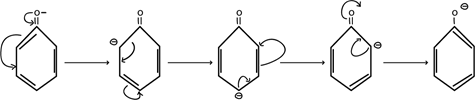
From above mechanism in phenoxide ion, it clearly understood negative charged electrons in oxygen atom of phenoxide is delocalized thus stabilizing the negative charge formed releasing hydrogen proton i.e ( it can exist on its own with combining with hydrogen proton). There is no such occusion alcoxide ion RO– formed in alcohol after releasing hydrogen proton.
ACIDIC THAN ALCOHOL
A. a) REACTION WITH ALKALINE SOLUTION
With alkaline solution like NaOH phenol tend to react with them
Example with 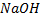 phenol form sodium phenoxide.
phenol form sodium phenoxide.
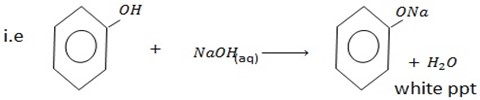
But
There is no such reaction with alcohol indicating that alcohol has basic character and hence phenol is more acidic than alcohol
Alcohol+ alkaline solution 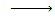 No reaction
No reaction
Note
The reaction is very important in separating phenol from other class of alcohol.
Qn. Without using the distillation explain how would you separate the following pair of organic compounds
i. Phenol and 1- hexanol
ii. Phenol and benzene
B.
b) REACTION WITH SODIUM CARBONATE
Acids react with carbonate to form carbon dioxide gas phenol like other acids react with sodium carbonate to evolve a gas.
Phenol like other acid react with sodium carbonate evolve a gas which turns lime water milky.
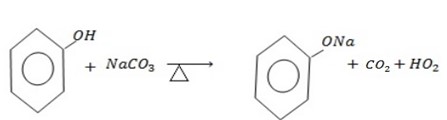
But
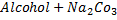
 No reaction
No reaction
c) REACTION WITH CARBOXYLIC ACID
Alcohol react with carboxylic acid in presence of sulphuric to form ester and water.
i.e.
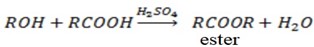
This verify that alcohol has basic character in this case phenol it does not react with carboxylic acid either in presence or in absence of suplhuric acid. This verify that phenol some alcohol character and hence phenol has higher strength than alcohol.

CHEMICAL REACTION OF ALCOHOL
Ø Chemical reaction of alcohol can be classified into the following
a. Reaction which involve replacement of whole OH– group
b. Reactions which involve replacement of H from OH– group
c. Reactions which involve OH– group and β- hydrogen
d. Oxidation
A. REACTION WHICH INVOLVE REPLACEMENT OF HYDROGEN ATOM
Ø Under this heading alcohol react with strong alkaline metals like Li, Na, K to form alkoxide and hydrogen gas is
Ø Generally

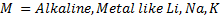
Example

Ø The main reaction under this heading is halogenations of alcohol.
Examples
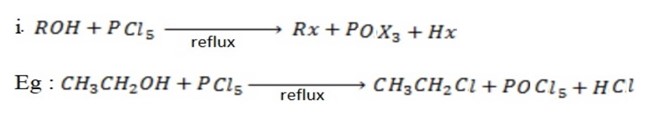
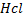 involved in the above reaction produce denser white fumes with ammonia so that reaction is used as test of presence of
involved in the above reaction produce denser white fumes with ammonia so that reaction is used as test of presence of 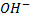 group in the compound.
group in the compound.
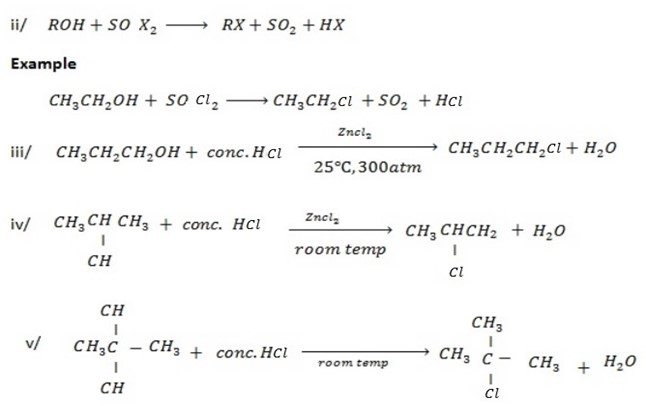
B. REACTION WHICH INVOLVE OH– GROUP AND B- HYDROGEN.
Under this heading alcohol undergo elimination reaction to from alkene.
Example
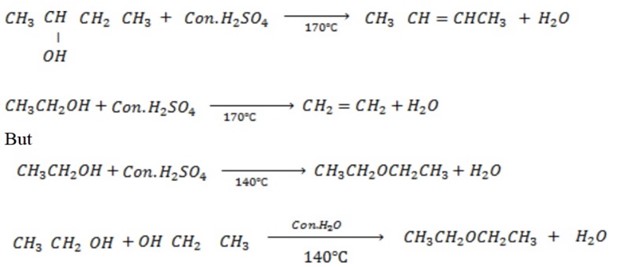
The production of either in above reaction is more favoured when 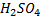 is dilute and cold.
is dilute and cold.
C. OXIDATION
Ø With weak oxidation agent like 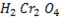 primary alcohol tend to form aldehyde.
primary alcohol tend to form aldehyde.
Example
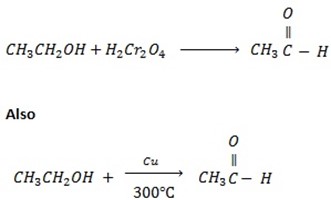
With strong oxidizing agent like 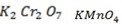 carboxylic acid is formed.
carboxylic acid is formed.
Example
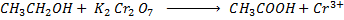
Orange Green

-With either weak oxidizing or strong oxiding agent secondary
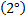 alcohol from Ketone.
alcohol from Ketone.
Generally
NOTE
Tertiary alcohol remit oxidation since there is no hydrogen to be removed.
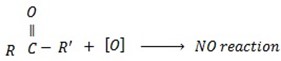
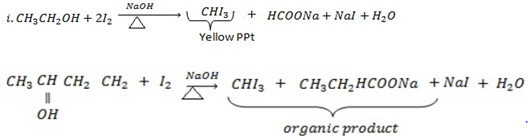
IODOFORM TEST
Ø This is the chemical test for presence of terminal methyl group which is directly bonded to carbon with OH– group or (to carbonyl group in the case of carbonyl compounds) by giving yellow ppt of trichloromethane ( Iodoform) CHI3.
Ø When compounds with terminal methyl group bonded to carbon with OH group is heated with 12 in presence of NaOH they give yellow ppt of Iodoform.
Example
CHEMICAL TEST TO DISTINGUISH BETWEEN PRIMARY, SECONDARY AND TERTIARY ALCOHOLS.
– Three classes of alcohol can be distinguished by using Lucas reagent.
– Lucas reagent is the mixture of concentrated HCl and ZnCl mixed at equal proportion.
– With Lucas reagent at room temperature, primary alcohol do not form cloudness or turbidity ( insoluble substance) at all.

– Secondary alcohol tends to form turbidity ( insoluble substance which is chloroalkane within 5 minutes).

– Tertiary alcohol, tend to form turbidity immediately.

Example
Qn. Gave chemical test to distinguish between
i. Ethanol and propanol ( I test)
ii. Butan – 1-ol and butan – 2- ol (2 test)
iii. Butan -2- ol and 2- methyl propan – 2-ol ( 2 test apart from using Lucas reagent)
ANS
i. Ethanol gives positive Iodoform test while propanol give negative Iodoform test.

ii. 1st TEST
With Lucas reagent at room temperature butan -2-ol give turbidity ( cloudness) within 5 minutes while butan -1-ol do not give turbidity at all.

2nd TEST ( Iodoform Test)
Butan -2- ol give positive iodoform test while but-1-ol give negative iodoform test.
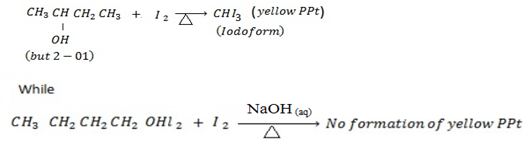
iii.1st TEST
When butan -2- ol is mixed with 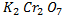 solution the orange colour of
solution the orange colour of 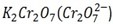 is changed to green while 2- methylpropan- 2 – ol do not show any change.
is changed to green while 2- methylpropan- 2 – ol do not show any change.
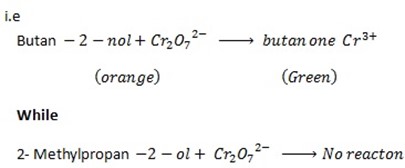
2nd TEST
Butan  decolourise KMnO4 with black ppt appearing at the bottom of the beaker which is deep purple while 2-methylpropan
decolourise KMnO4 with black ppt appearing at the bottom of the beaker which is deep purple while 2-methylpropan  do not.
do not.